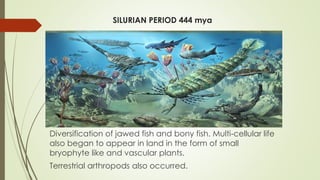
The document explains the geologic time scale, detailing the Earth's history through rock records that contain fossils. It describes the main eons, eras, periods, and epochs, along with the methods of relative and absolute dating used to establish this timeline. Significant events and life forms are highlighted from the Hadean eon to the Quaternary period, showcasing the evolution of life and major extinctions.