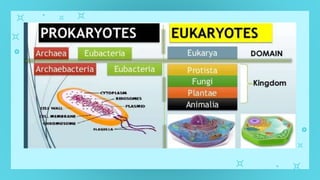
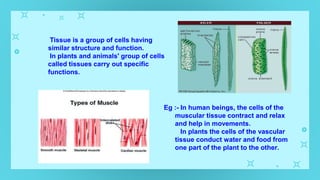
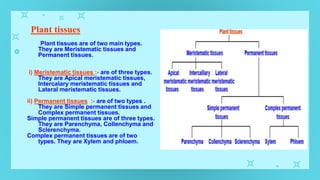
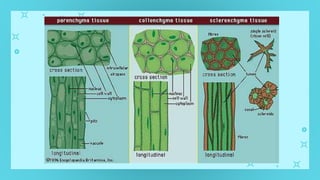
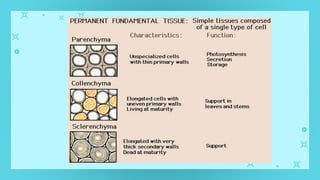
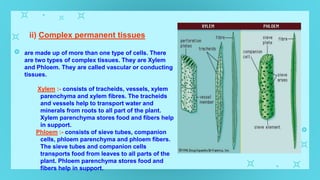
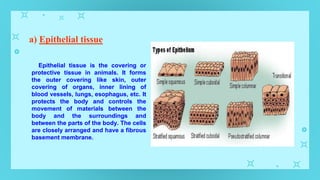
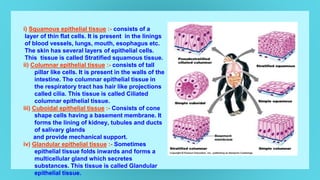
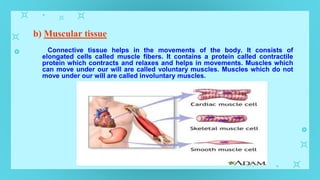
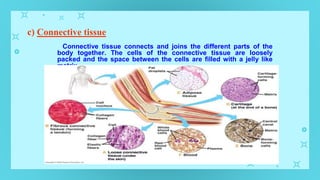
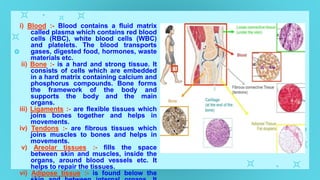
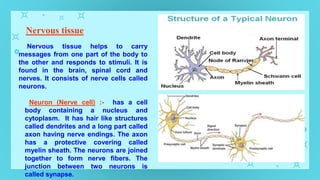
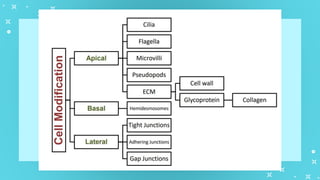
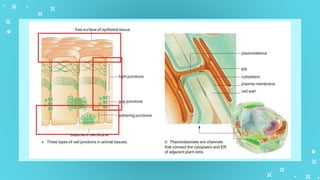
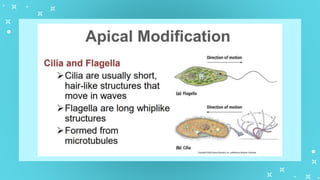
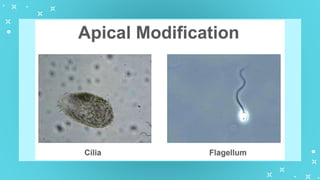
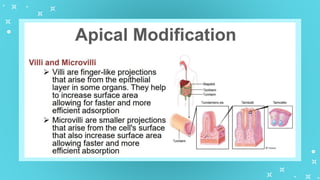
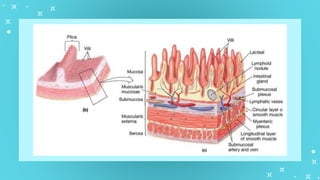
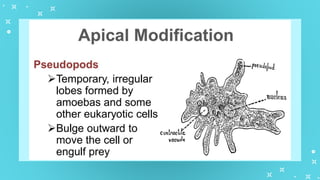
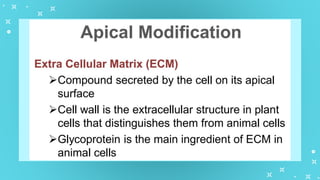
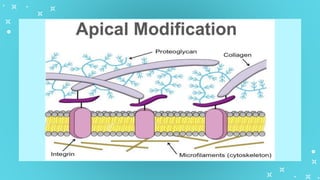
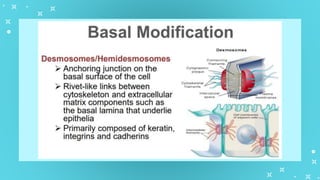
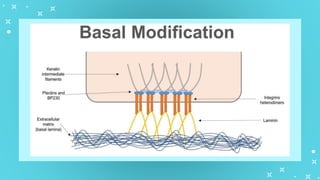
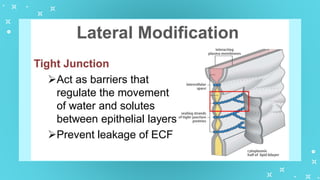
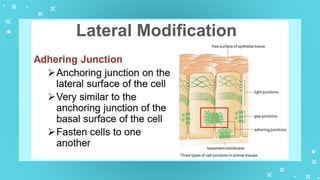
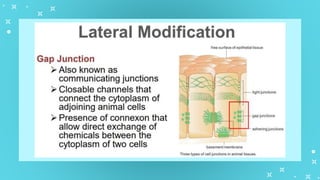
This document provides an overview of cell types and cell modification. It discusses the distinguishing features of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. It describes different types of plant and animal cells, including their classification and functions. Specific cell types covered include meristematic and permanent plant tissues, as well as epithelial, muscular, connective and nervous animal tissues. The document also examines some cell modifications that allow cells to perform specialized functions, such as microvilli and root hairs in plants.