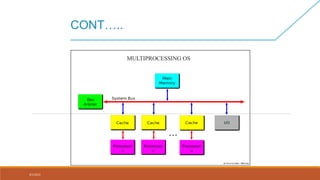
This document discusses different types of operating systems, including single-user operating systems designed for one user, multi-user operating systems that allow multiple simultaneous users, and real-time operating systems designed for applications that require fast and predictable responses to events. It provides examples of operating systems for each type, such as Windows and Mac OS for single-user multi-tasking, UNIX and VMS for multi-user, and QNX and RTLINUX for real-time applications. The document also covers embedded operating systems designed for small devices, multiprogramming systems that run multiple programs concurrently, and multiprocessing systems that utilize multiple CPUs.