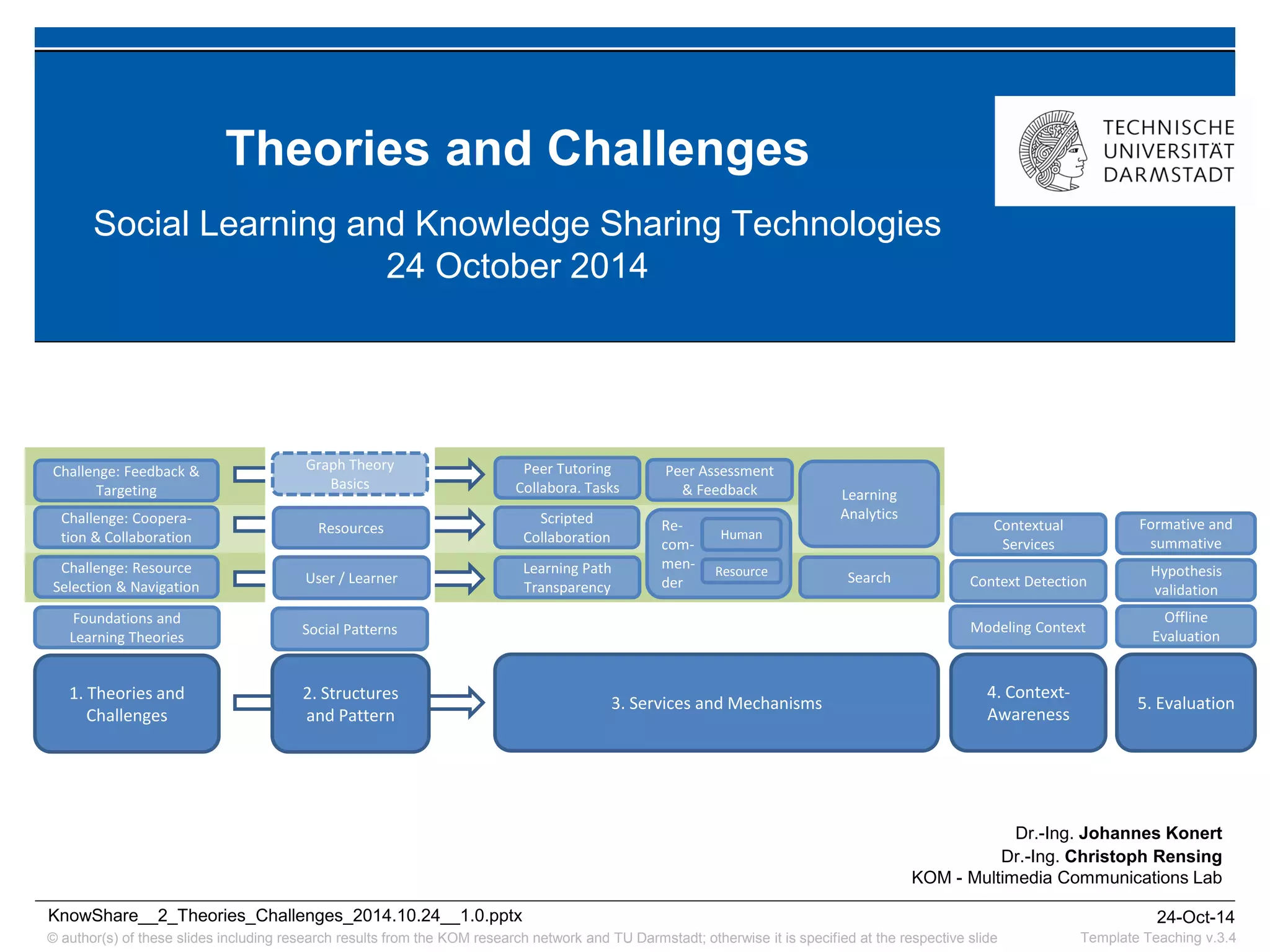
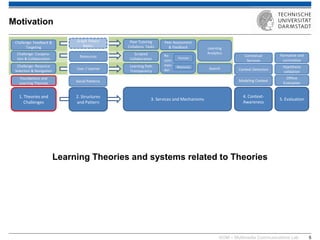
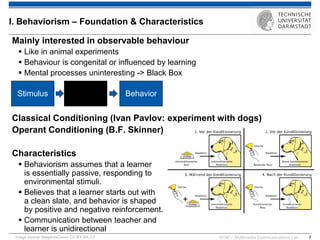
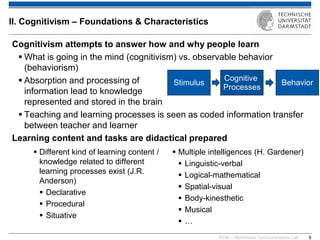
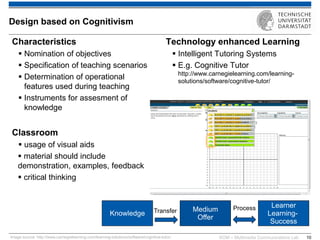
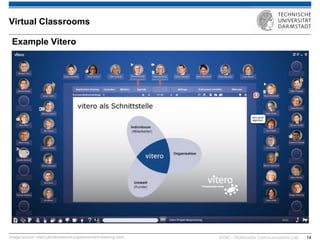
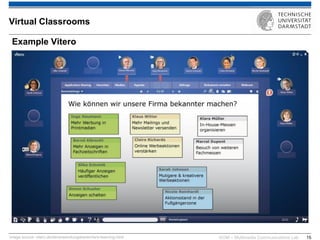
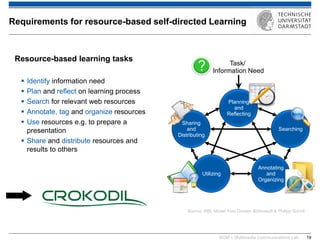
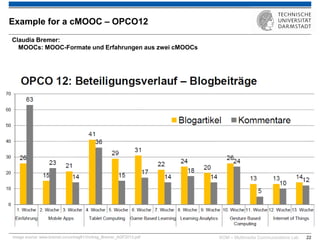
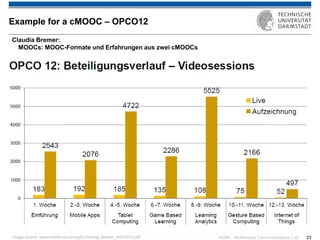
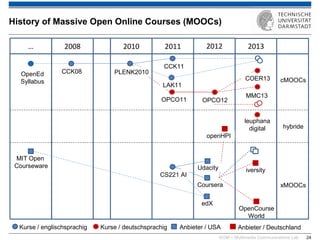
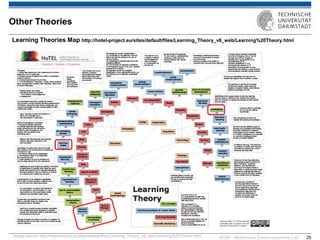
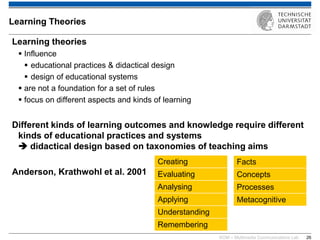
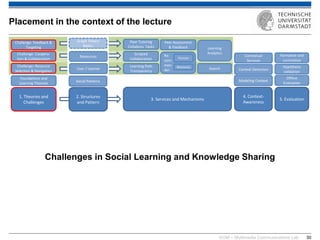
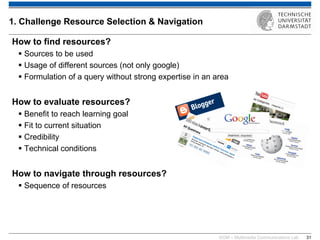
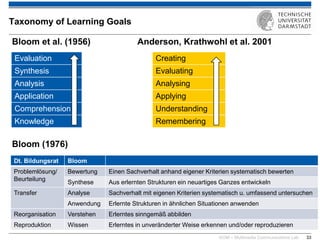
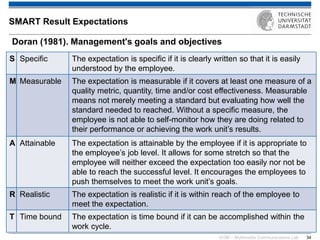
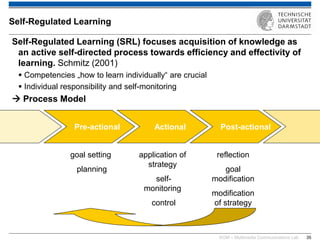
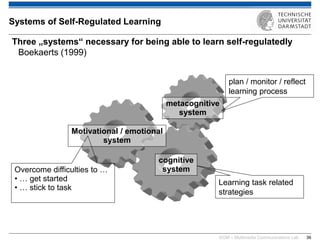
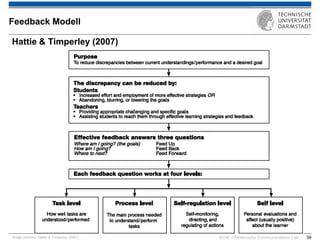
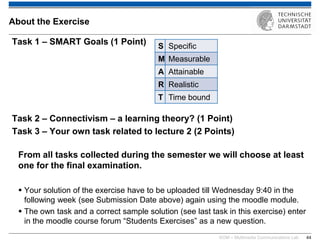
The document discusses various learning theories including behaviorism, cognitivism, constructivism, and connectivism, highlighting their foundations and practical applications in educational settings. It addresses challenges in social learning and knowledge sharing, such as resource selection, cooperation, and feedback mechanisms. Additionally, it emphasizes the role of technology in enhancing learning experiences and outlines the significance of self-regulated learning and effective assessment strategies.