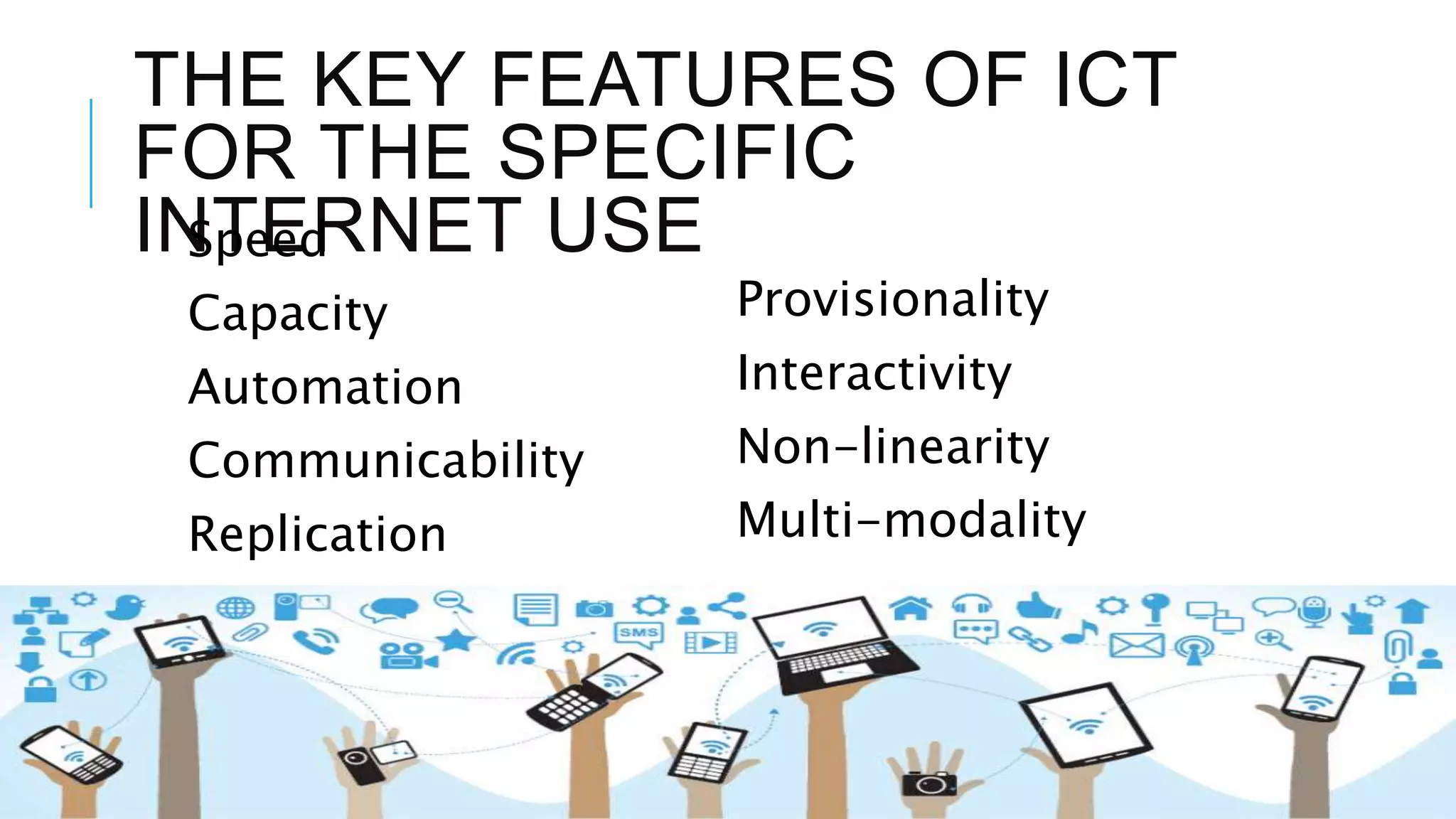
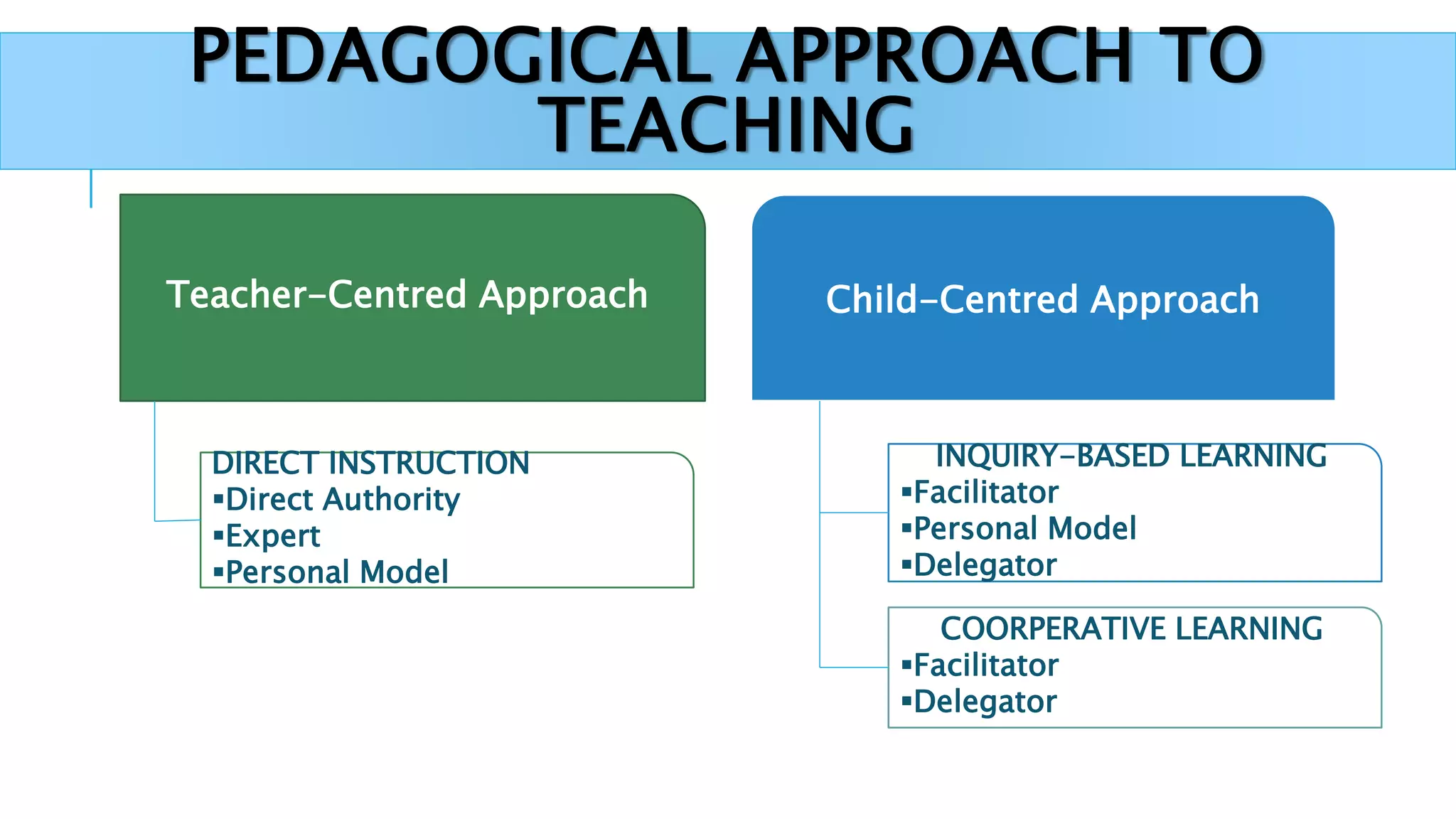
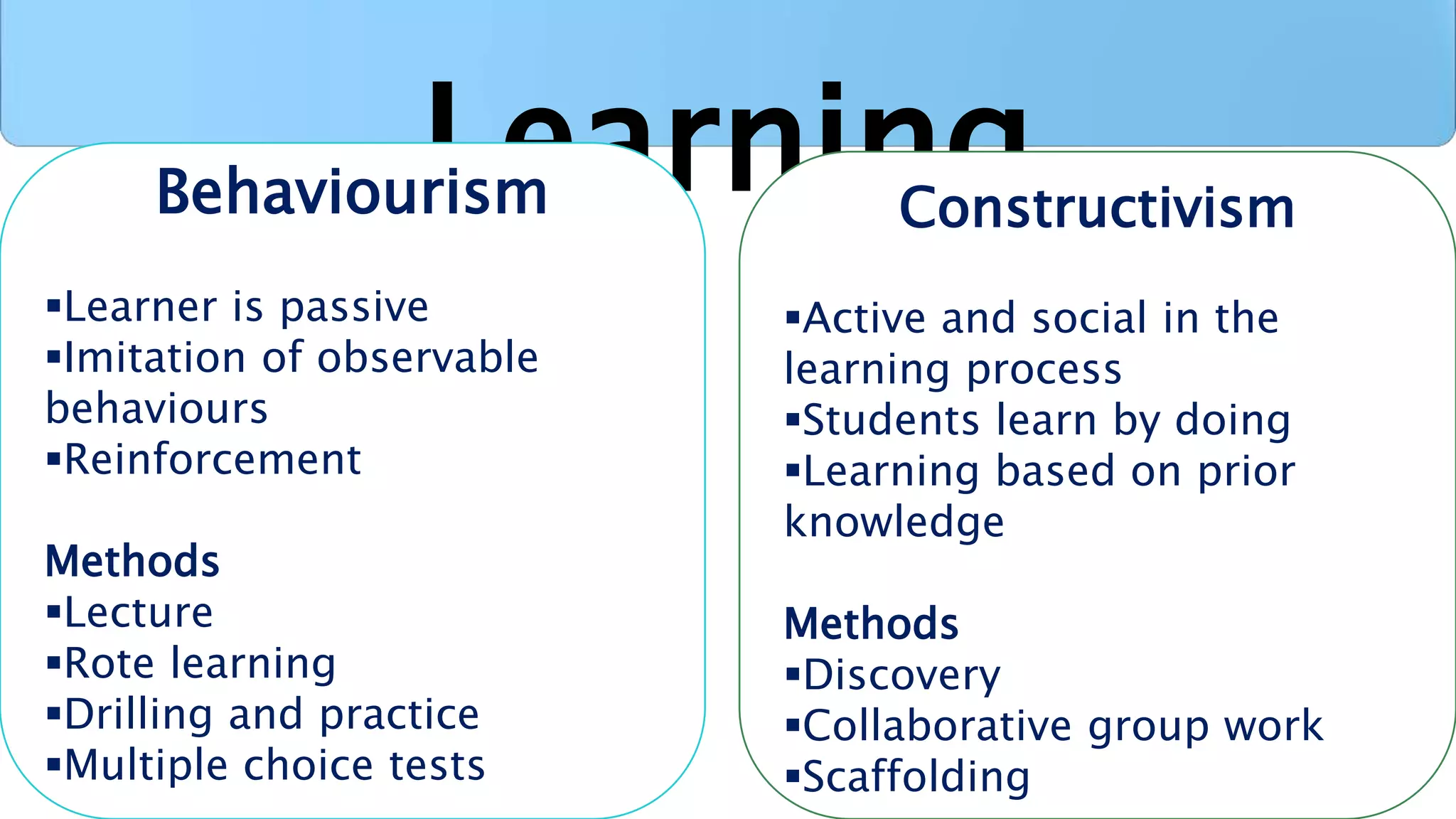
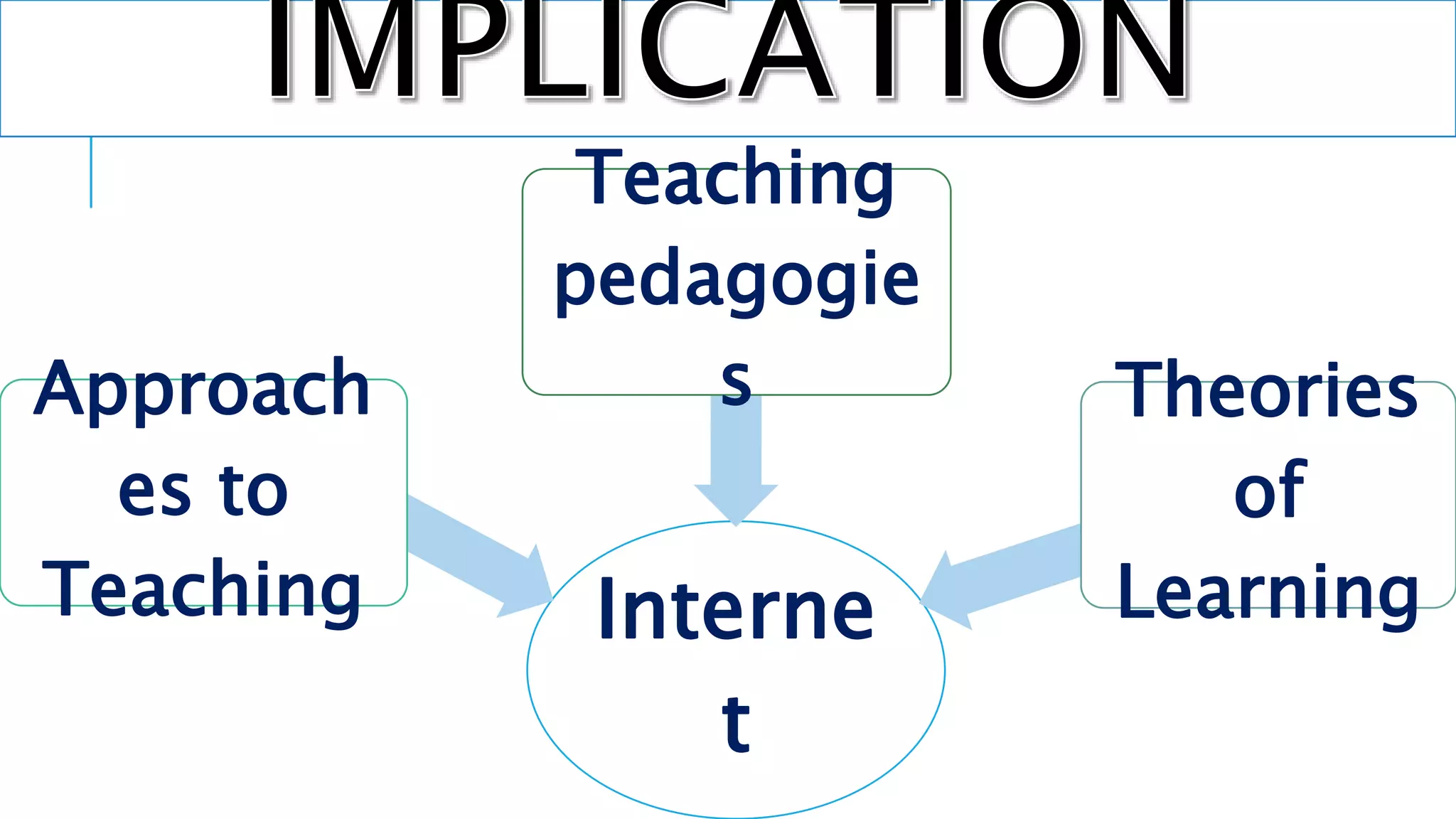
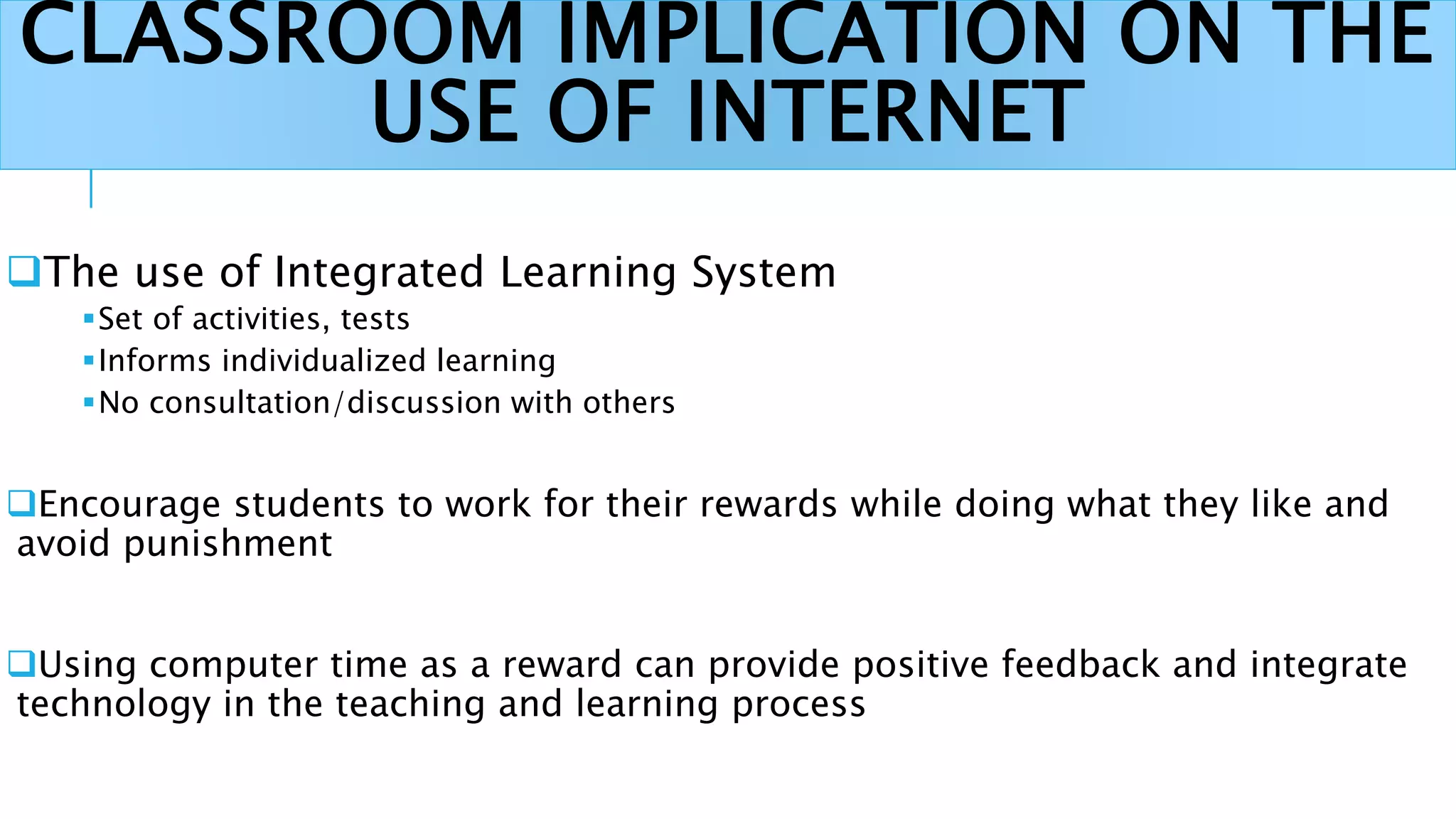
This document discusses the history and use of the internet in schools. It describes how the internet allows for non-linear and interactive learning experiences. Teachers can take on different pedagogical roles from direct instructors to facilitators. Constructivist learning theories emphasize active and social learning processes where students construct knowledge rather than just receiving facts. The internet supports constructivist approaches by enabling problem-solving, inquiry-based activities, and sharing of knowledge through online discussions and collaborations.