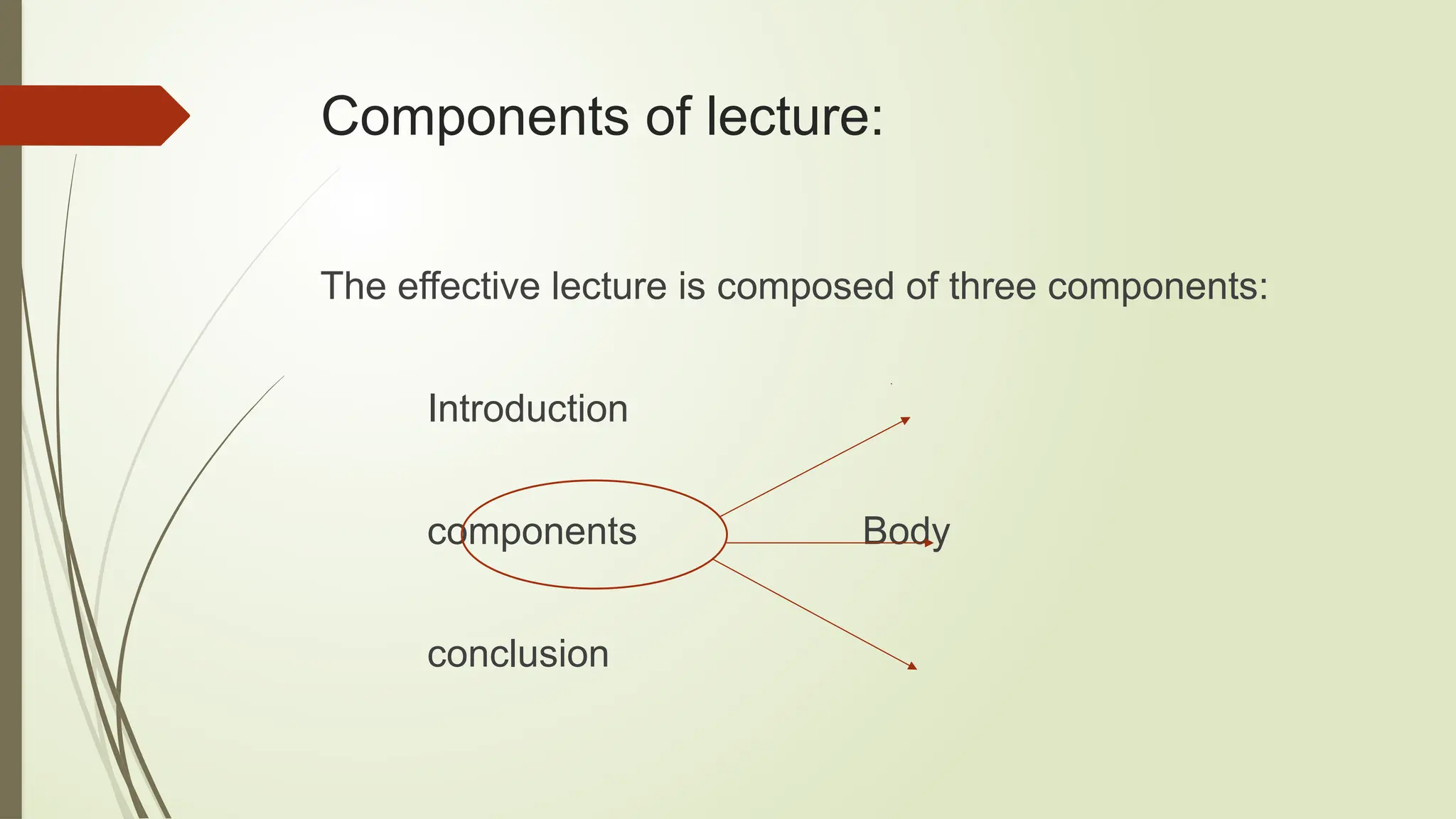
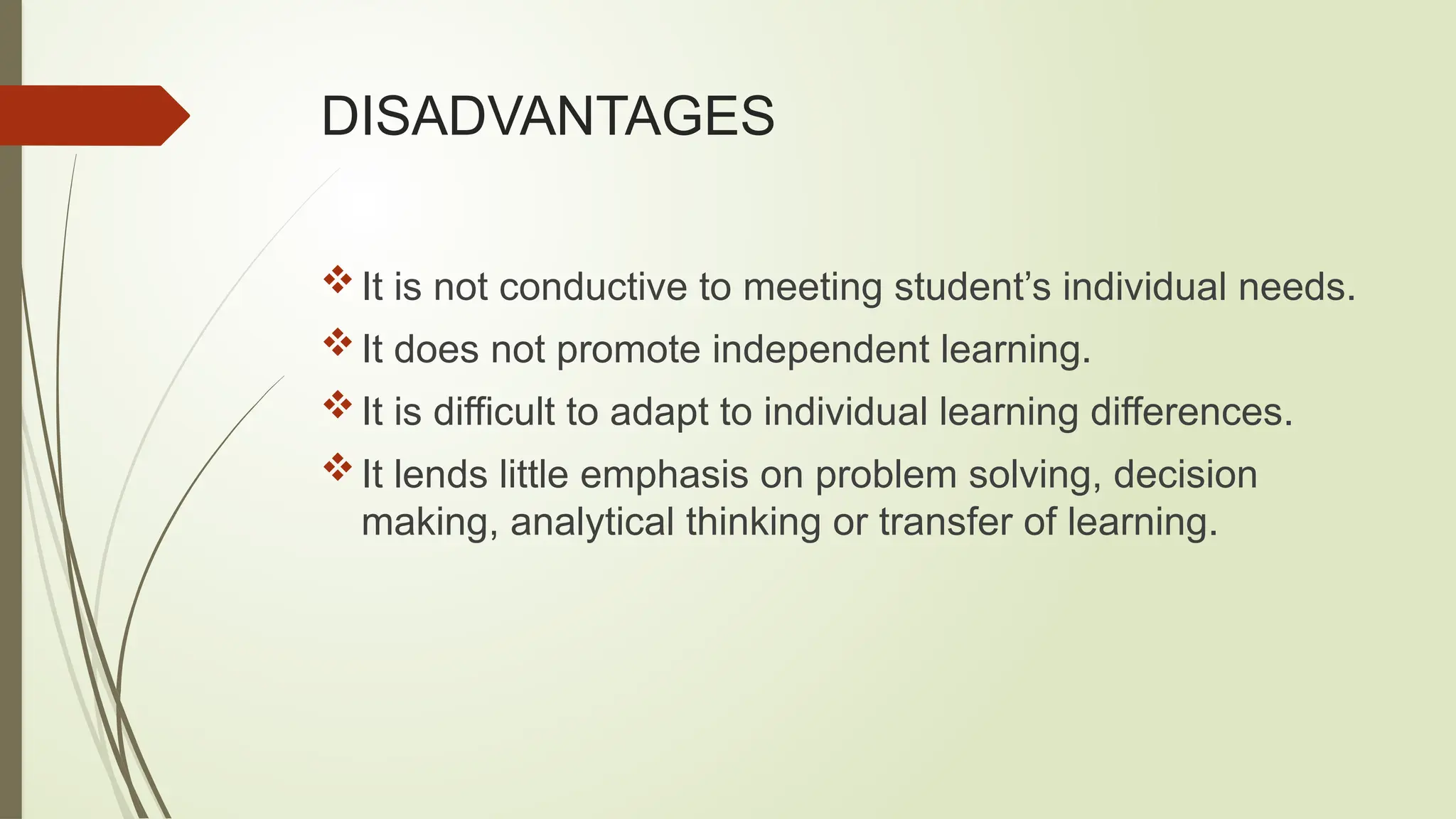
The lecture method is a traditional pedagogical approach where the teacher communicates structured information to a large audience, often resulting in passive student engagement. Key components of an effective lecture include an engaging introduction, well-organized body content, and a conclusive summary that encourages interaction. While lectures can efficiently deliver information and foster concentration, they have limitations, such as not accommodating individual learning needs or promoting critical thinking.