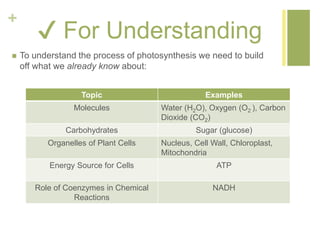
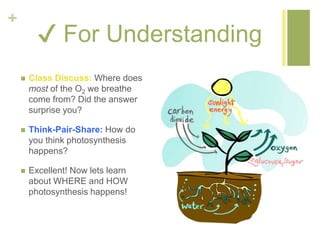
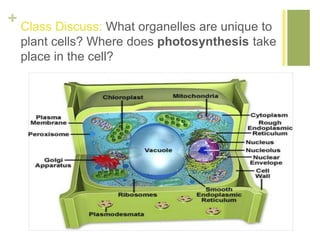
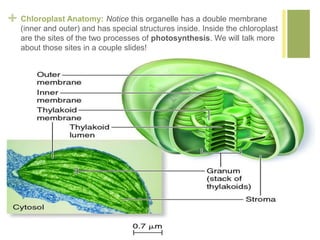
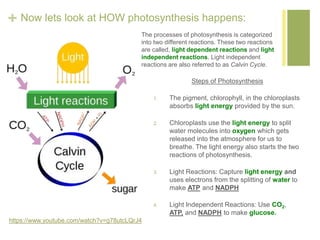
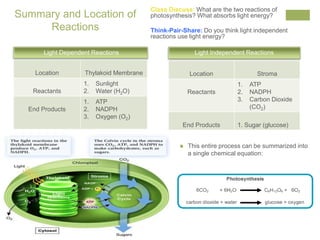
Photosynthesis converts light energy from the sun into chemical energy stored in glucose. It occurs in two stages - the light dependent reactions in the thylakoid membrane that use light energy to produce ATP and NADPH, and the light independent reactions in the stroma that use ATP, NADPH, and CO2 to produce glucose. Most of the oxygen produced as a byproduct of photosynthesis comes from phytoplankton in the ocean, not land plants.