This document summarizes key points from a physics lecture on magnetism:
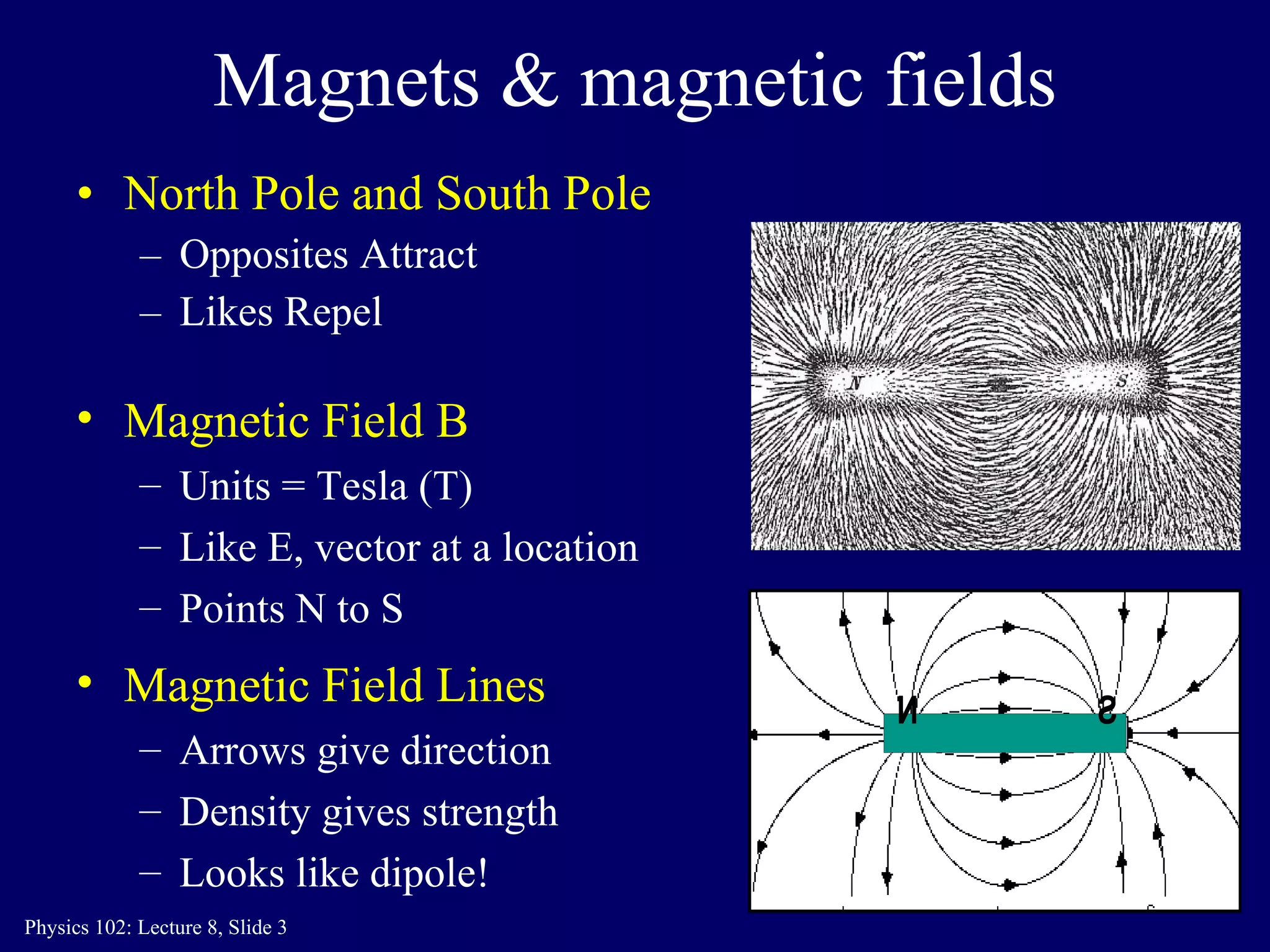
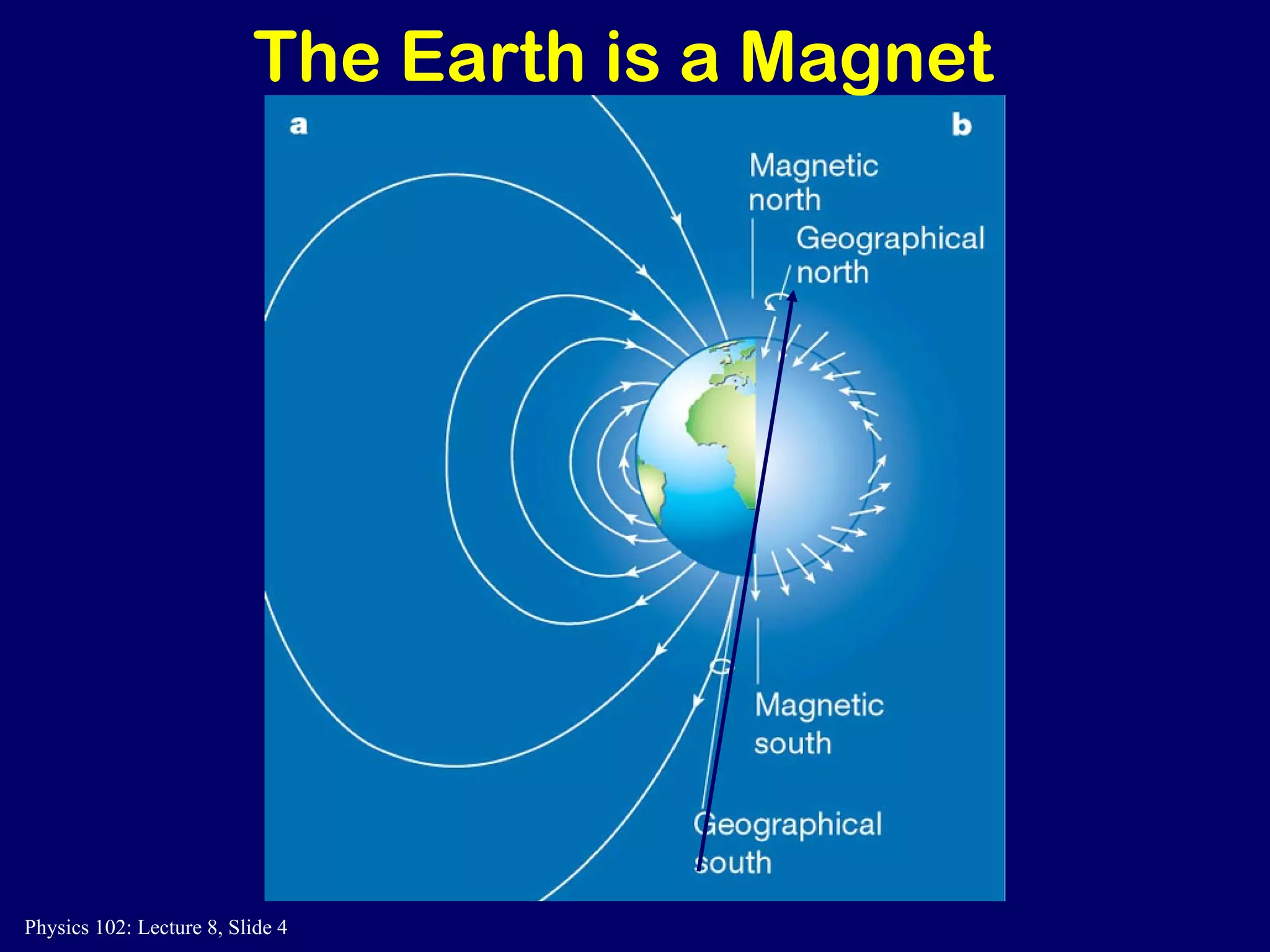
1) Magnetic fields B are created by moving electric charges like electrons orbiting an atom's nucleus or electron spin. Magnetic fields exert forces on moving charges.
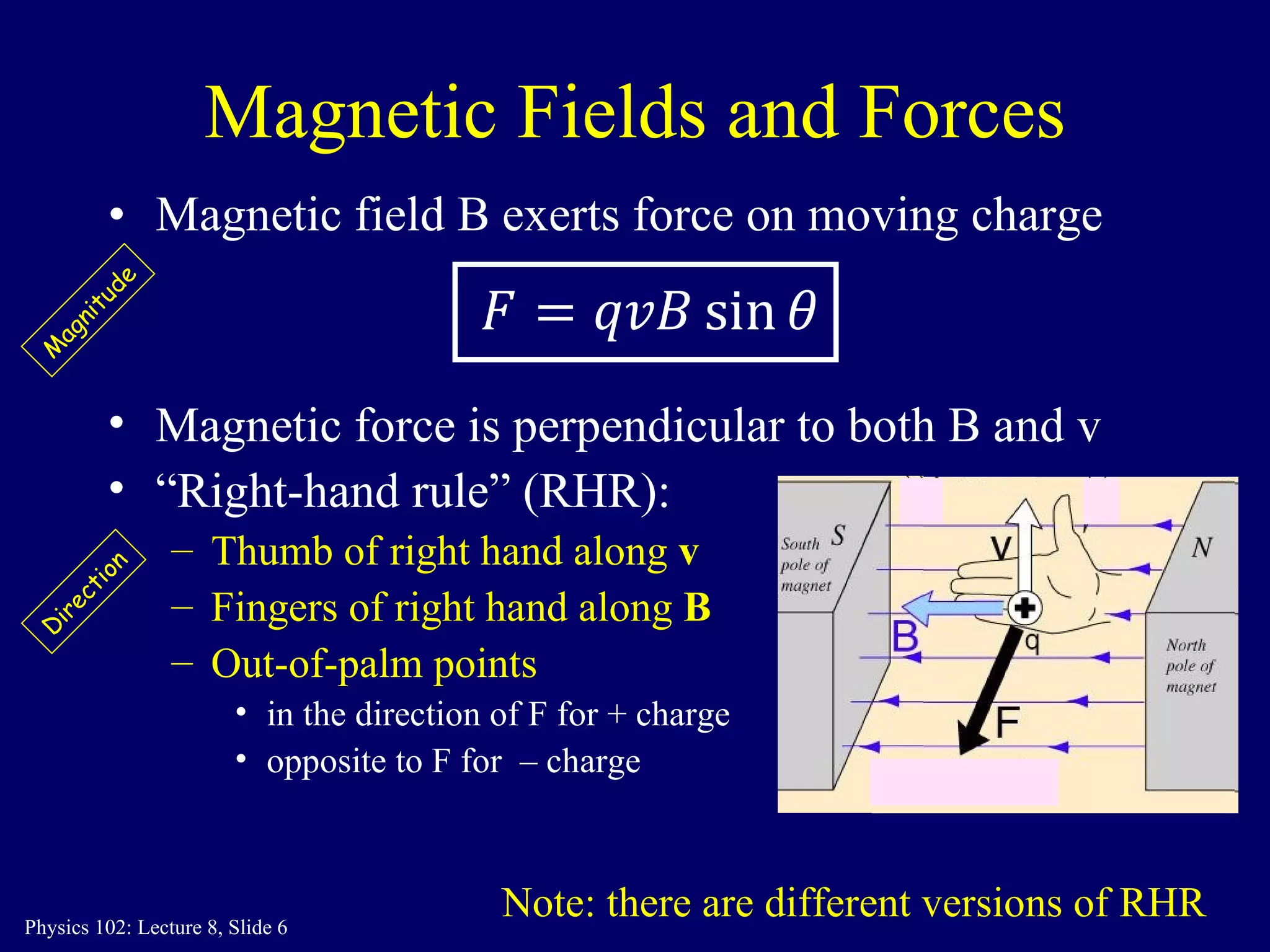
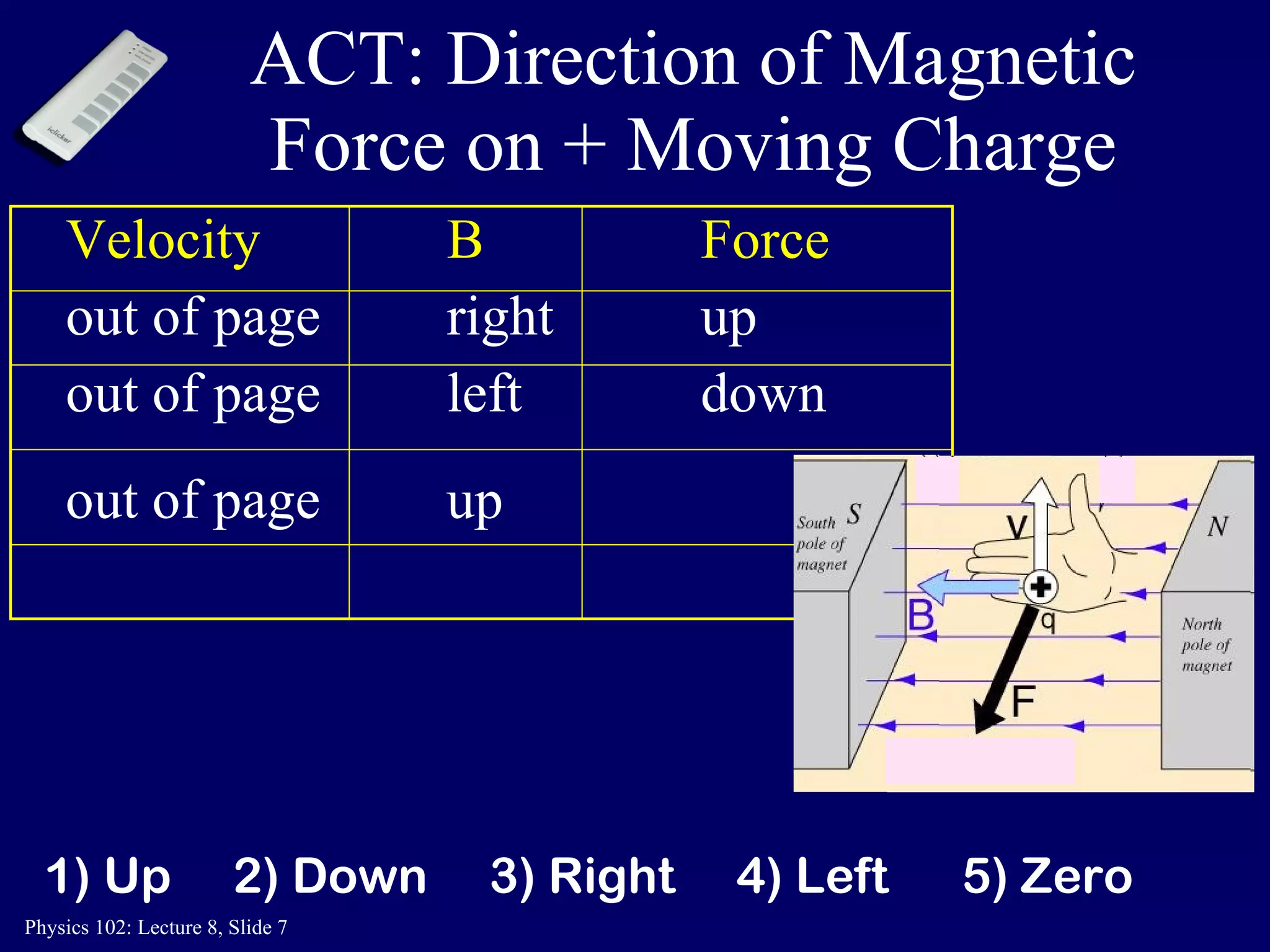
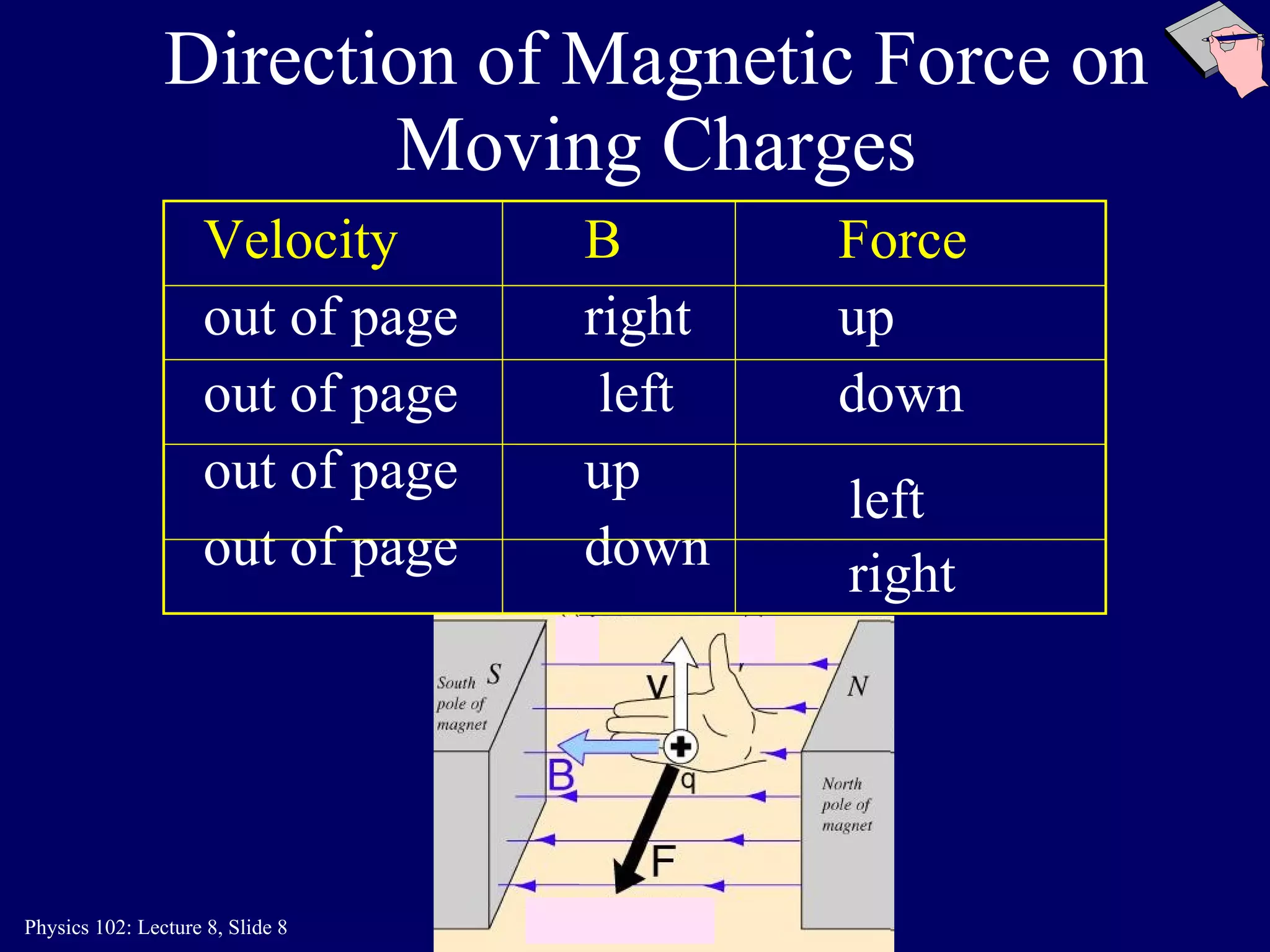
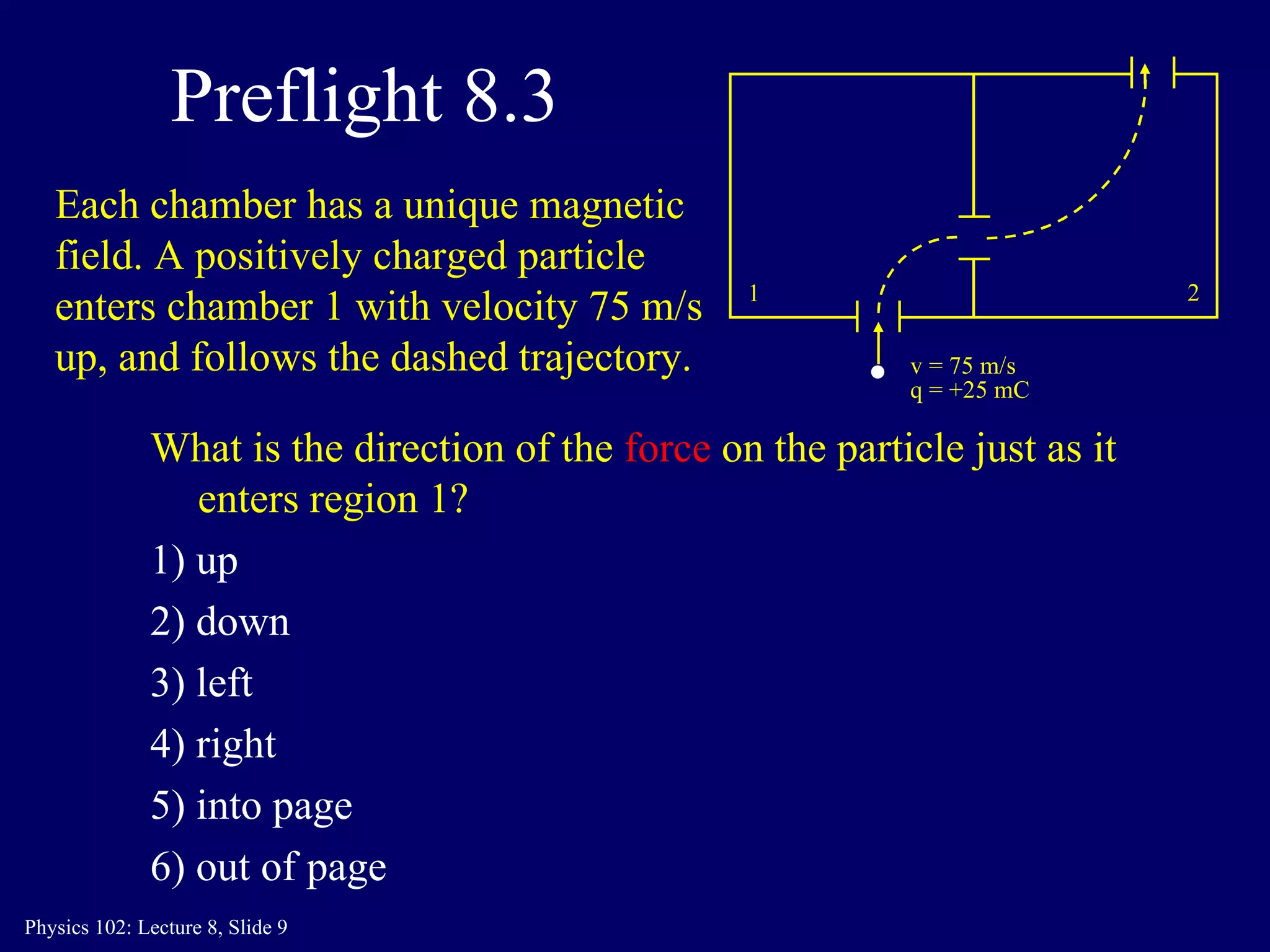
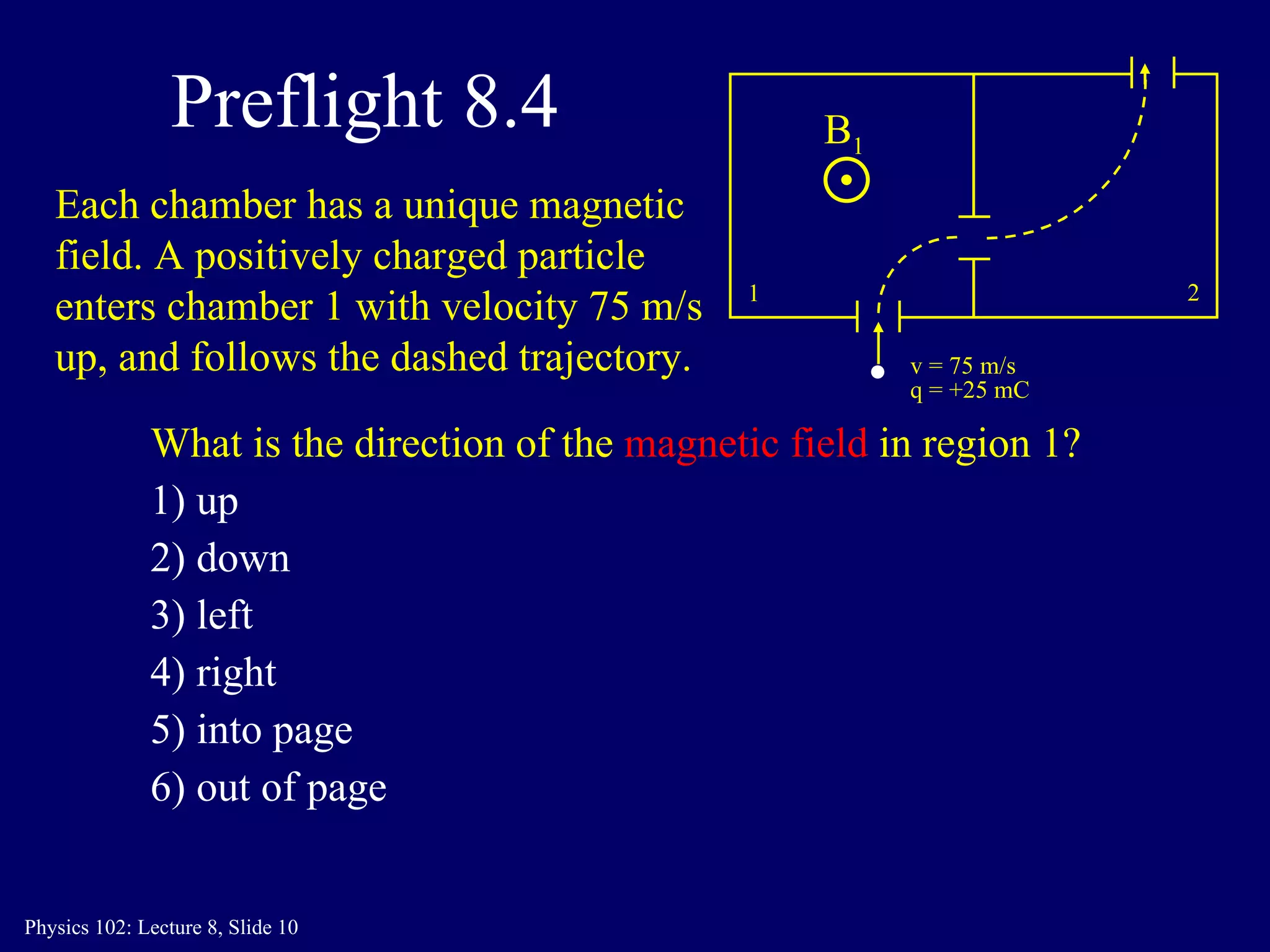
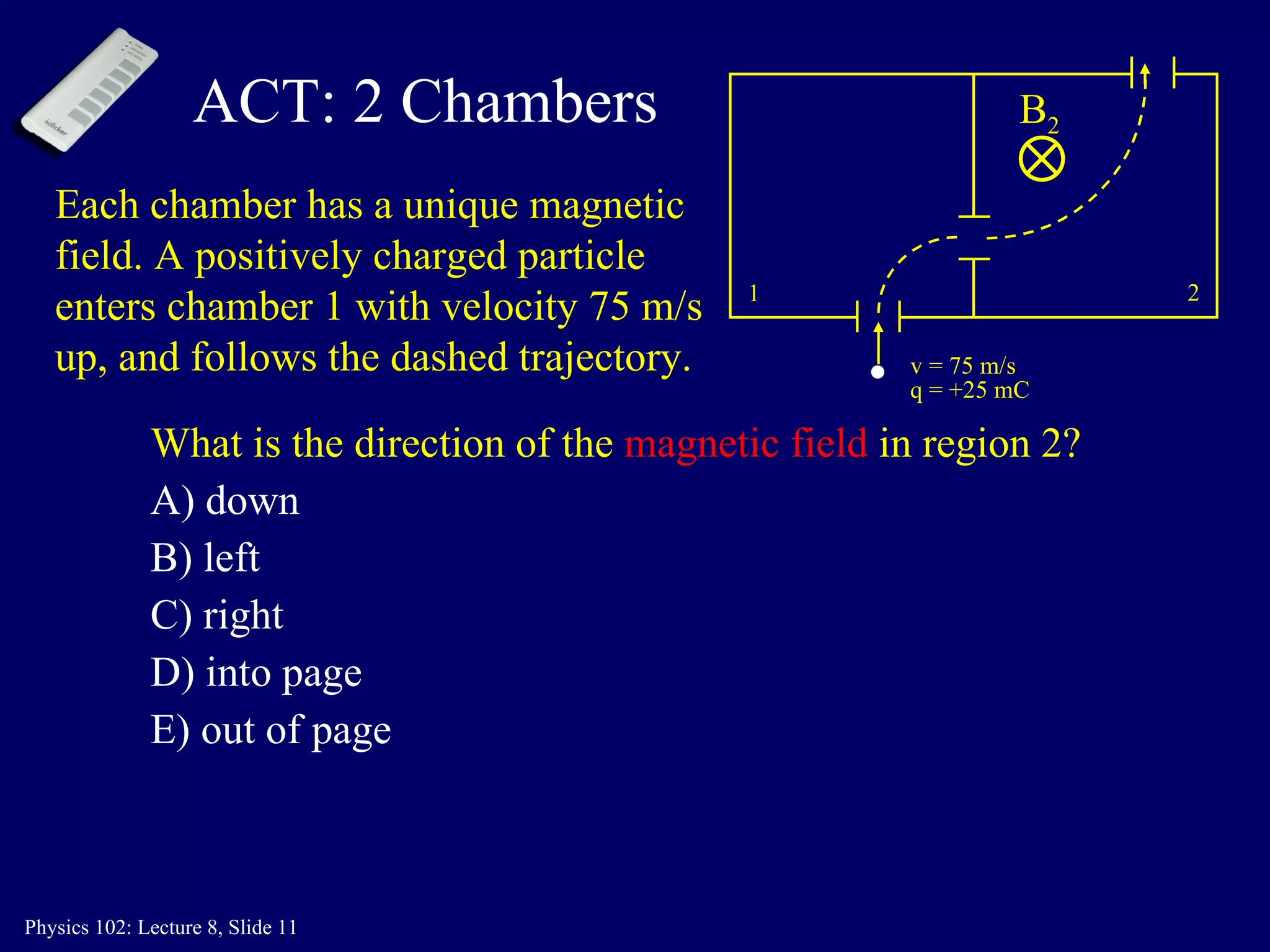
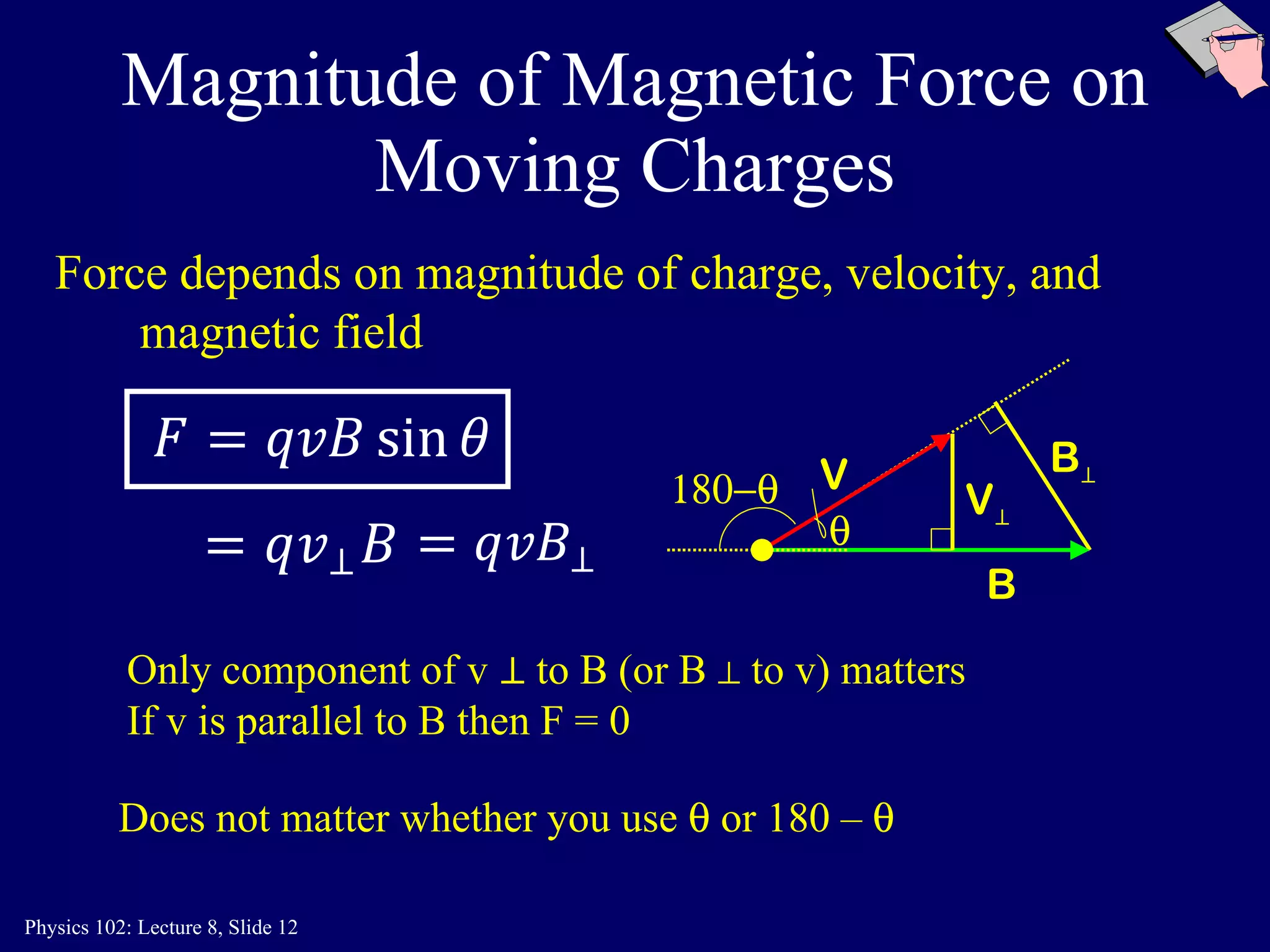
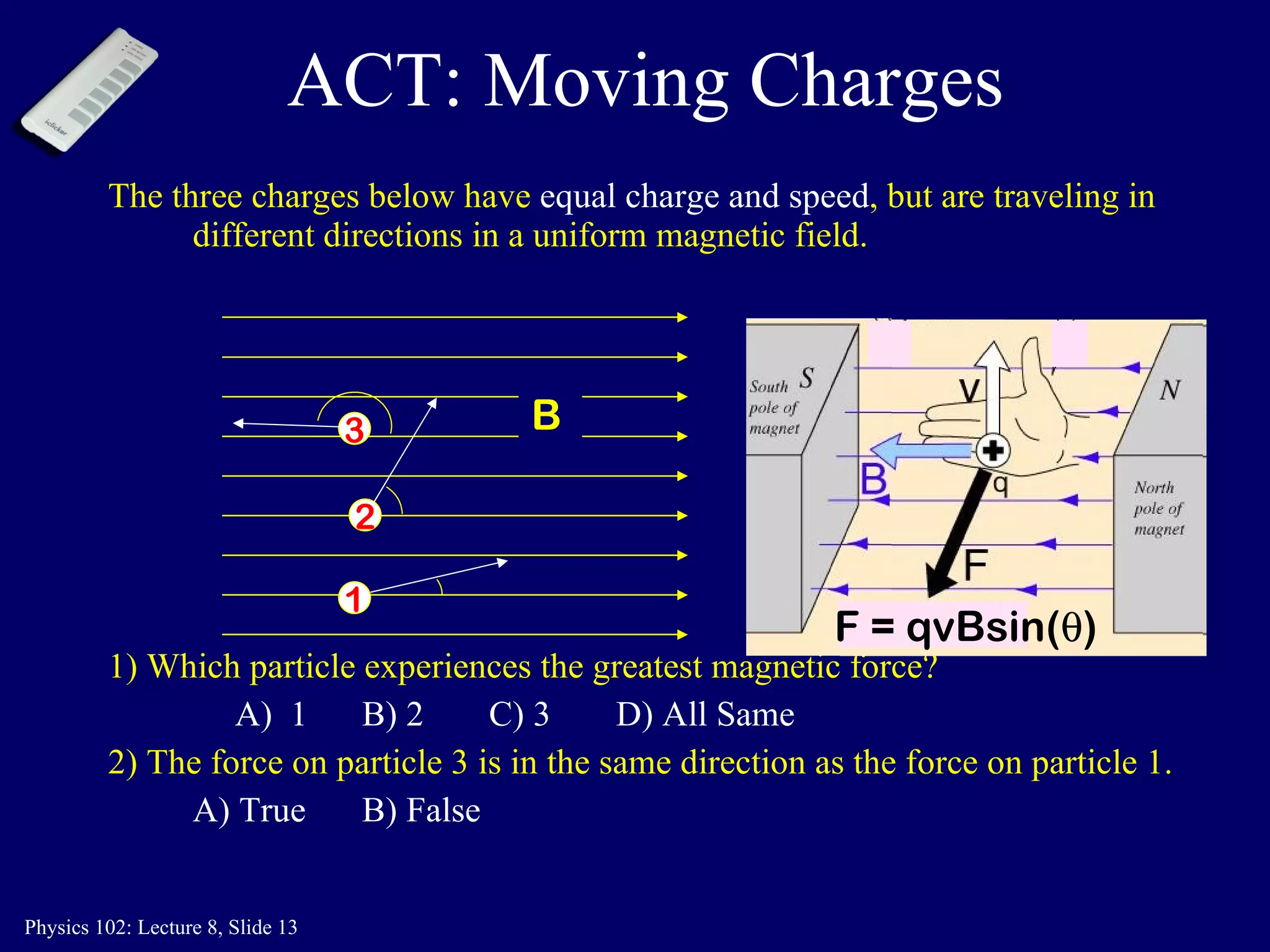
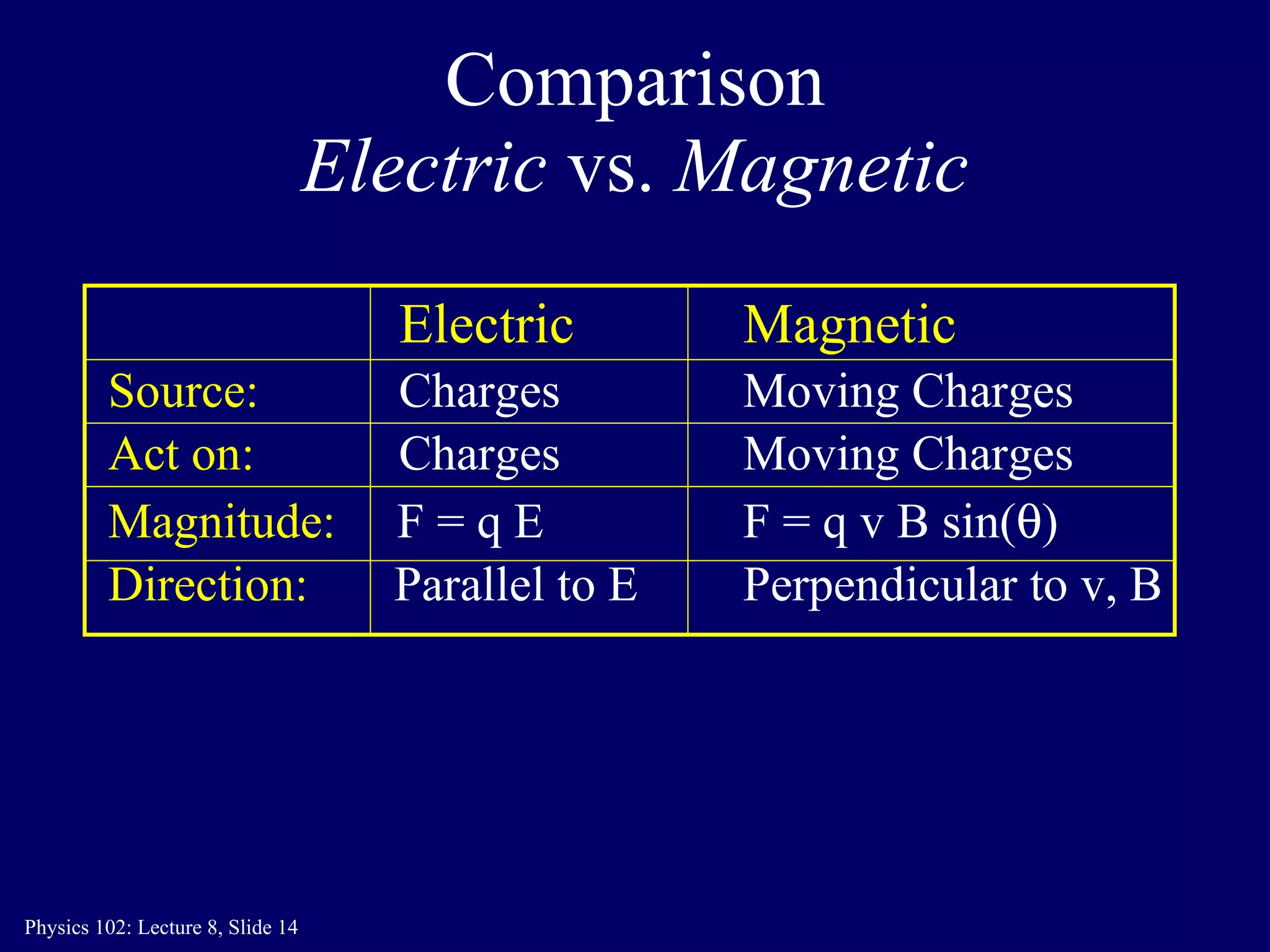
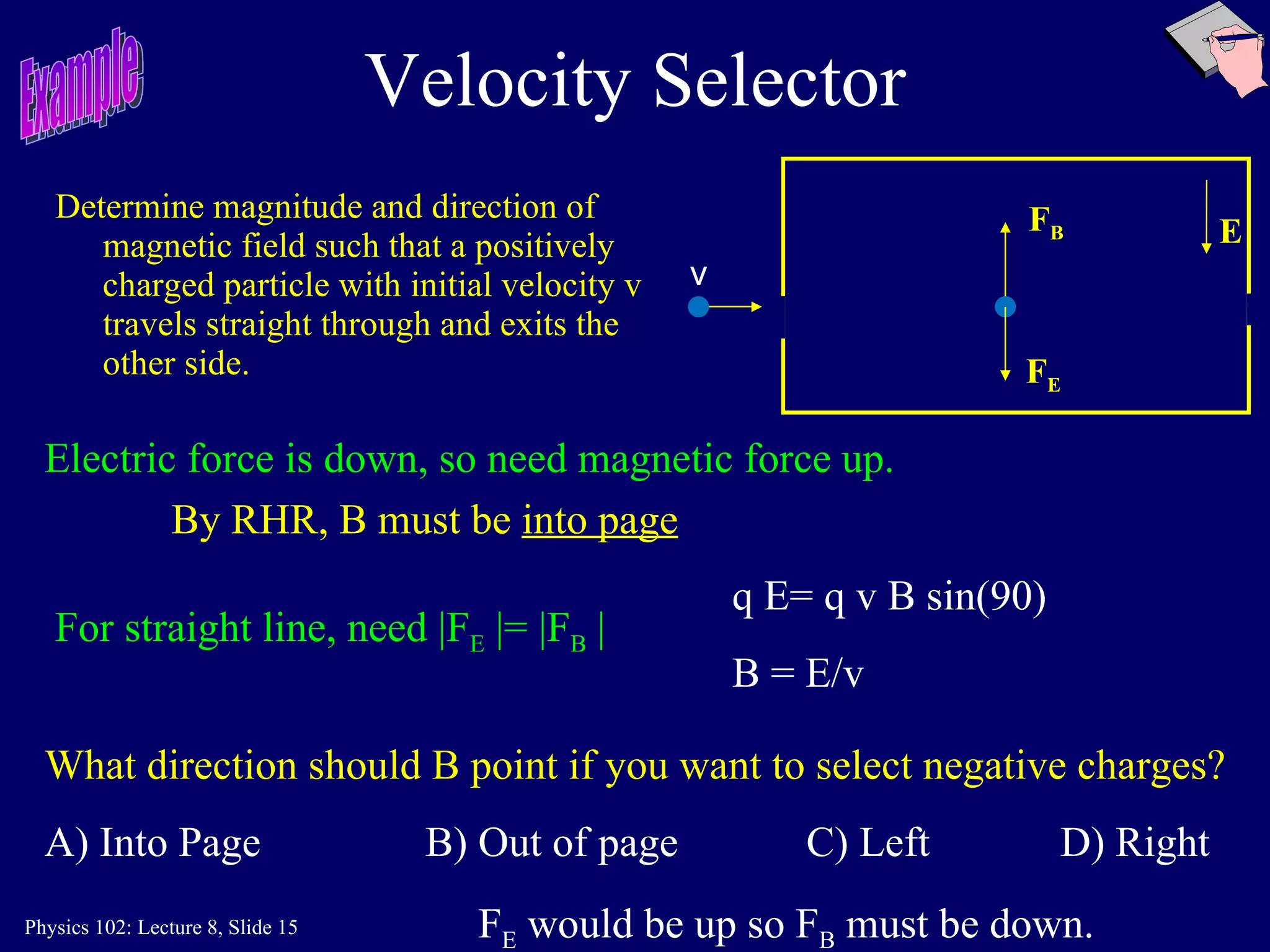
2) The direction of the magnetic force on a moving charge is perpendicular to both the magnetic field B and the charge's velocity v, as described by the right-hand rule. The magnitude depends on the charge q, velocity v, and magnetic field strength B.
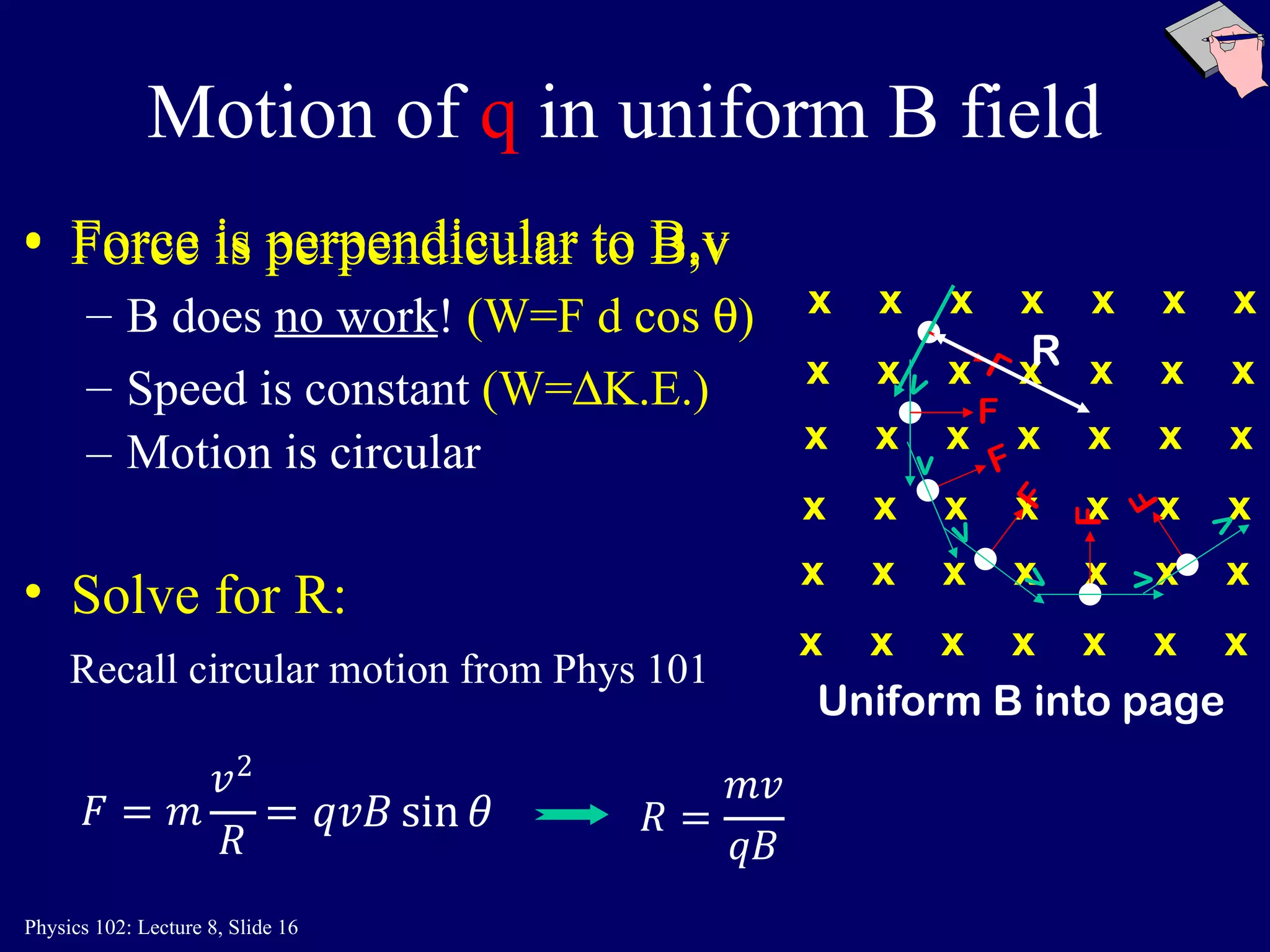
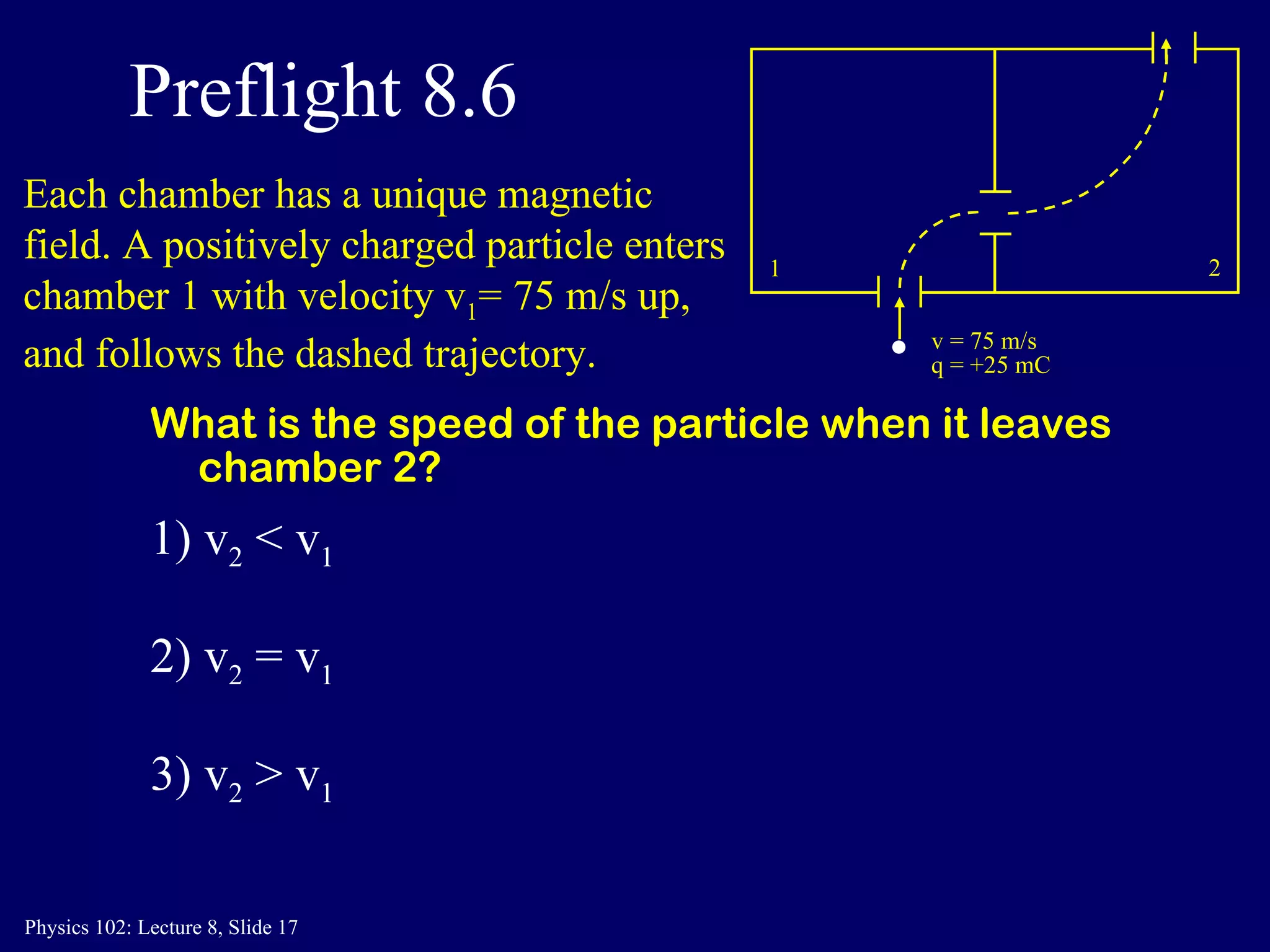
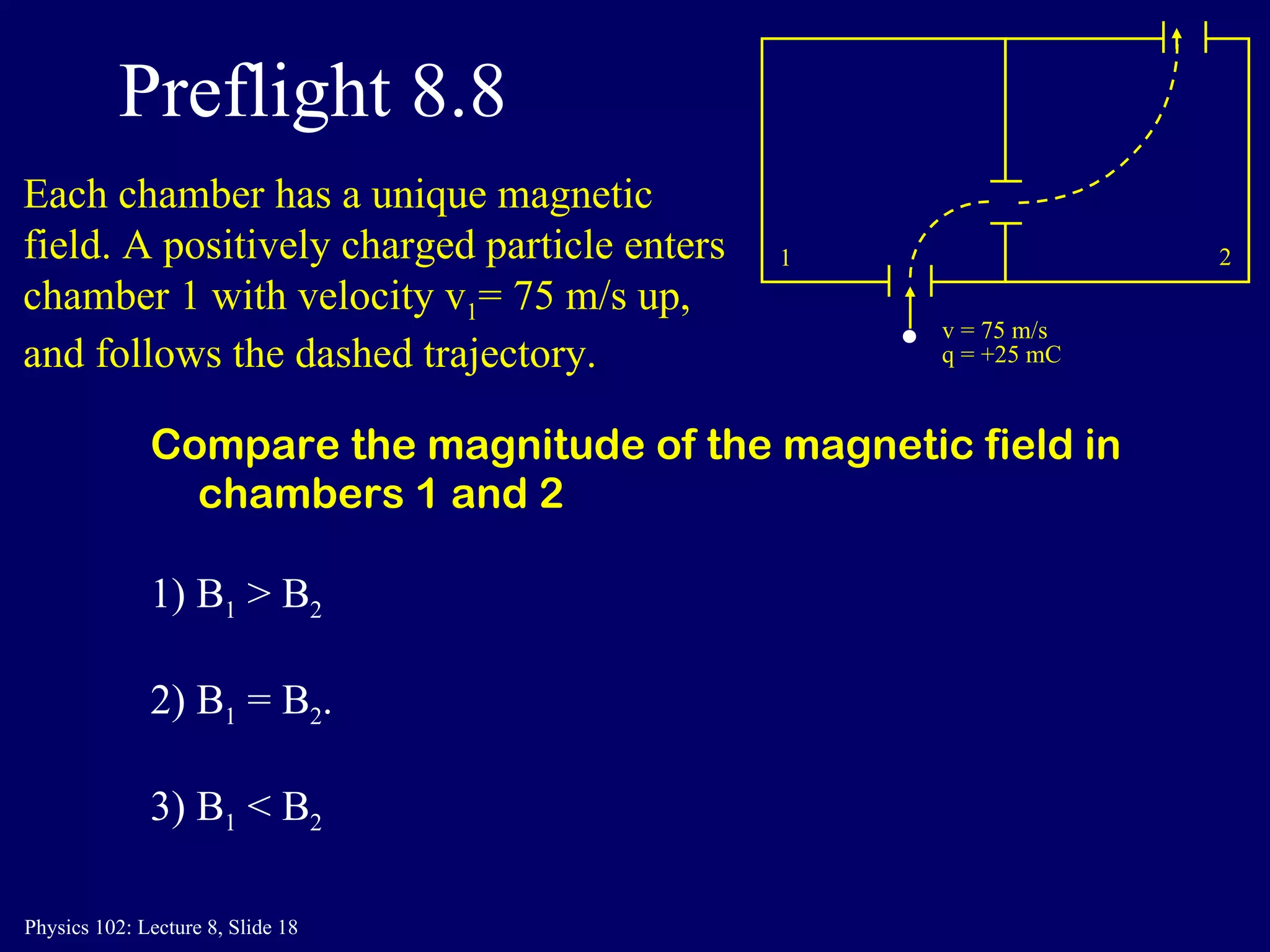
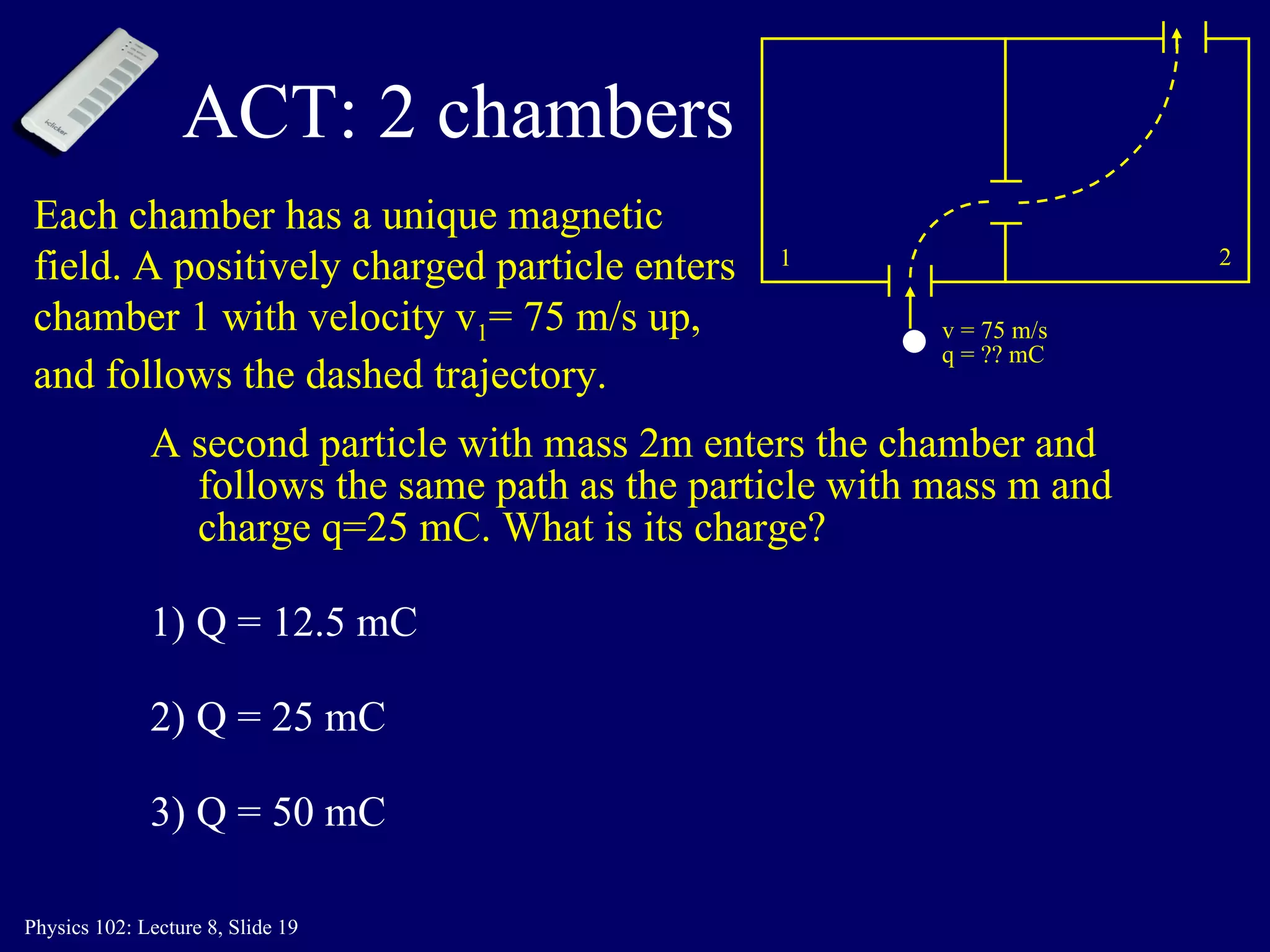
3) In a uniform magnetic field, the motion of a charged particle is circular, with the magnetic force always perpendicular to the velocity. The speed remains constant and the particle travels in a circular path.