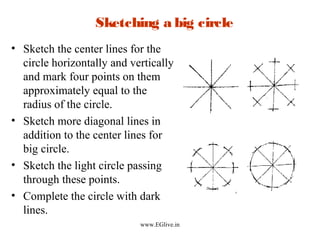
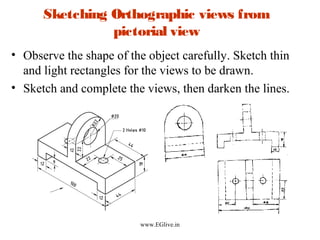
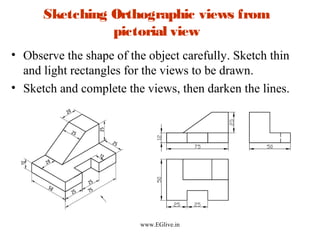
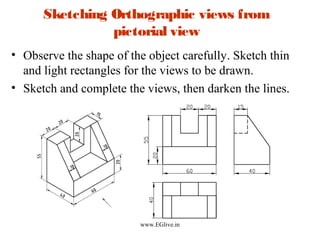
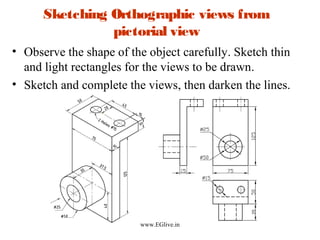
The document discusses freehand sketching techniques that are important for engineers and designers. It states that freehand sketching allows engineers to initially conceive 3D objects on paper and convey their ideas to others. Good practice in freehand sketching helps engineers think about designs rather than focusing on drawing methods. The basics of sketching straight lines, circles of different sizes, and orthographic views from pictorials are covered. Guidelines for materials, marking points, and proportion are provided to help sketch objects accurately without using scales.