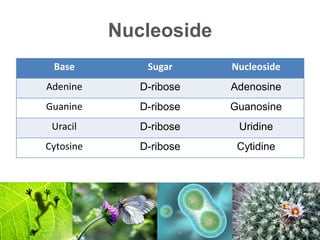
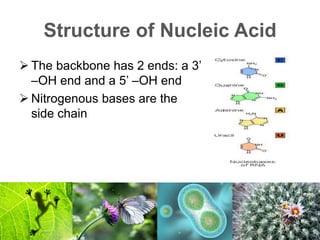
This document defines nucleic acids and their components. Nucleic acids are made of nucleotides, which contain a nitrogenous base, a 5-carbon sugar called ribose, and a phosphate group. There are two types of nucleic acids: DNA contains the sugar deoxyribose and is found in cells, while RNA contains ribose and helps synthesize proteins. DNA and RNA are made of strands with complementary nucleotide bases that allow them to pair up in structures like the DNA double helix. The "central dogma" of biology describes how DNA is transcribed into RNA and then translated into proteins.