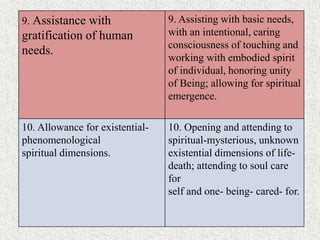
Jean Watson developed the Theory of Human Caring, which views caring as the essence of nursing. The theory outlines 10 carative factors and caritas processes that are intended to help nurses develop caring relationships with patients. Watson's theory emphasizes caring for the whole person, including their mind, body, and spirit. It also stresses the importance of environmental factors and the nurse-patient relationship on the patient's health and well-being. While widely adopted in nursing education and practice, some criticisms of Watson's theory include that it is complex and difficult to empirically study concepts like transpersonal caring.