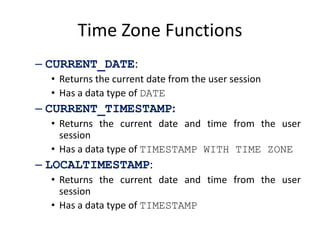
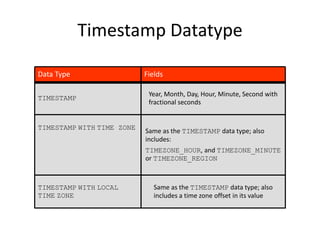
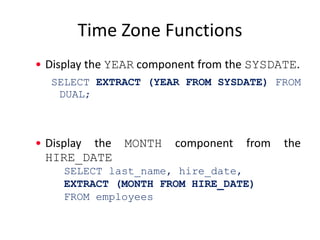
This document discusses time zones and functions related to timestamps and time zones in databases. It explains that time is measured in 24 time zones based on Greenwich Mean Time. It provides examples of functions like CURRENT_DATE, CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, and LOCALTIMESTAMP that return date and time values based on the user or database time zone. It also demonstrates functions like TO_TIMESTAMP, EXTRACT, and operations like adding intervals to timestamps to change them to different time zones or adjust relative dates.