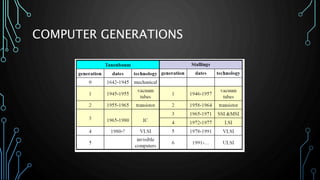
This document outlines the key milestones in computer architecture from mechanical devices (Generation 0) to modern computers with artificial intelligence capabilities (Generation 5). It discusses the transition from vacuum tubes to transistors to integrated circuits. Important innovators mentioned include Charles Babbage, Ada Lovelace, John Atanasoff, John von Neumann, and founders of companies like IBM, Microsoft, Apple, Intel and Texas Instruments.