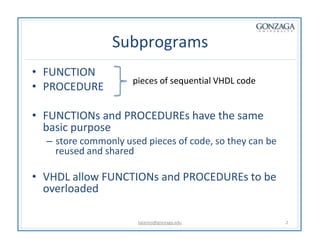
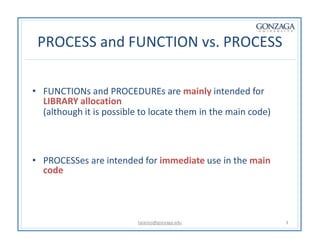
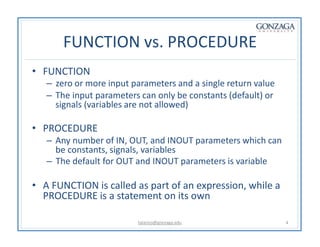
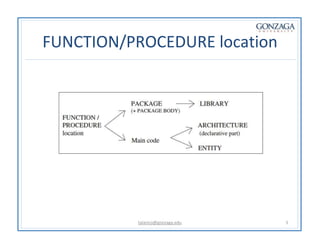
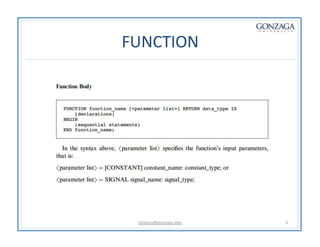
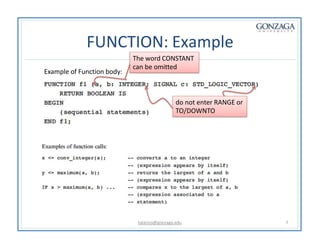
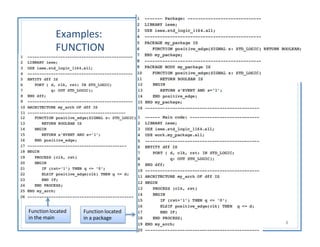
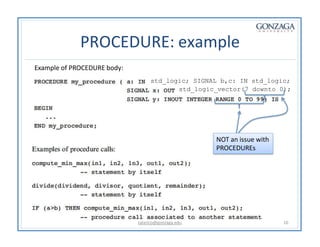
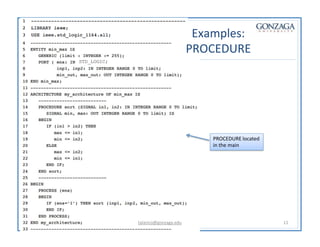
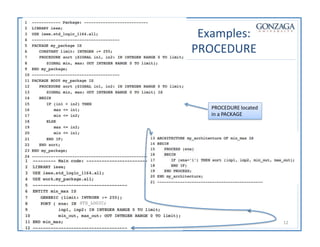
Functions and procedures in VHDL serve to store reusable code. Functions return a single value while procedures can have input, output, and in-out parameters. Functions can only accept constant or signal inputs, while procedures can accept constants, signals, and variables. Functions are used as part of expressions, while procedures are standalone statements. Functions and procedures can be defined in the main code or in libraries and packages.