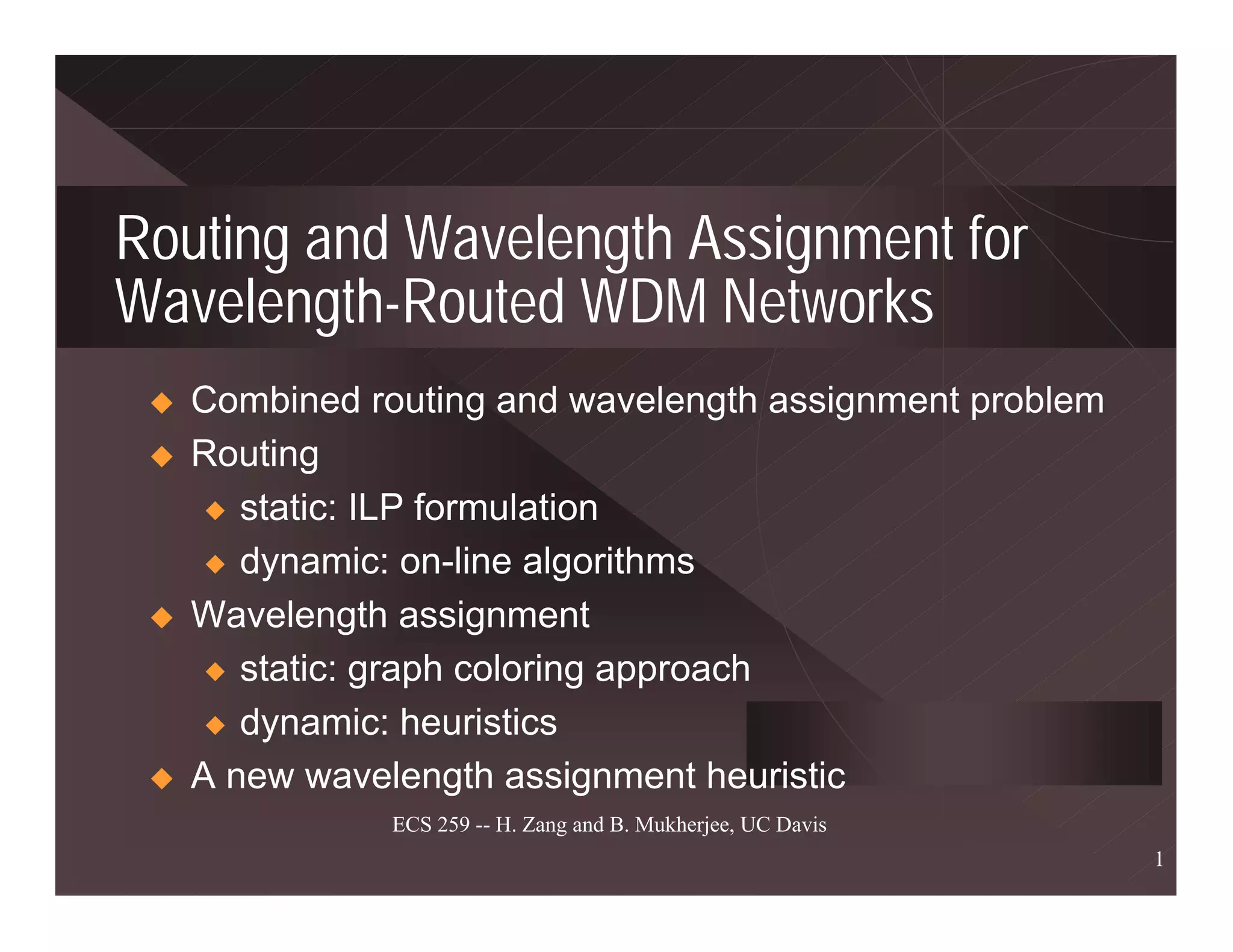
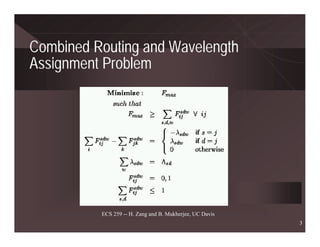
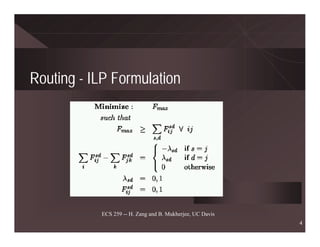
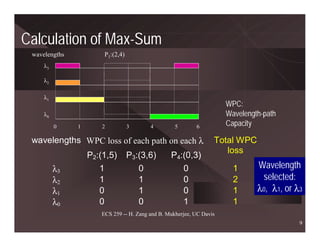
The document discusses routing and wavelength assignment (RWA) in wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) networks. It covers both static and dynamic RWA problems. For routing, it discusses integer linear programming formulations for static routing and online algorithms for dynamic routing. For wavelength assignment, it discusses graph coloring approaches for static assignment and heuristics like first-fit for dynamic assignment. Several heuristics for RWA are presented, along with their computational complexities and performance. Future research directions like survivable RWA and managing multicast connections are also outlined.







![Future Research
Survivable wavelength-routed WDM networks
x previous work: static traffic & single link failure
[S. Ramamurthy 1998]
x higher layer protection -logical topology design
with bundle cut in mind
x WDM layer protection - dynamic traffic
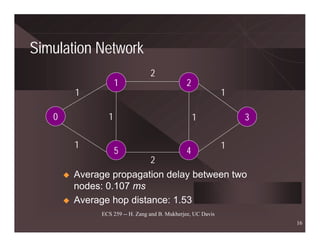
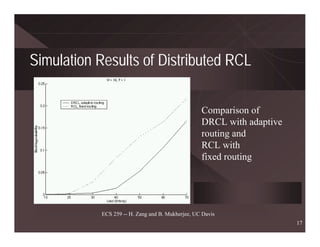
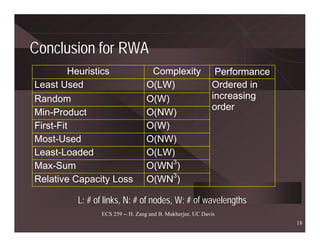
ECS 259 -- H. Zang and B. Mukherjee, UC Davis
19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture5c-100810011021-phpapp02/85/Lecture5c-19-320.jpg)
