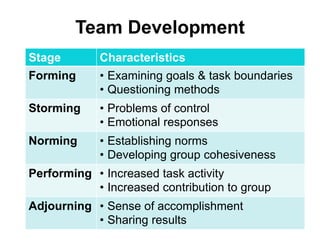
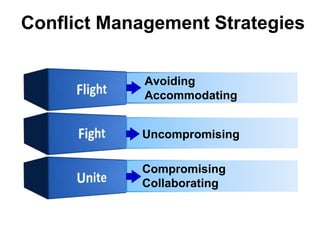
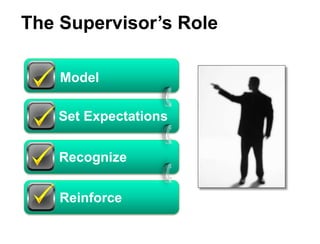
This document is a lesson on interpersonal skills from the USDA Specialty Crops Inspection Division. It covers effective communication, building teamwork, managing conflict, and professionalism. The key points are: effective communication is important for sharing information and building relationships; teamwork leads to cohesive work units and high morale; conflict should be managed constructively to find solutions; and supervisors should model and promote professionalism among their staff. The lesson emphasizes the supervisor's role in developing these skills among employees.