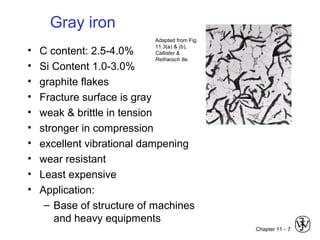
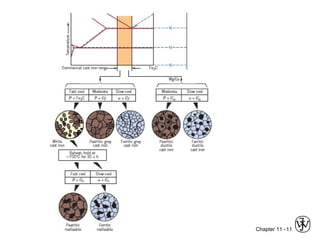
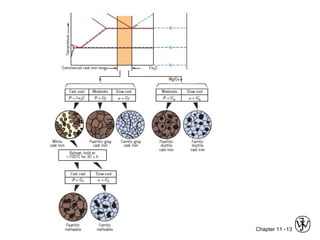
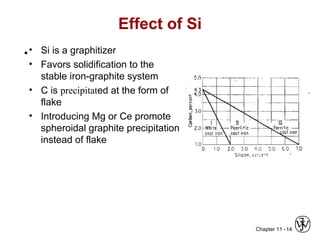
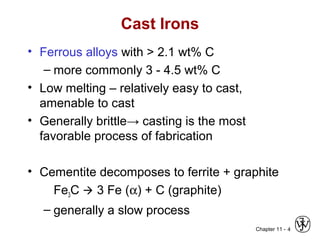
This document discusses types of cast iron and their properties and applications. It covers gray iron, which contains graphite flakes and is strong in compression; ductile iron, which contains graphite nodules and has improved mechanical properties through heat treatment; white iron, which is very hard and brittle; and malleable iron, made by heat treating white iron to form graphite rosettes. Silicon promotes graphite formation while sulfur promotes cementite formation and brittleness. The next class will cover the relationship between structure and properties of cast irons.


![Chapter 11 - 5
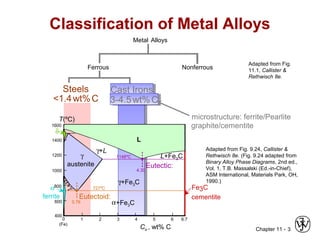
Fe-C True Equilibrium Diagram
Graphite formation
promoted by
• Si > 1 wt%
• slow cooling
Adapted from Fig. 11.2,
Callister & Rethwisch 8e.
[Fig. 11.2 adapted from
Binary Alloy Phase
Diagrams, 2nd ed.,
Vol. 1, T.B. Massalski (Ed.-
in-Chief), ASM International,
Materials Park, OH, 1990.]
1600
1400
1200
1000
800
600
400
0 1 2 3 4 90
L
γ +L
α + Graphite
Liquid +
Graphite
(Fe) C, wt% C
0.65
740ºC
T(ºC)
γ + Graphite
100
1153ºCγ
Austenite 4.2 wt% C
α + γ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec05-150114115107-conversion-gate02/85/Lec-05-5-320.jpg)