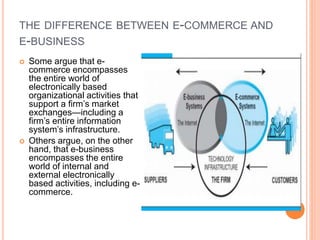
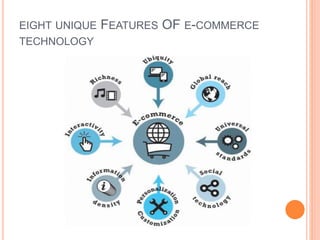
E-commerce refers to business transactions conducted online over the internet. It differs from traditional commerce by its ubiquity - it can be accessed anywhere at any time. Key features of e-commerce include its global reach, universal technical standards, lower market entry costs, richness of information, interactivity, high information density, personalization, and social networking aspects. The evolution of e-commerce has seen early experimentation in the 1990s, a market crash in the early 2000s, and now a new vibrant model combining social, mobile and local aspects alongside traditional online retail.