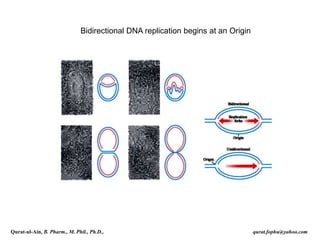
The document discusses DNA replication in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. In prokaryotes, replication begins with initiation at the origin of replication (oriC) mediated by DnaA and other proteins. Bidirectional replication forks are established with the help of helicases and DNA polymerases. Elongation involves continuous synthesis of leading and discontinuous synthesis of lagging strands in Okazaki fragments. Termination occurs when the replication forks from opposite directions converge. In eukaryotes, replication is regulated by cyclin-dependent kinases and occurs at multiple origins of replication with similar initiation and elongation processes as prokaryotes.