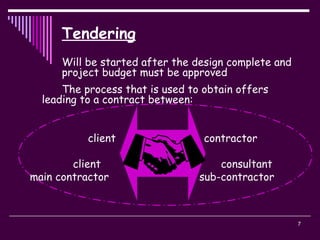
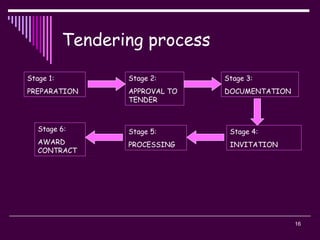
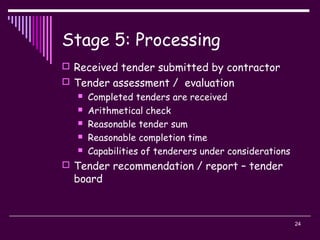
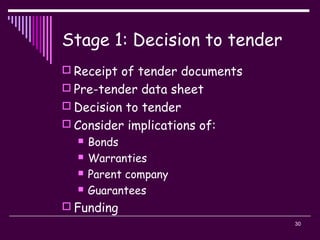
The document discusses the tender process and documentation. It describes the typical stages of a tendering project, including:
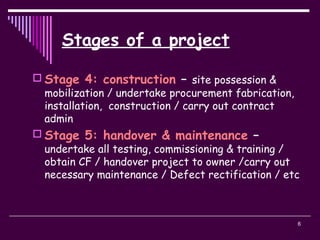
1) Inception and feasibility, design, tendering, construction, and handover.
2) The tendering process, which includes selecting a procurement method, developing a tender list, preparing documentation, inviting tenders, evaluating submissions, and awarding a contract.
3) The responsibilities and activities involved for both the client/project managers and contractors, such as estimating costs, assessing risks, and submitting a final bid.