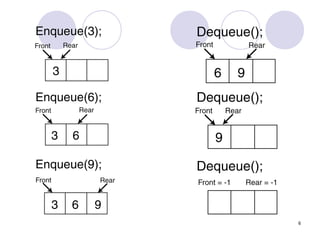
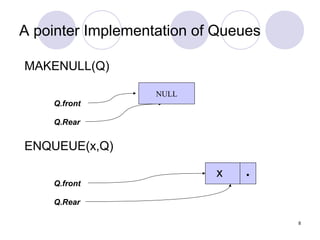
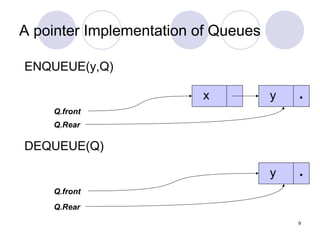
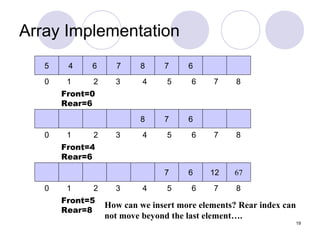
1. A queue is a first-in, first-out (FIFO) data structure where items are inserted at the rear of the queue and deleted from the front.
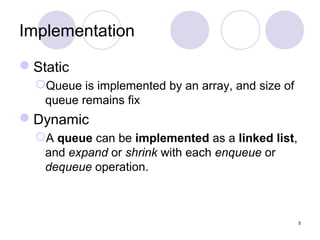
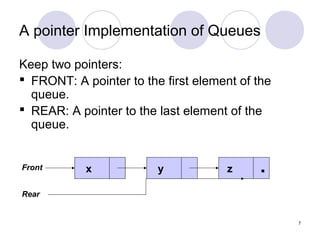
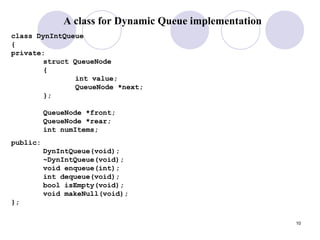
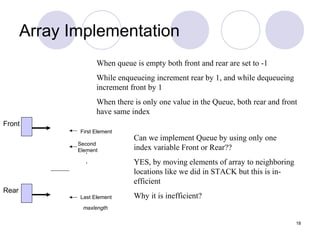
2. Queues can be implemented using arrays or linked lists, with operations including enqueue to add an item to the rear, and dequeue to remove an item from the front.
3. Queues have many applications where processing or accessing data in a first-come, first-served order is important, such as in operating systems, communication software, and printing.













![24
IntQueue::IntQueue(int s) //constructor
{
queueArray = new int[s];
queueSize = s;
front = -1;
rear = -1;
numItems = 0;
}
IntQueue::~IntQueue(void) //destructor
{
delete [] queueArray;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec-12queues-140316023216-phpapp01/85/Algo-Queues-24-320.jpg)
![25
//********************************************
// Function enqueue inserts the value in num *
// at the rear of the queue. *
//********************************************
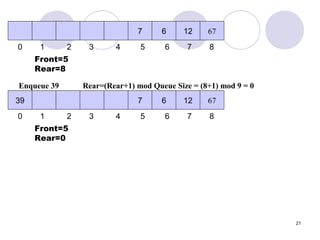
void IntQueue::enqueue(int num)
{
if (isFull())
cout << "The queue is full.n";
else
{
// Calculate the new rear position
rear = (rear + 1) % queueSize;
// Insert new item
queueArray[rear] = num;
// Update item count
numItems++;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec-12queues-140316023216-phpapp01/85/Algo-Queues-25-320.jpg)
![26
//*********************************************
// Function dequeue removes the value at the *
// front of the queue, and copies t into num. *
//*********************************************
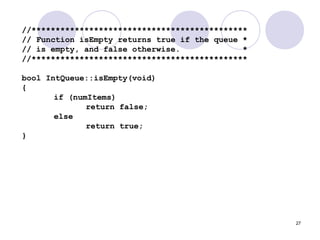
int IntQueue::dequeue(void)
{
if (isEmpty())
cout << "The queue is empty.n";
else
{
// Move front
front = (front + 1) % queueSize;
// Retrieve the front item
int num = queueArray[front];
// Update item count
numItems--;
}
return num;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec-12queues-140316023216-phpapp01/85/Algo-Queues-26-320.jpg)




![33
CQueue::CQueue(int size)
{
Front=Rear=-1;
Data=new int[size];
}
void CQueue ::Enqueue(int num);
{
if (IsFull()) { cout<<“Overflow” return; }
if (IsEmpty() Rear=Front=0;
else Rear=(Rear+1) % QueueSize;
Data[Rear]=num;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec-12queues-140316023216-phpapp01/85/Algo-Queues-33-320.jpg)
![34
int CQueue ::Dequeue(int num);
{
if (IsEmpty()) { cout<<“Underflow”; return; }
int ReturnValue=Data[Front];
if (Front==Rear) //only one element in the queue
Front=Rear=-1;
else
Front=(Front+1) % QueueSize;
return ReturnValue;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec-12queues-140316023216-phpapp01/85/Algo-Queues-34-320.jpg)
