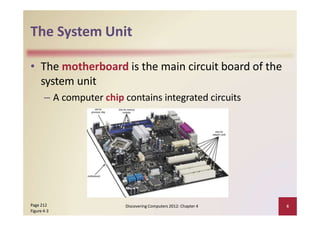
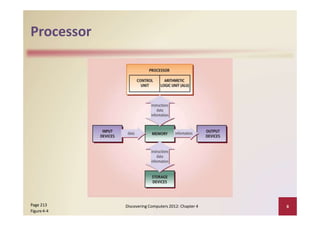
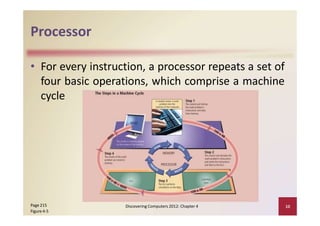
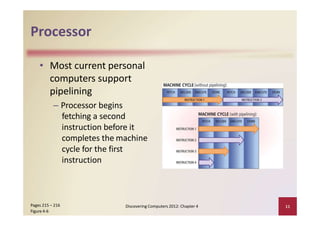
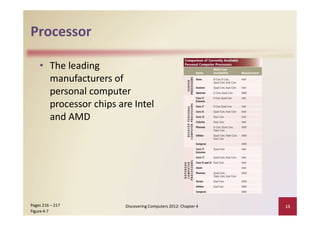
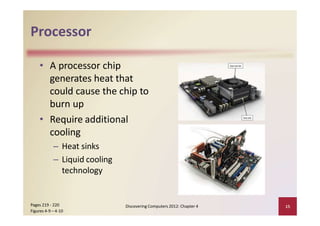
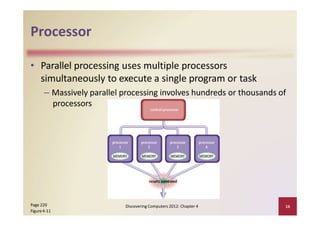
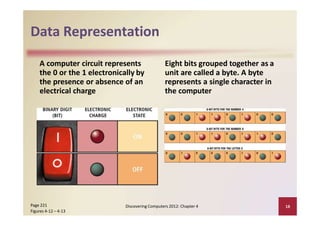
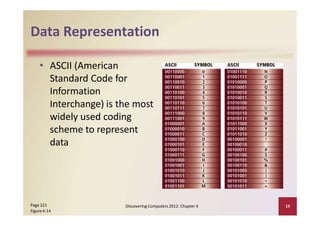
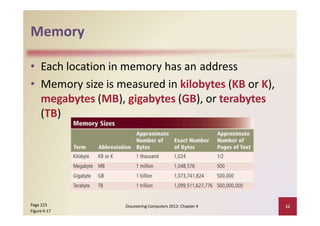
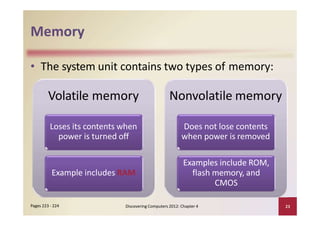
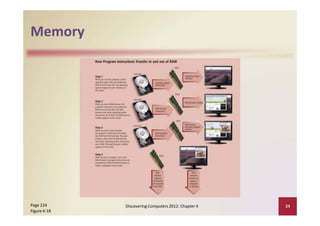
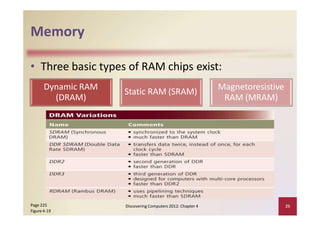
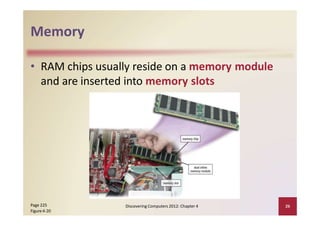
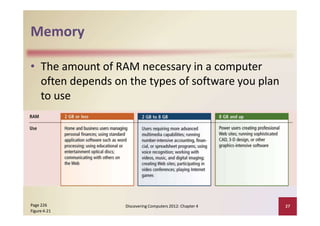
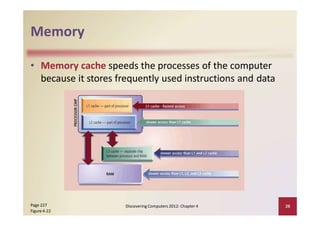
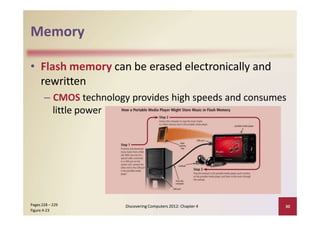
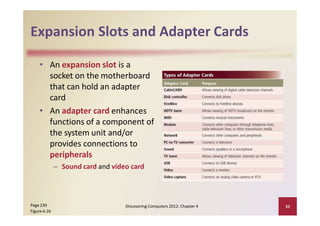
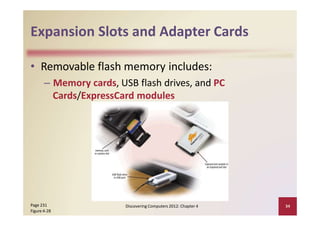
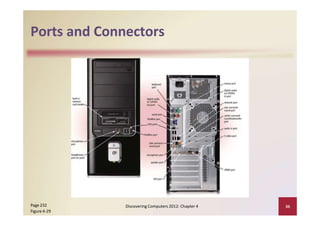
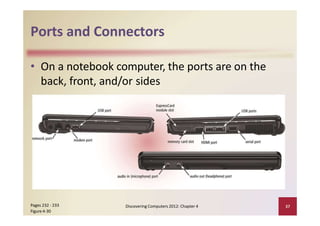
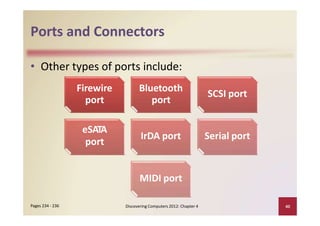
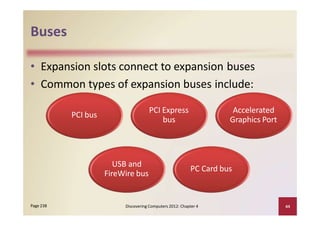
This document provides an overview of the key components and functions of a computer system unit. It describes the motherboard, processor, memory, expansion slots, ports, buses, and power supply. The processor contains a control unit and arithmetic logic unit and executes a four-step machine cycle. Memory stores operating systems, applications, and data in volatile RAM and non-volatile ROM chips. Expansion slots hold adapter cards that enhance functions. Various ports connect peripherals using standards like USB, FireWire, and Bluetooth. Buses allow communication between components. Regular cleaning helps maintain a computer's performance.