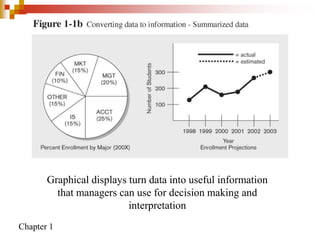
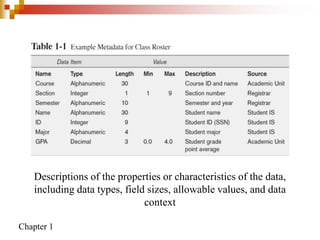
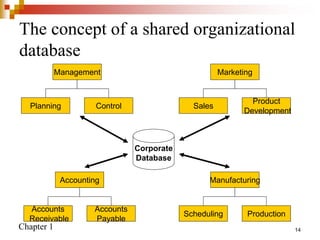
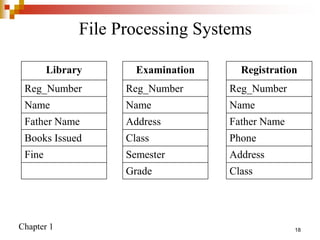
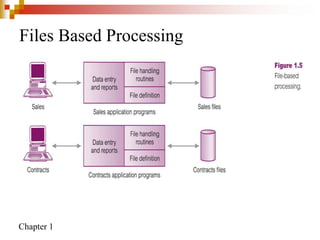
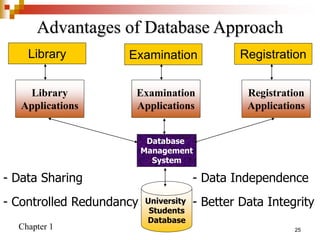
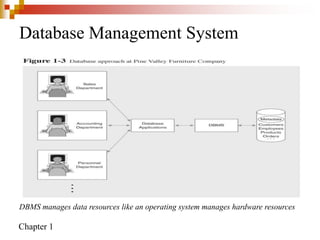
This document provides an overview of database systems and database management systems (DBMS). It defines what a database is, the problems with traditional file-based data storage, and how DBMS solutions address those problems. Specifically, it discusses how DBMS allow for centralized, shared data access which improves data integrity while reducing redundancy. It also outlines some typical applications of database systems and the components and personnel involved in DBMS environments.