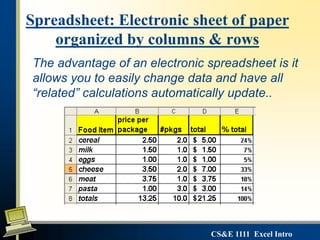
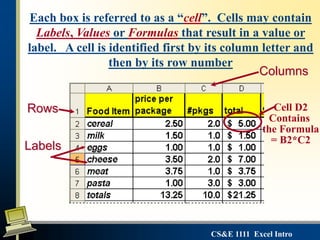
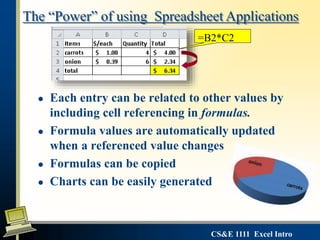
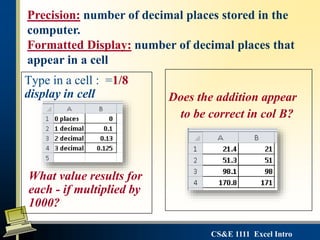
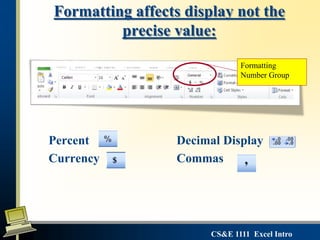
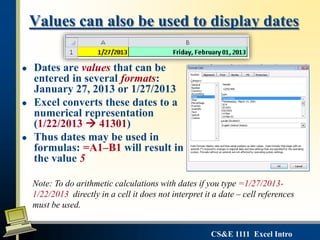
This document provides an introduction to Microsoft Excel. It defines key Excel concepts like spreadsheets, worksheets, cells, formulas and functions. It explains how to enter and format data, write formulas, and create basic charts. It also covers best practices for building a simple spreadsheet, including inserting and deleting rows/columns, formatting cells, and naming worksheets. The objectives are to define spreadsheets, introduce basic Excel features, and review important vocabulary.