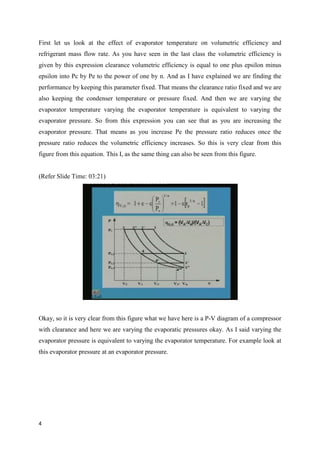
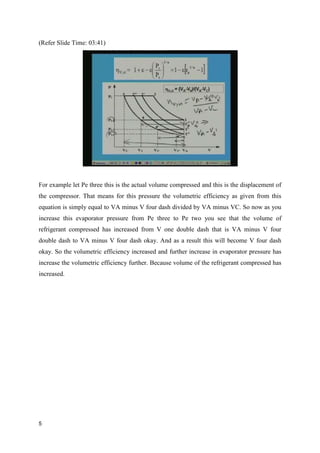
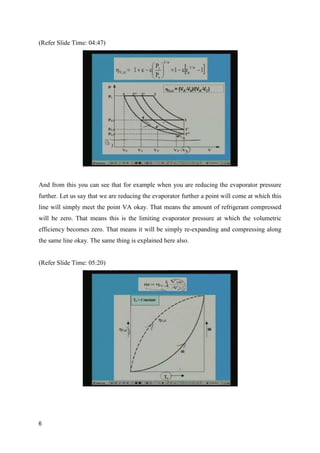
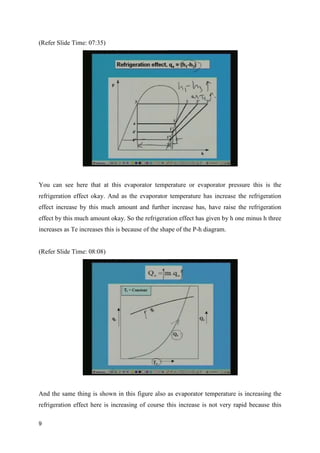
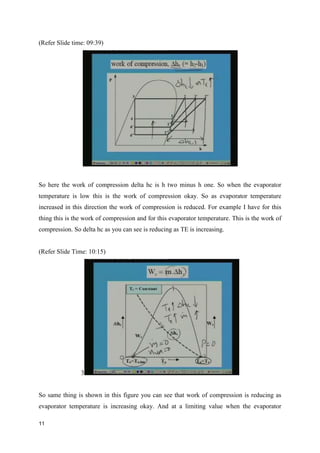
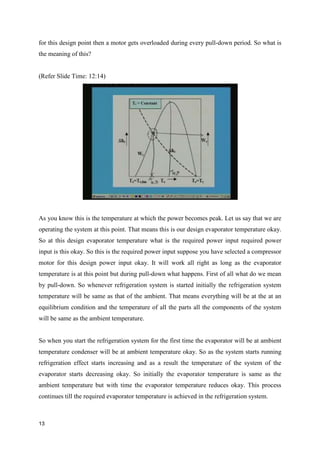
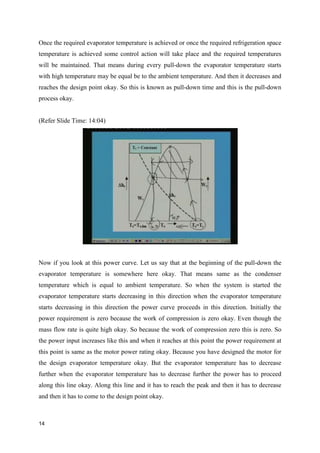
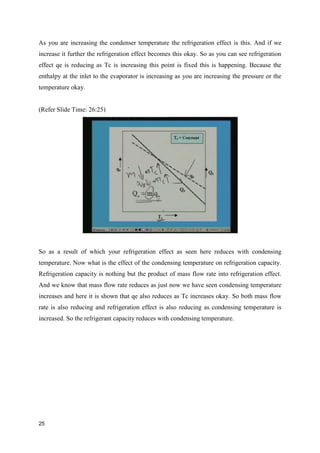
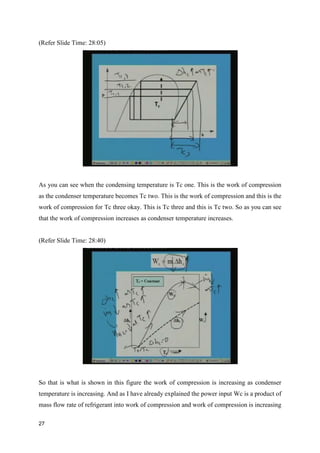
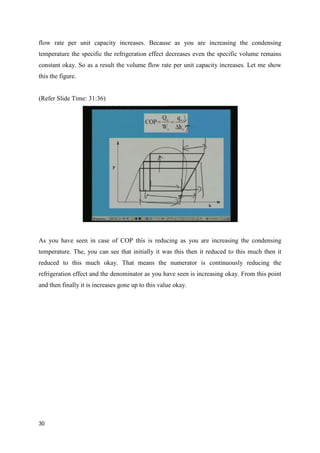
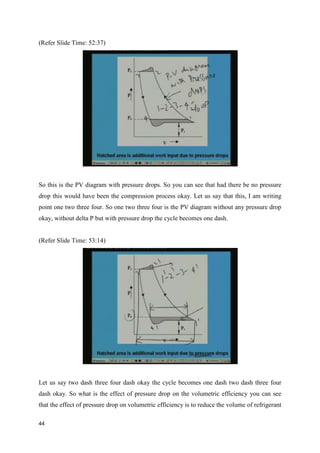
The document discusses the effects of evaporator temperature on the performance of an ideal reciprocating compressor. It states that as evaporator temperature increases, volumetric efficiency and mass flow rate increase rapidly while work of compression and power requirement decrease, following a peaked curve. The maximum power occurs at an intermediate evaporator temperature. During the compressor's pull-down process, when the evaporator temperature decreases from ambient to the design point, the motor may overload if not designed for the peak power. Throttling the suction during pull-down or unloading some compressor cylinders are offered as solutions.