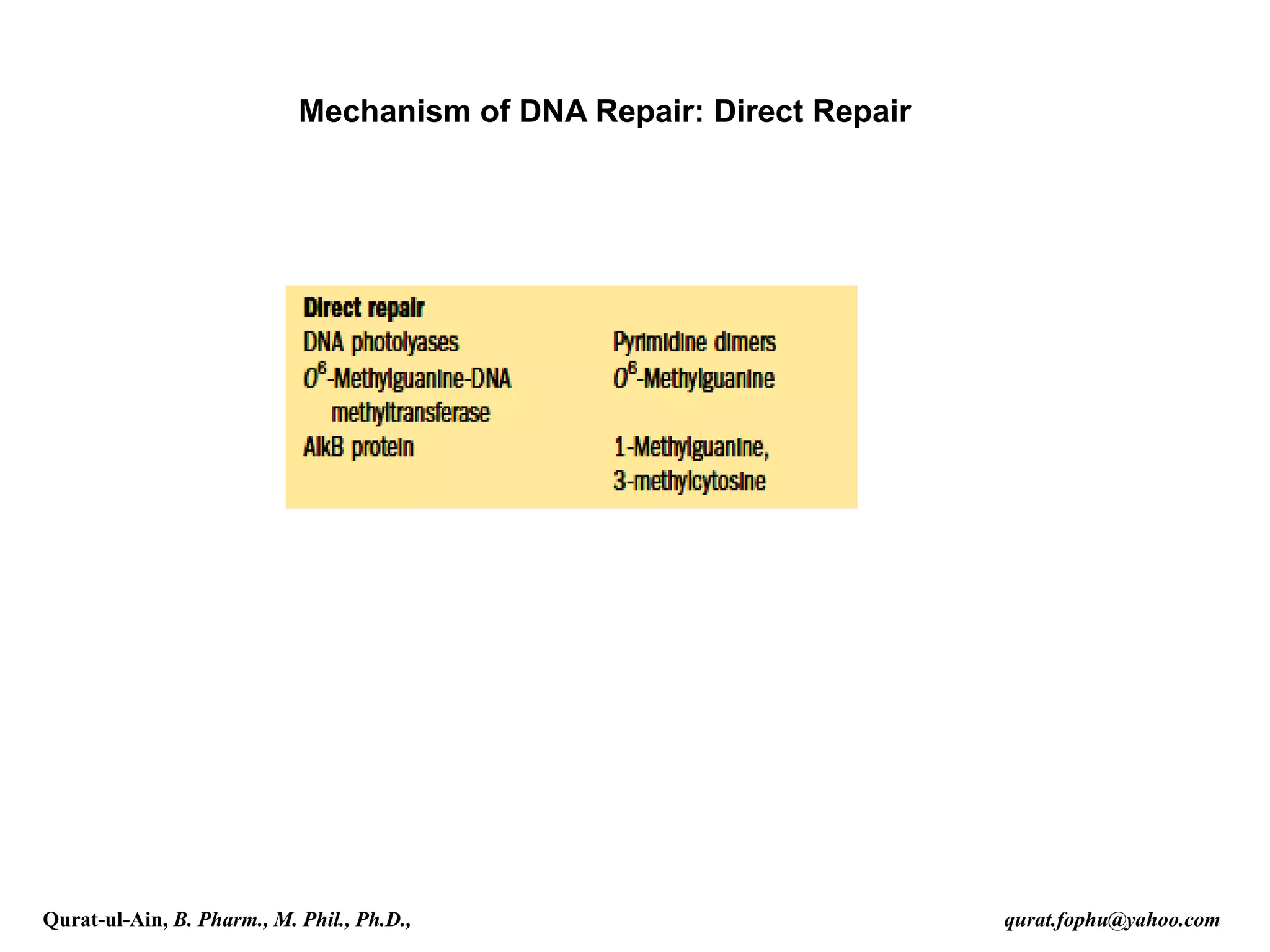
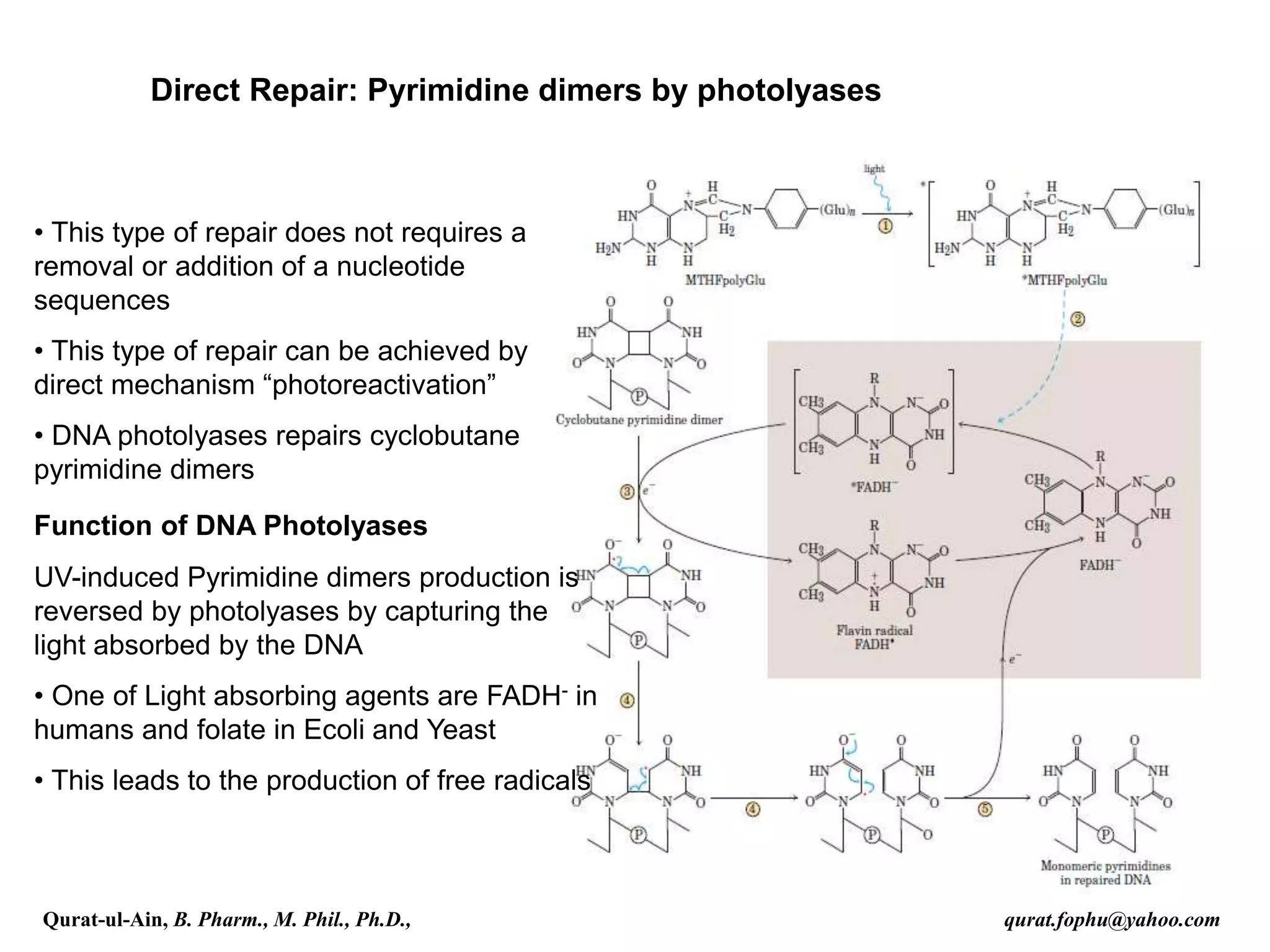
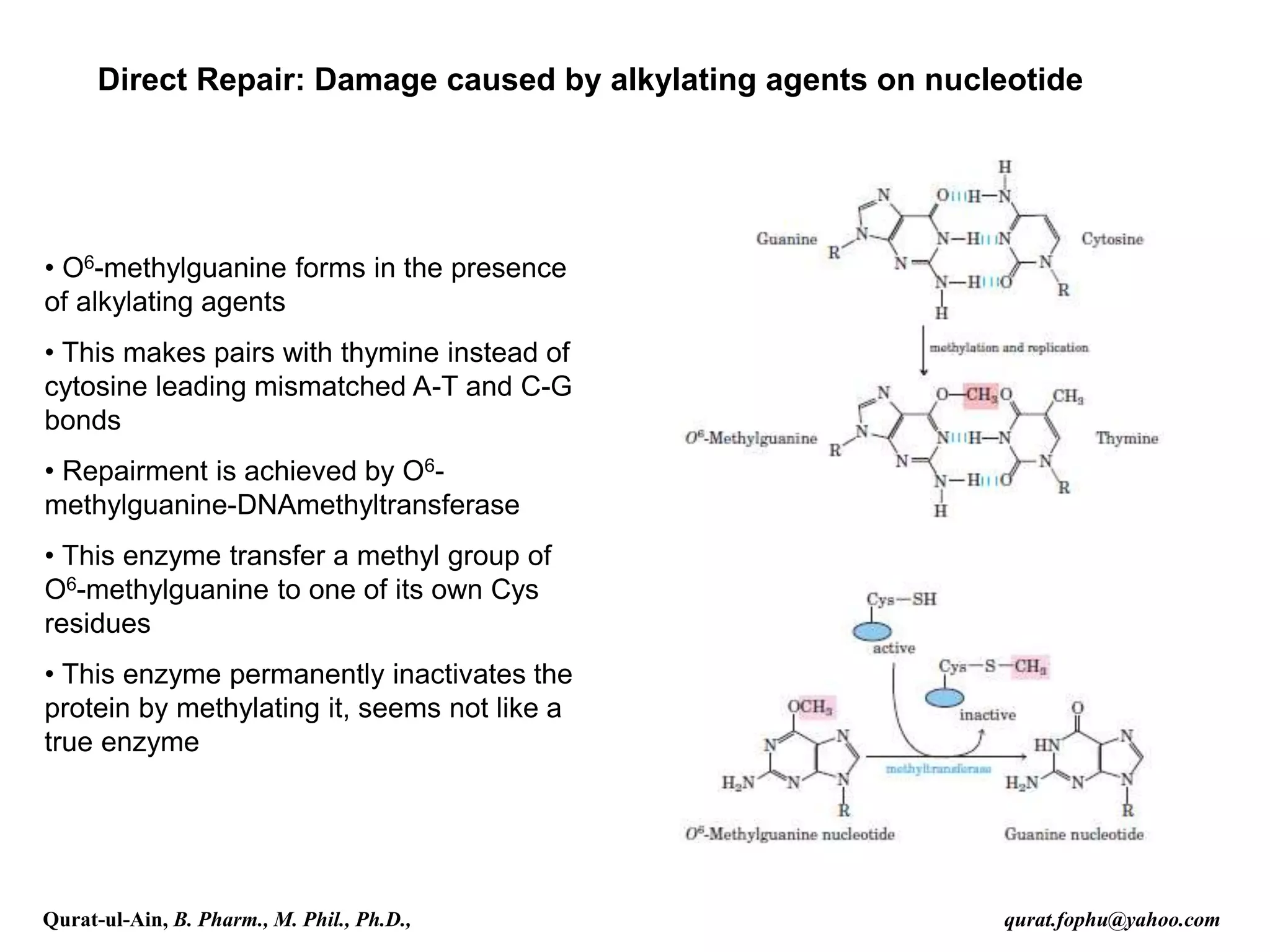
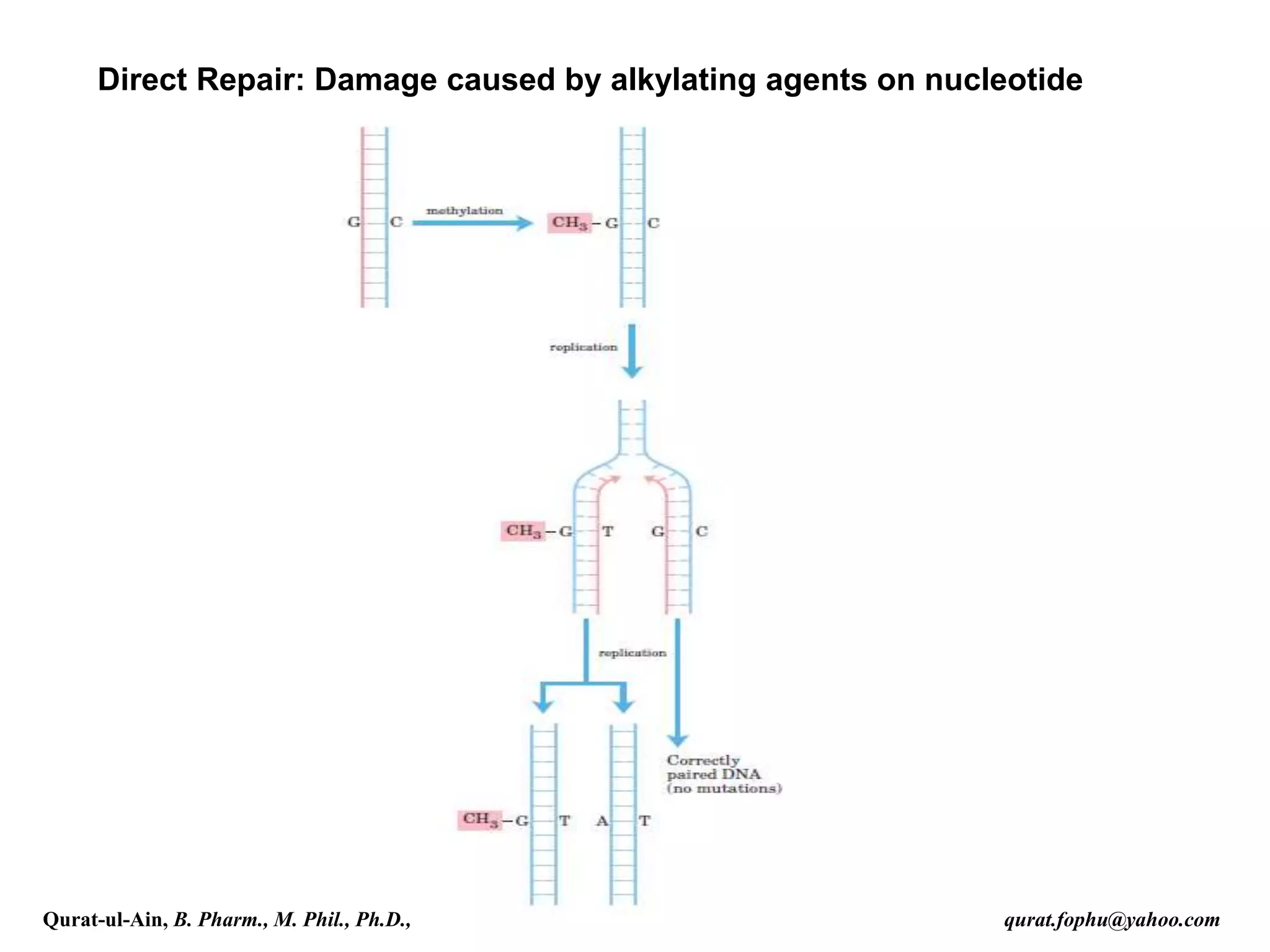
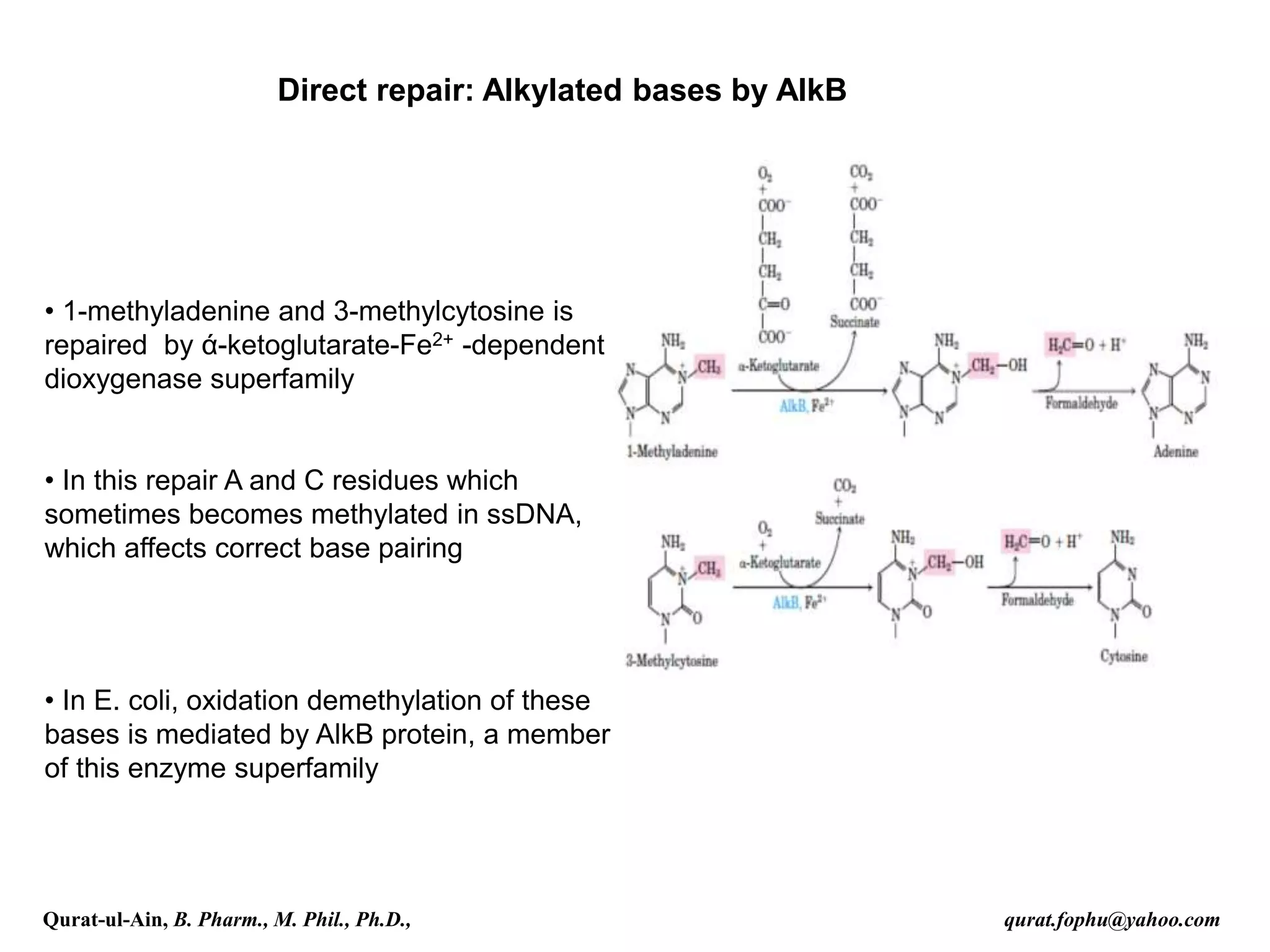
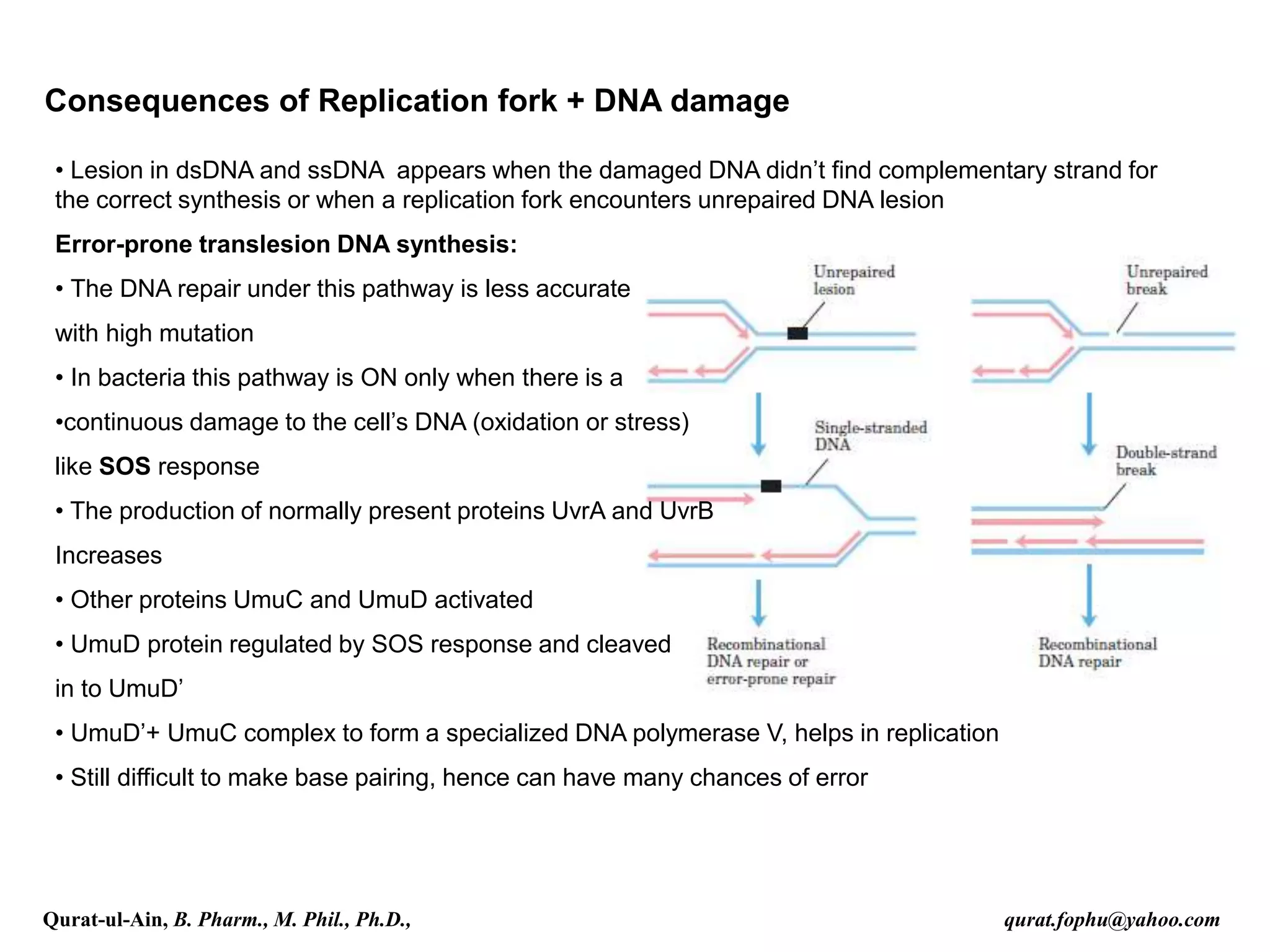
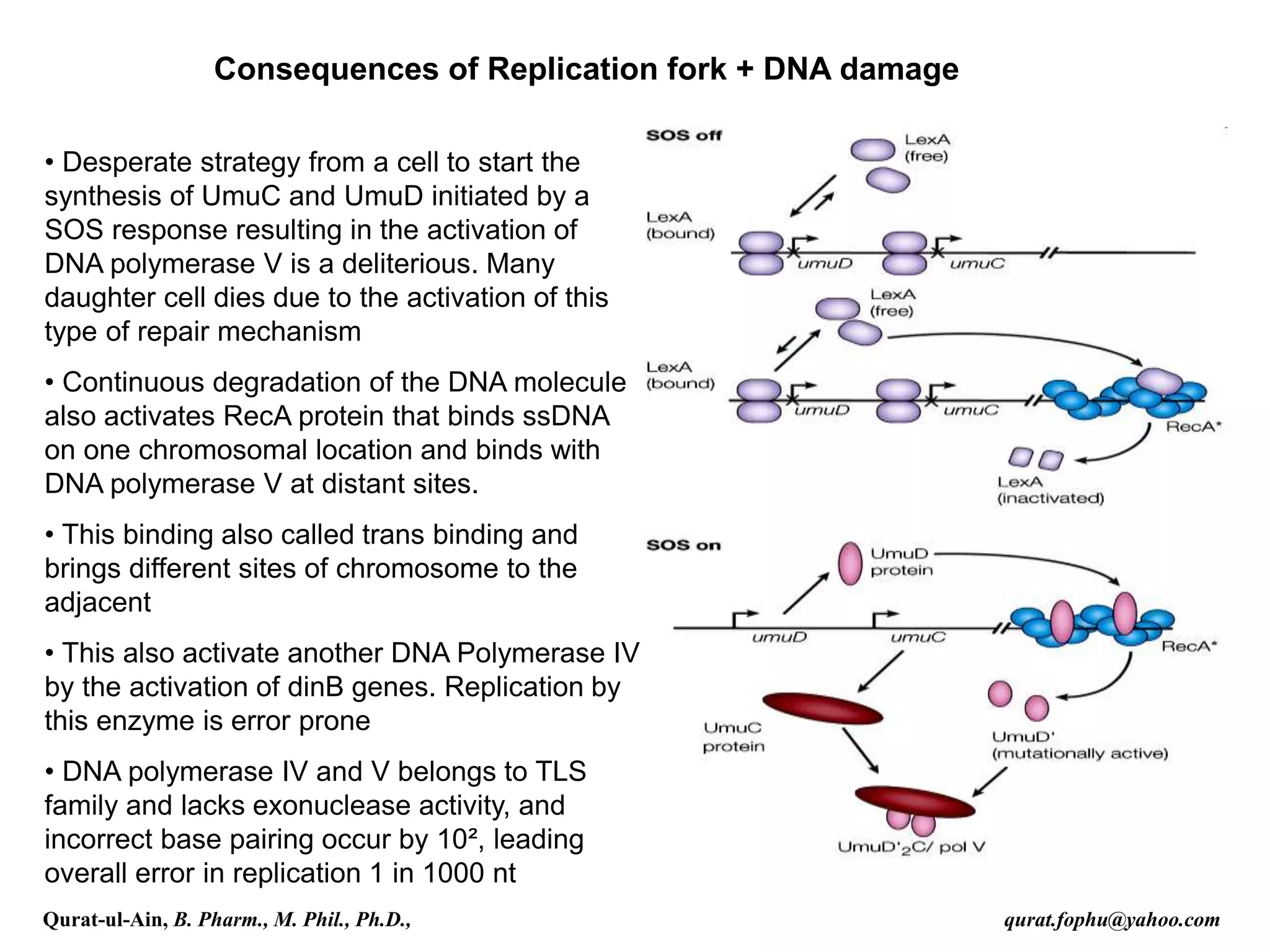
1) The document discusses various mechanisms of DNA repair, including mismatch repair, base excision repair, nucleotide excision repair, direct repair, and error-prone translesion synthesis.
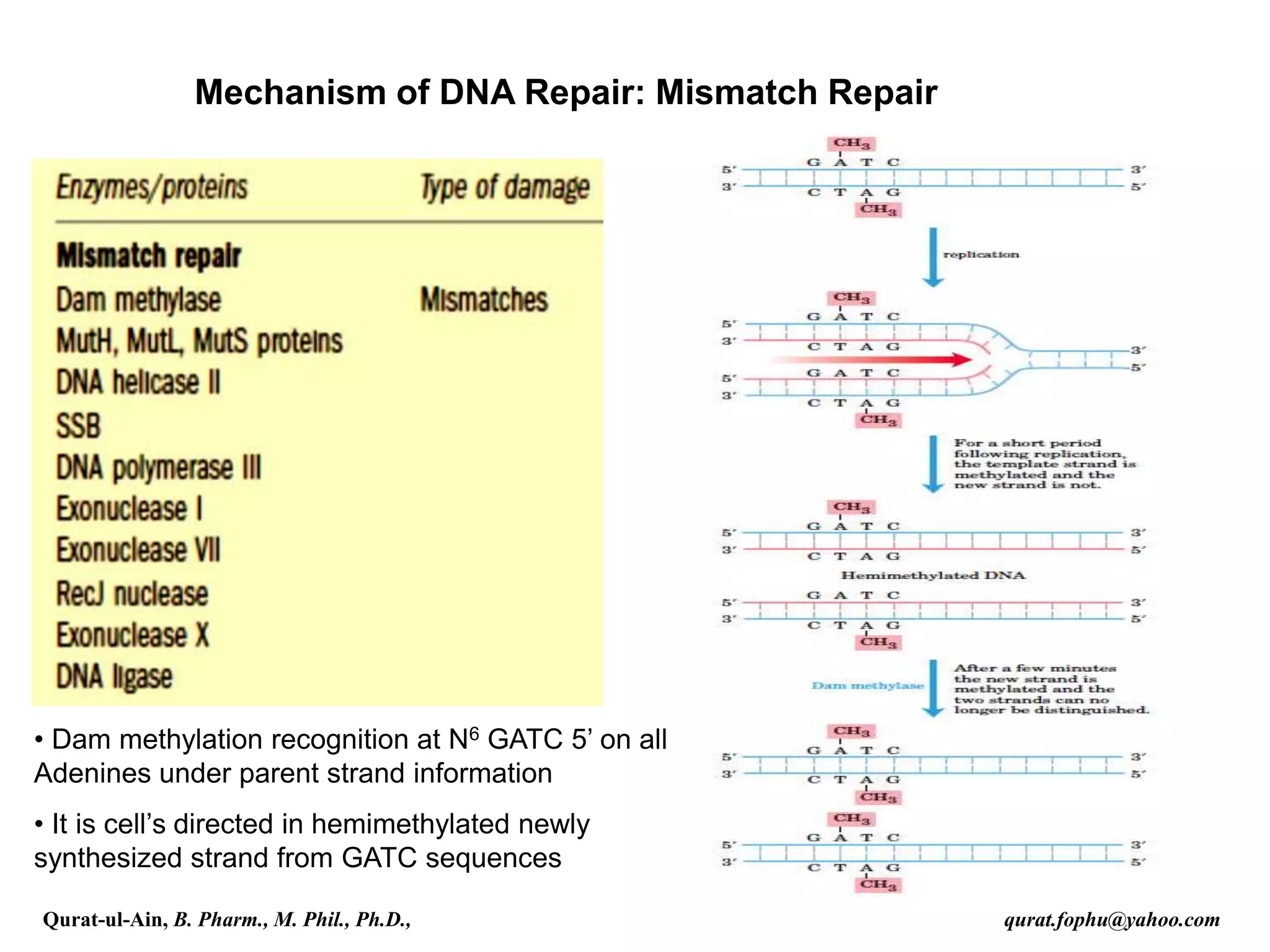
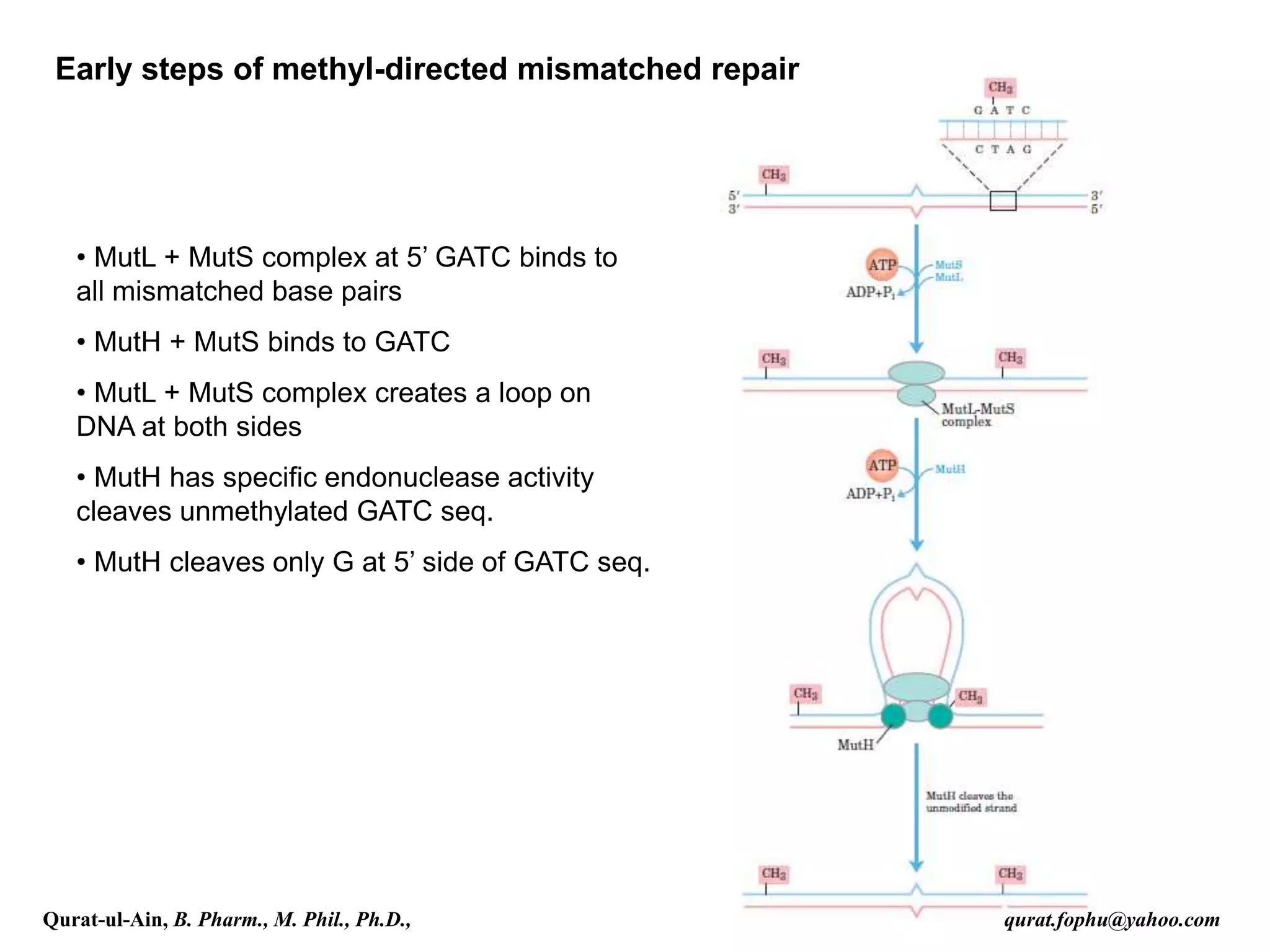
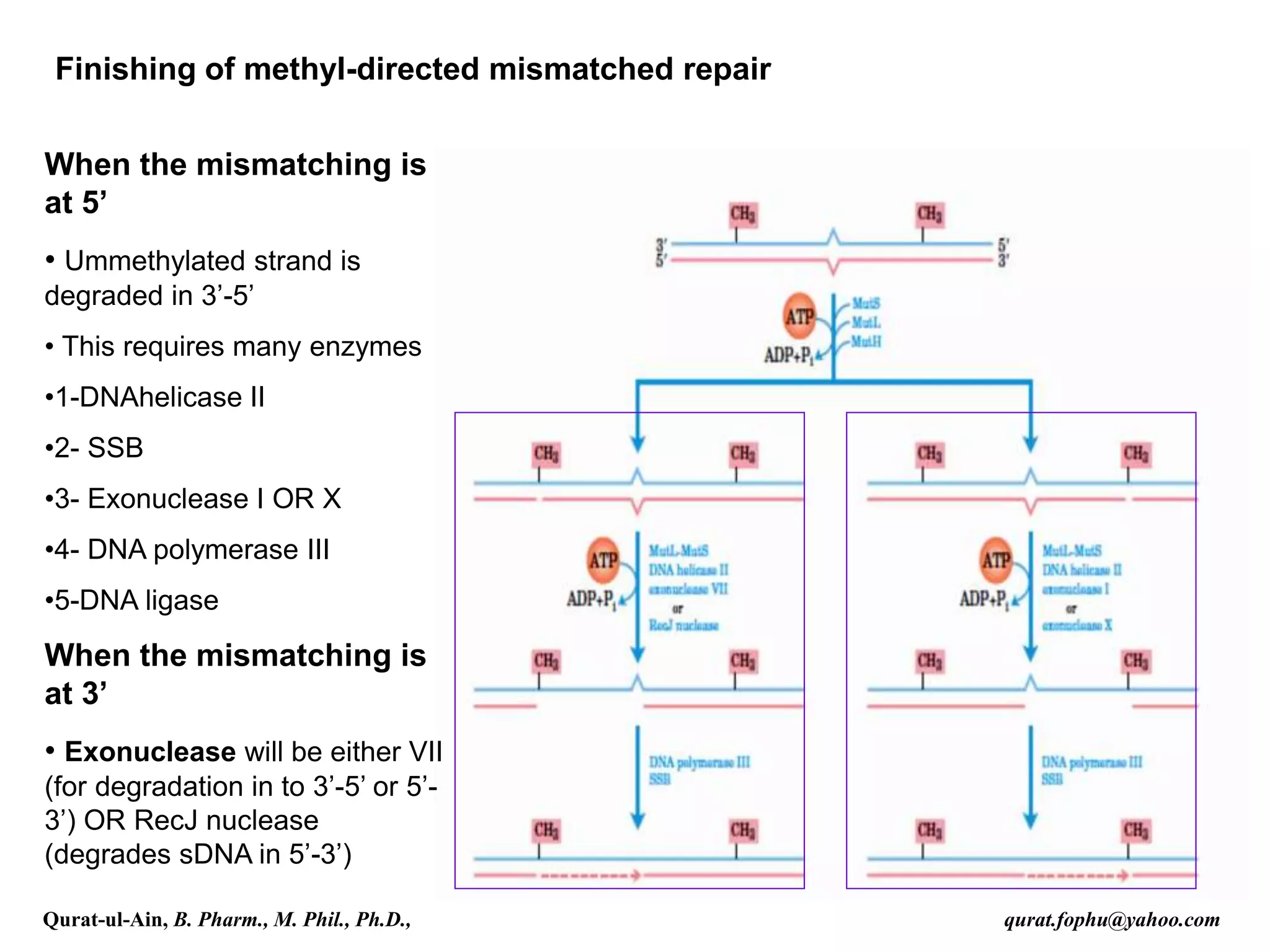
2) Mismatch repair involves methyl-directed repair of mismatched base pairs using MutS and MutL complexes in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
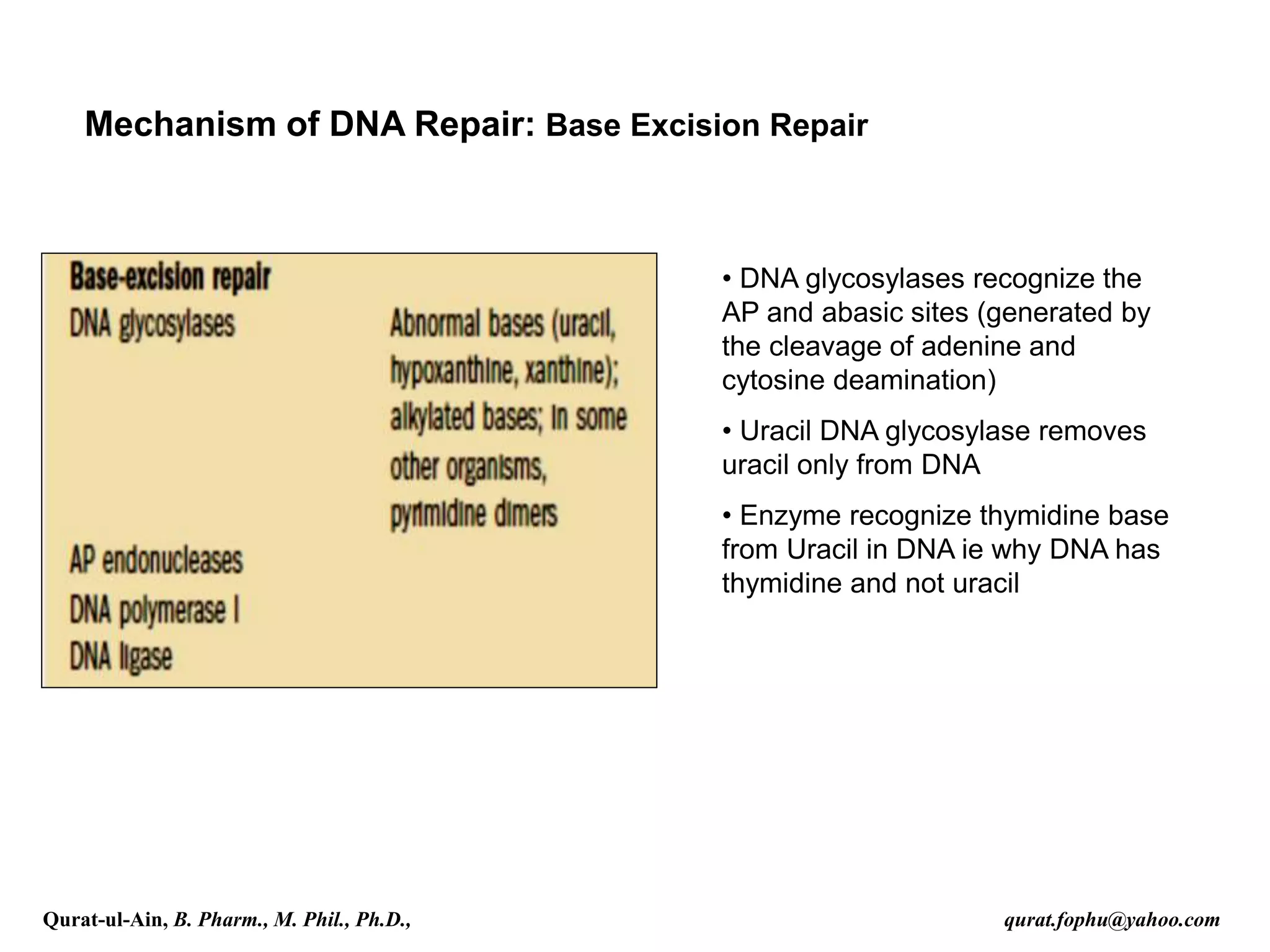
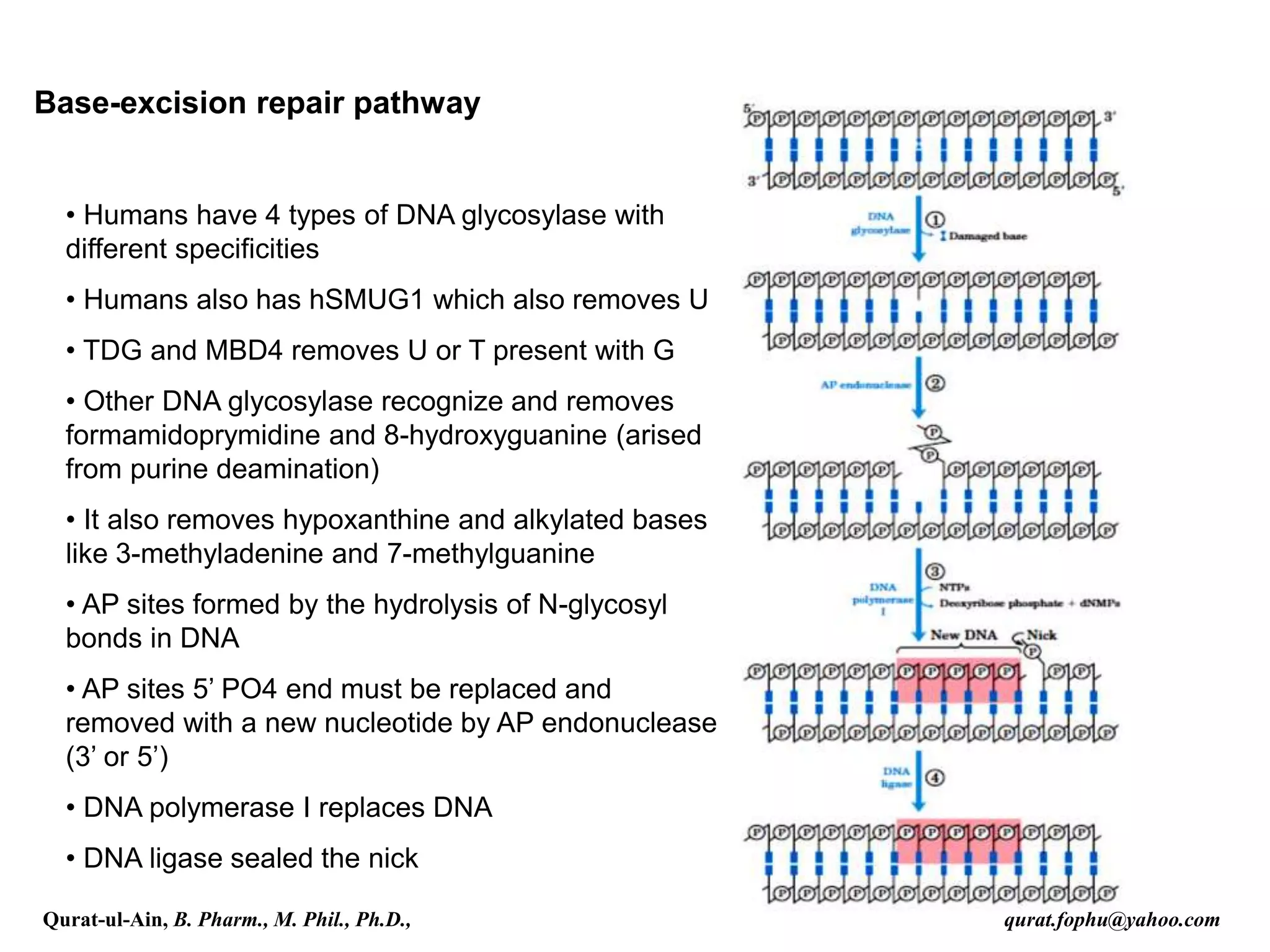
3) Base excision repair removes damaged or inappropriate bases using DNA glycosylases and follows with endonuclease cleavage, DNA synthesis, and ligation.
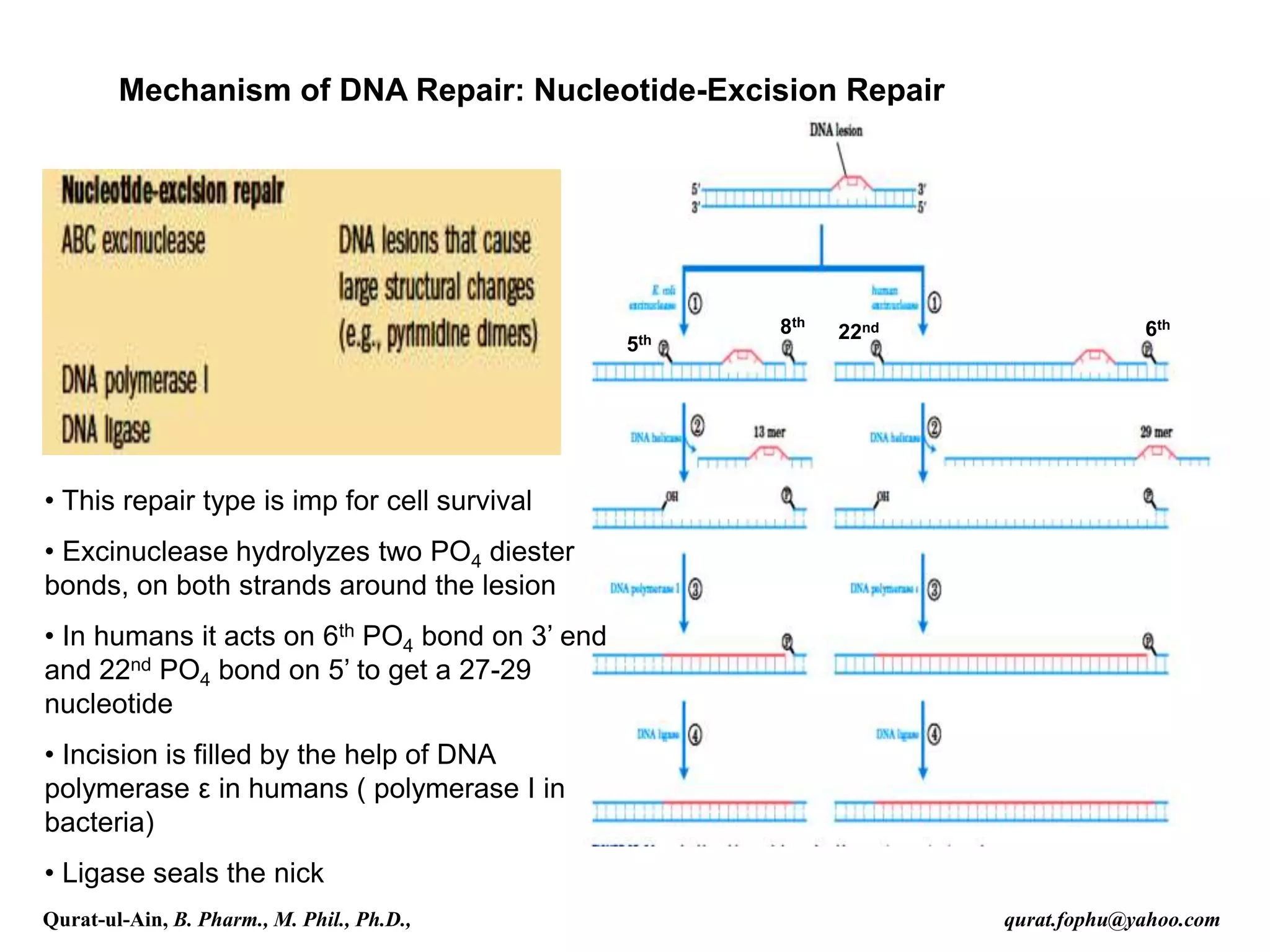
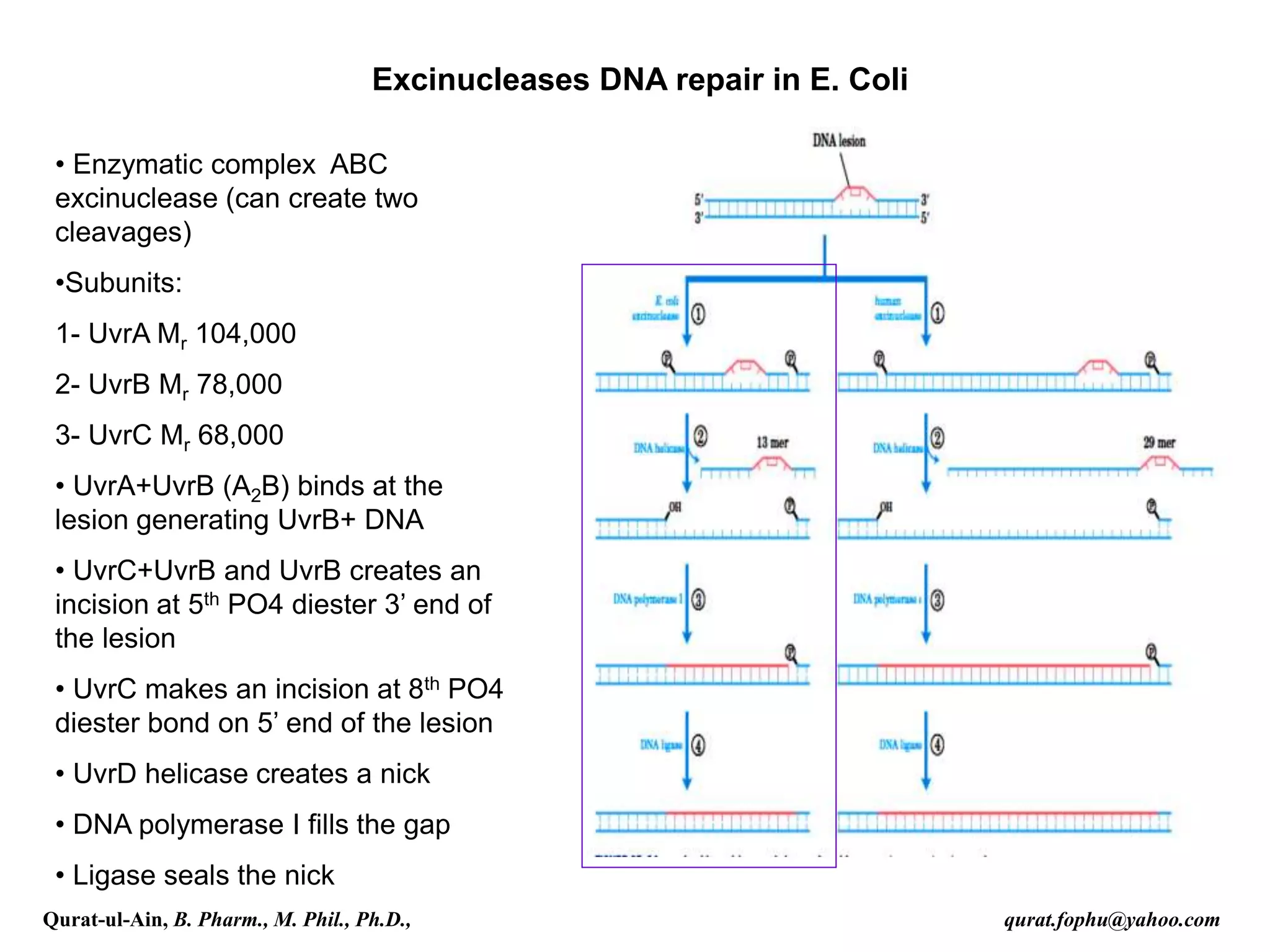
4) Nucleotide excision repair removes oligonucleotides containing damaged bases by dual incisions around the lesion, followed by filling in and ligation.
![• Repair mechanism like nucleotide-
excision repair and base-excision repair
is tied to transcription in eukaryotes
• Deficiencies in any of the repair
enzymes leads to many serious illness
• This pathway helps to repair DNA from
various carcinogens like benzo[ά]
pyrene-guanine, cyclobutane pyrimidine
dimers and 6-4 photoproducts
Eukaryotic excinucleases DNA repair system : DNA damages caused by
cigarette smoke can be repair by this repair mechanism
Qurat-ul-Ain, B. Pharm., M. Phil., Ph.D., qurat.fophu@yahoo.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture-211206054725/75/Lecture-4-part-2-DNA-Repair-9-2048.jpg)