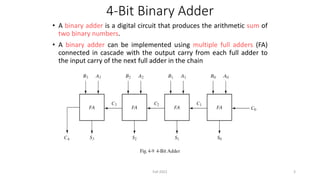
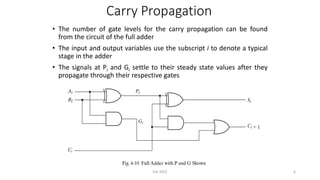
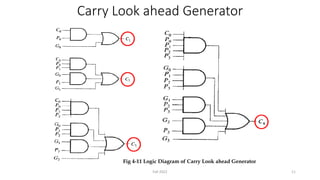
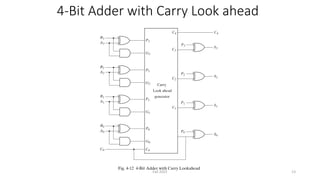
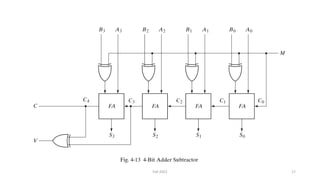
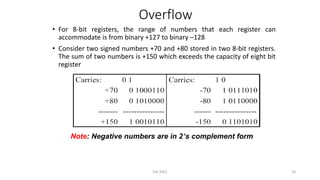
This document discusses the design of a 4-bit lookahead carry binary adder-subtractor circuit. It begins by describing the objectives of studying significant delay problems in ripple carry binary adders and designing a 4-bit lookahead carry adder. It then provides details on 4-bit binary adders using multiple full adders, carry propagation delays in ripple carry adders, and implementing carry lookahead using generate and propagate signals to reduce delay. The document concludes by discussing how to extend the design to a 4-bit binary subtractor and how to detect overflow in arithmetic circuits.