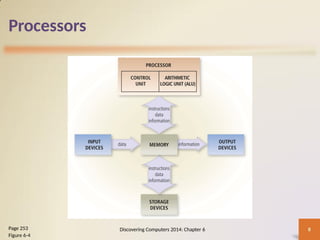
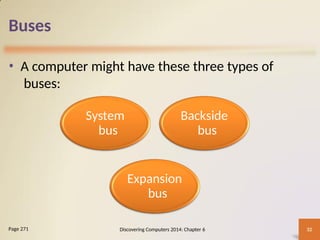
Chapter 6 of 'Discovering Computers' discusses the internal components of computers and mobile devices, including the roles of processors, memory types, and the significance of multi-core processors. It explores cloud computing advantages such as cost savings and scalability, as well as data representation using bits and bytes. Additionally, the chapter covers the functionality of adapter cards, buses, power supply systems, and best practices for device care.