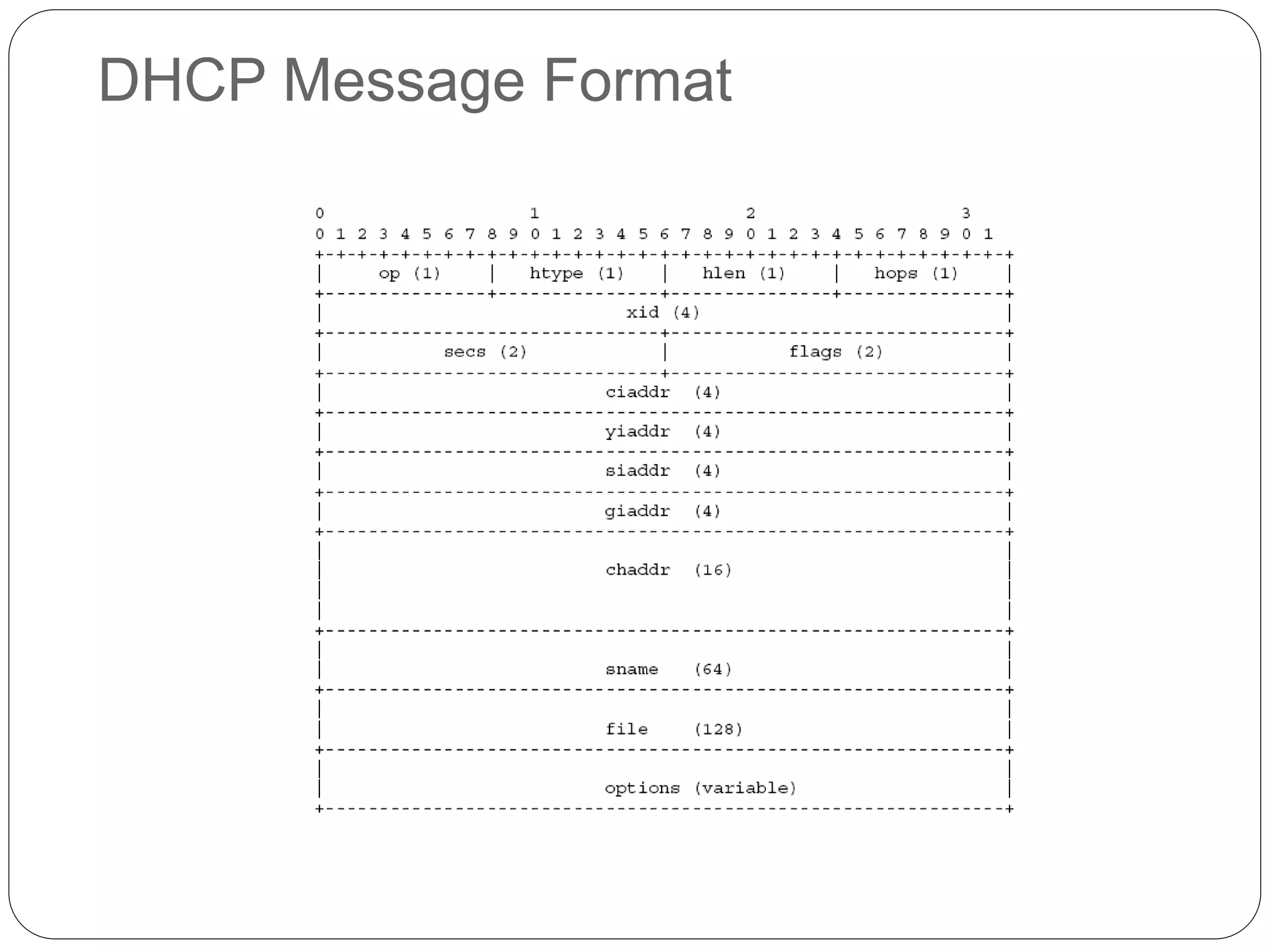
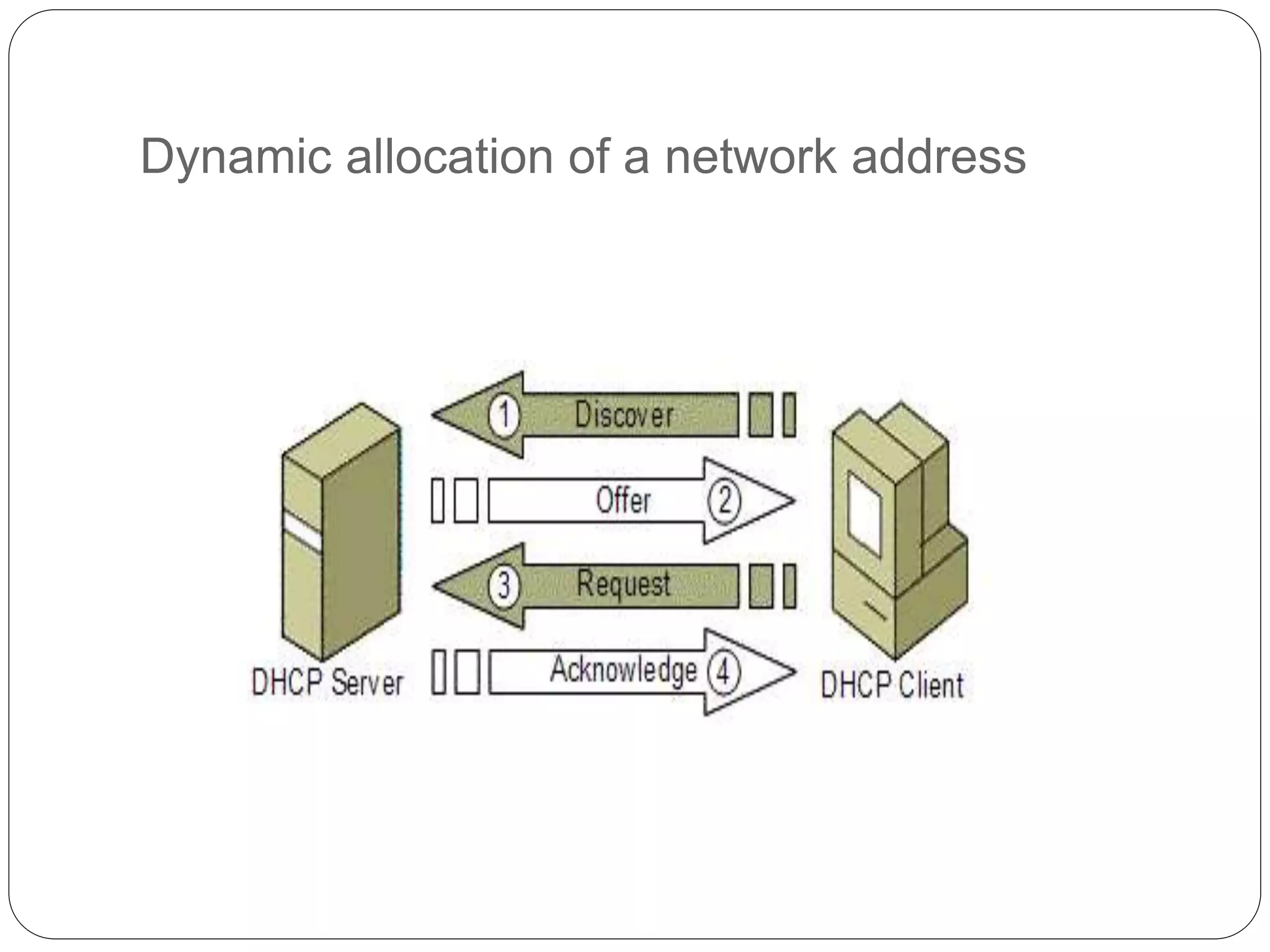
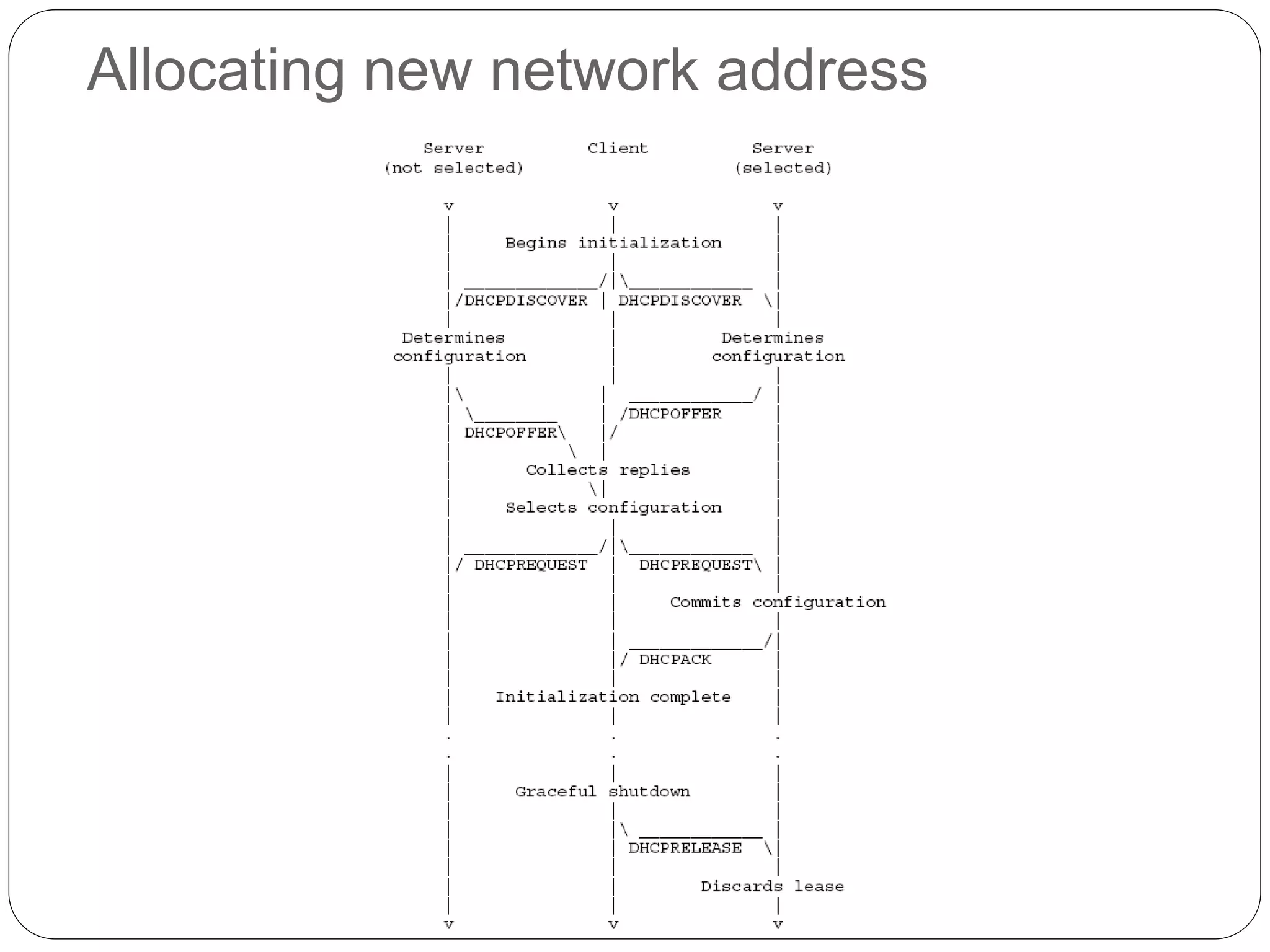
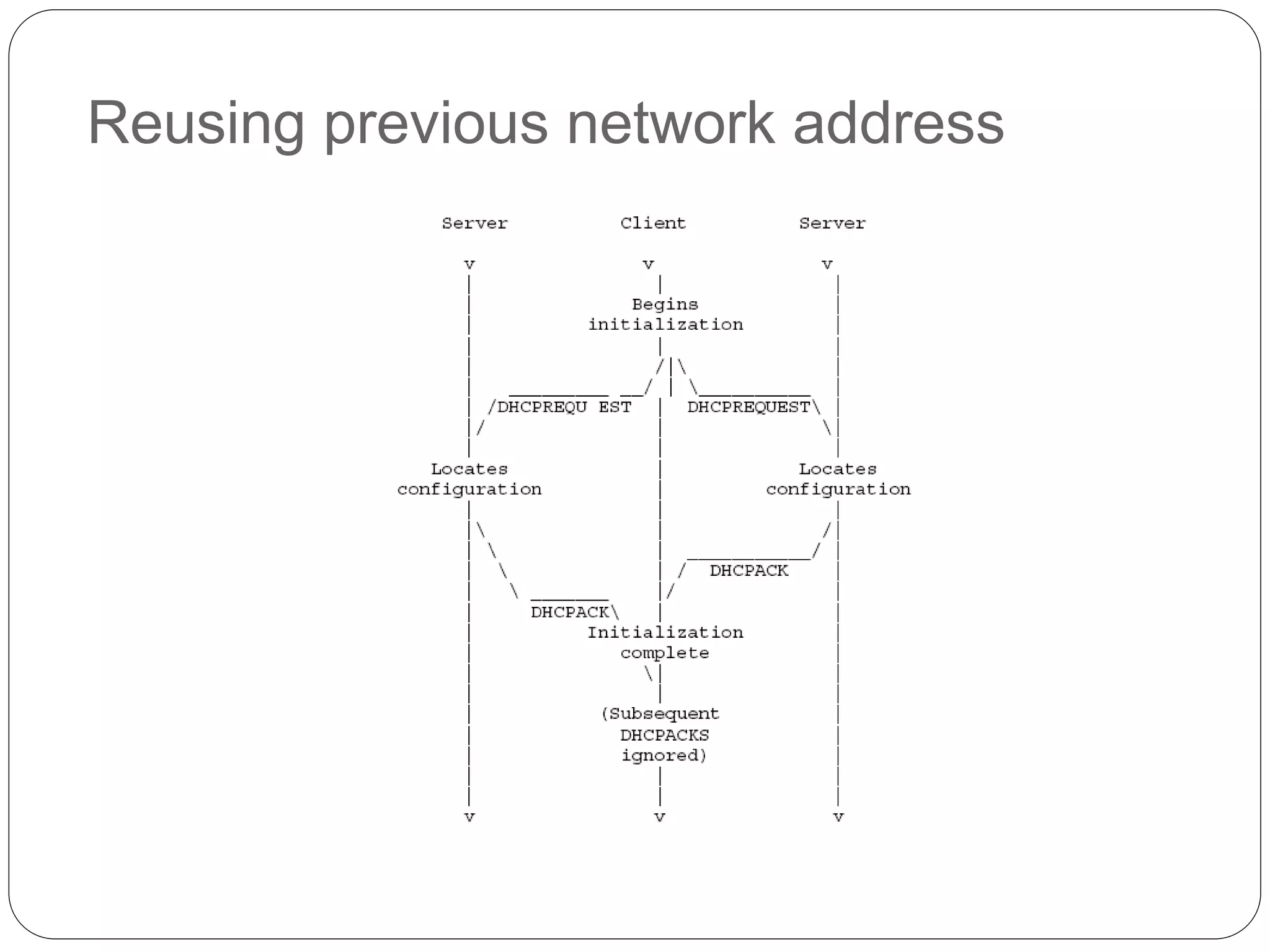
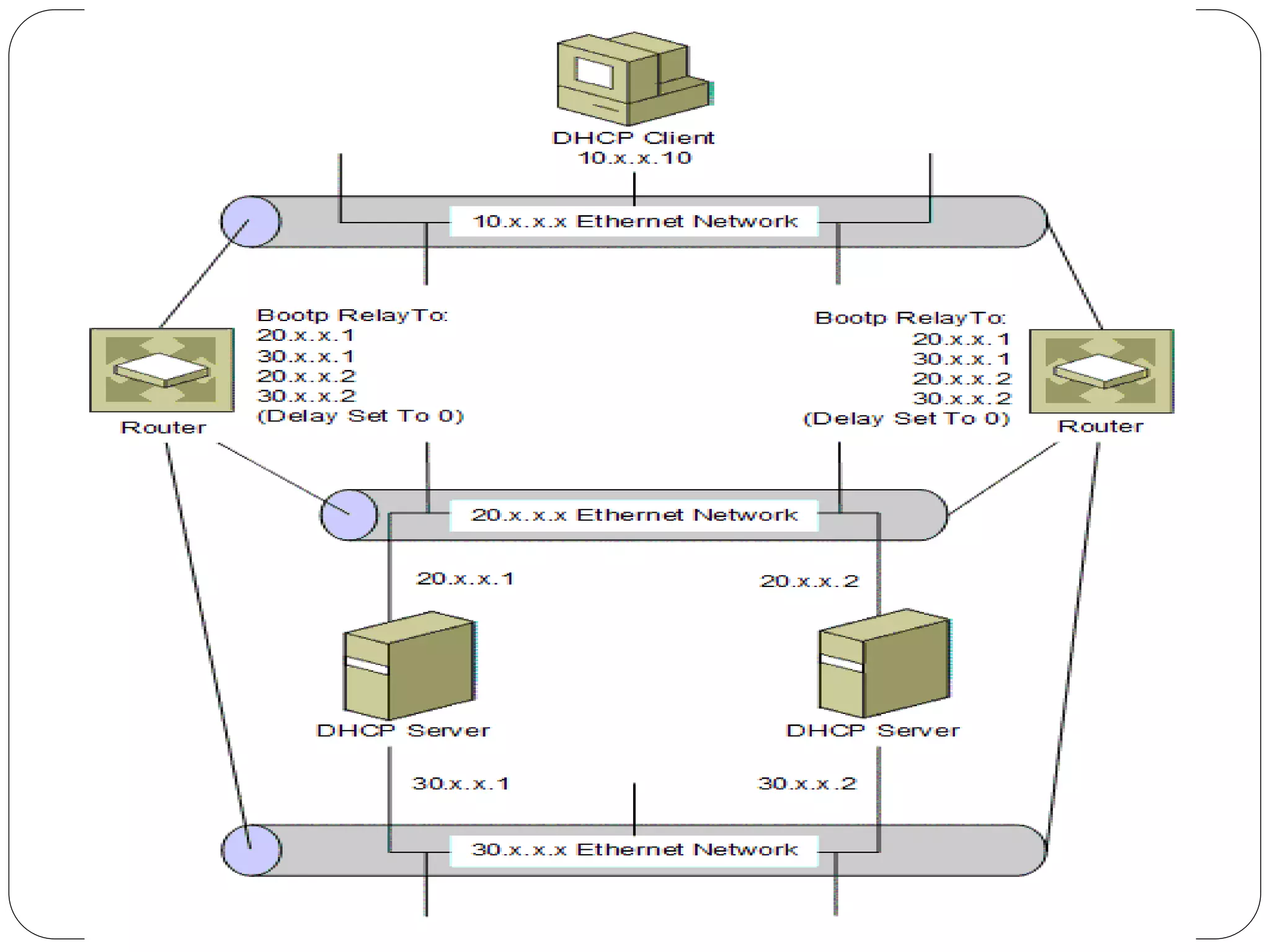
DHCP is a protocol that automatically assigns IP addresses to devices on a network to simplify network administration. It was created in 1987 to extend the BOOTP protocol. DHCP runs on UDP ports 67 and 68. The main purposes of DHCP are to allocate network addresses to clients and deliver configuration parameters. It uses messages like DHCPDISCOVER, DHCPOFFER, and DHCPACK to dynamically allocate IP addresses and handle requests from clients to reuse addresses.