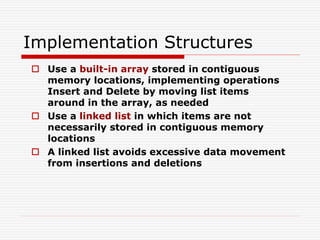
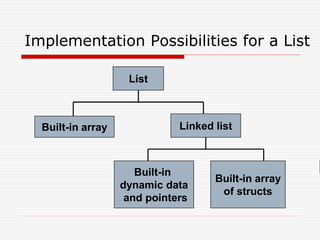
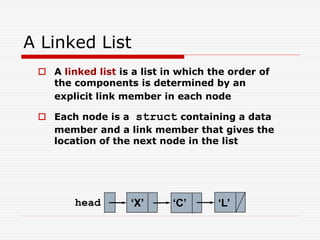
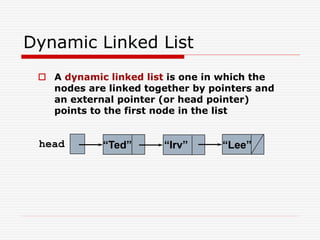
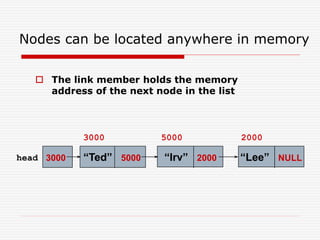
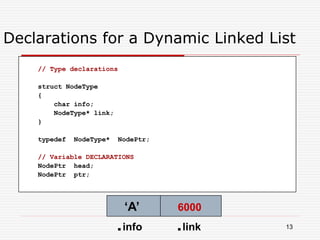
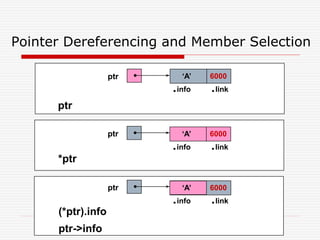
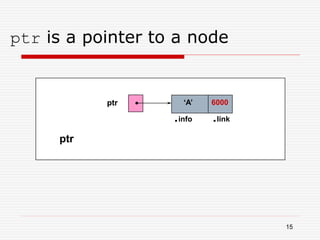
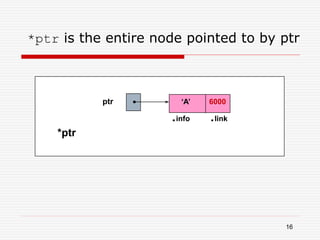
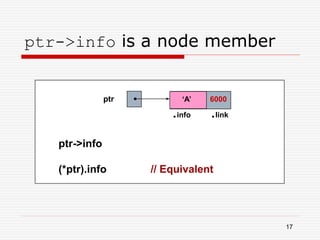
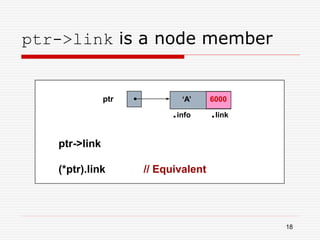
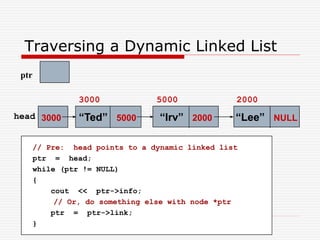
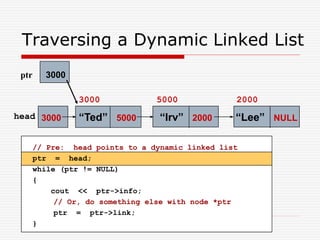
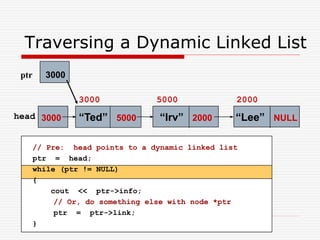
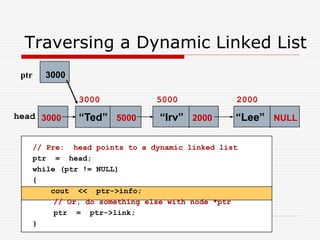
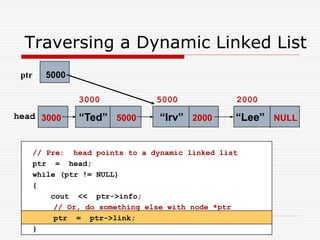
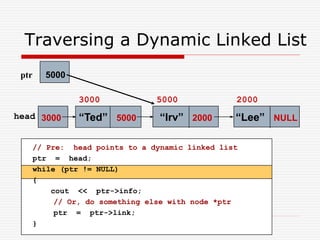
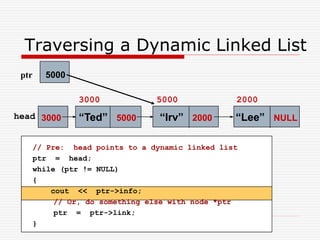
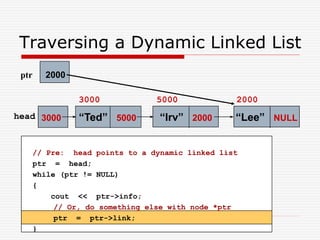
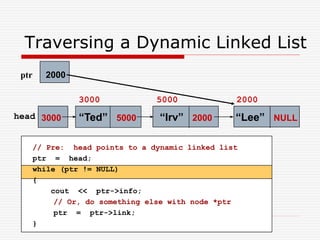
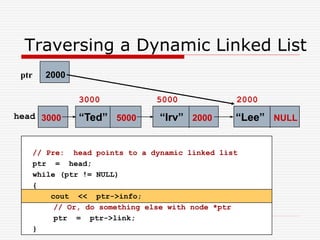
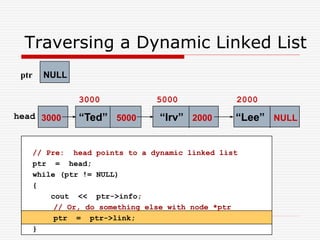
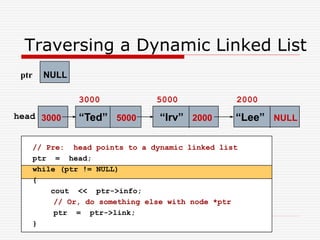
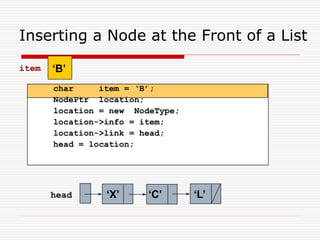
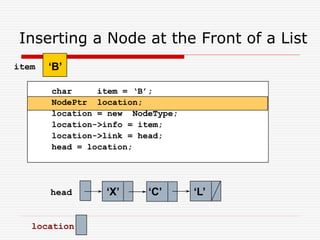
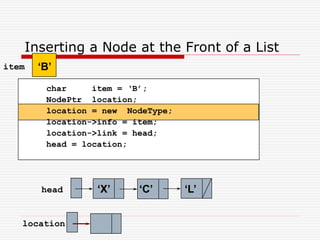
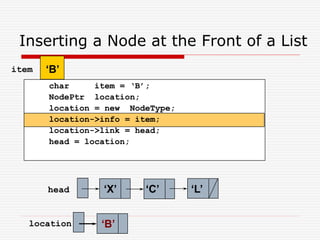
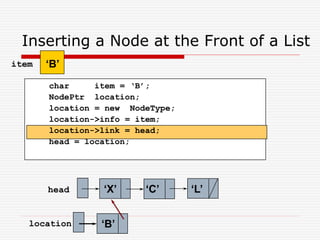
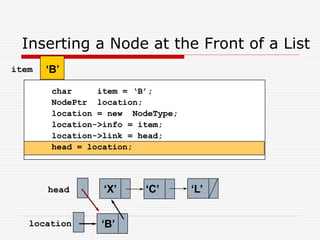
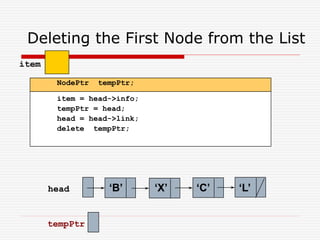
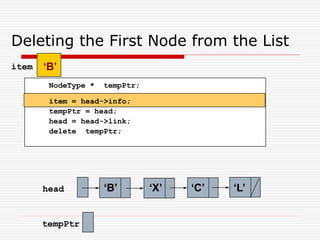
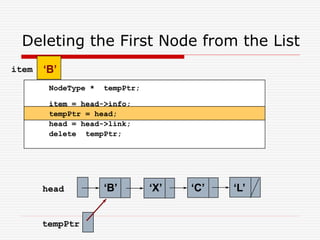
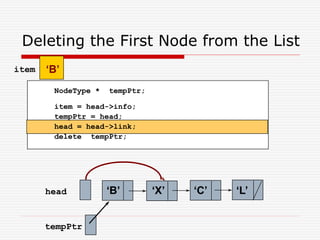
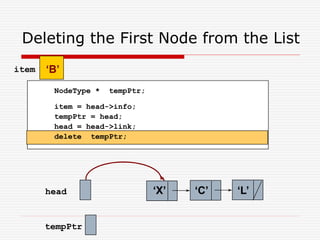
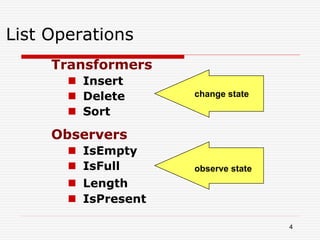
The document discusses various topics related to dynamic linked lists including their meaning, traversal, insertion, and deletion operations. It describes implementing a list abstract data type using either an array or linked list as the underlying data structure. Key points covered include traversing a linked list using pointers, inserting and deleting nodes by allocating and deallocating memory dynamically, and the additional operations needed for a sorted linked list such as insert as first and remove first elements.


![Array-based class List
Reset
IsFull
Length
IsPresent
Delete
IsEmpty
Insert
GetNexItem
Private data:
length
data [0]
[1]
[2]
[MAX_LENGTH-1]
currentPos
SelSort](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec6mod-linkedlist-101201072120-phpapp02/85/Lec6-mod-linked-list-6-320.jpg)
![// Specification file array-based list (list.h)
const int MAX_LENGTH = 50;
typedef int ItemType;
class List // Declares a class data type
{
public: // Public member functions
List(); // constructor
bool IsEmpty () const;
bool IsFull () const;
int Length () const; // Returns length of list
void Insert (ItemType item);
void Delete (ItemType item);
bool IsPresent(ItemType item) const;
void SelSort ();
void Reset ();
ItemType GetNextItem ();
private: // Private data members
int length; // Number of values currently stored
ItemType data[MAX_LENGTH];
int CurrentPos; // Used in iteration
};
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec6mod-linkedlist-101201072120-phpapp02/85/Lec6-mod-linked-list-7-320.jpg)