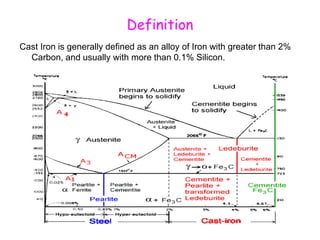
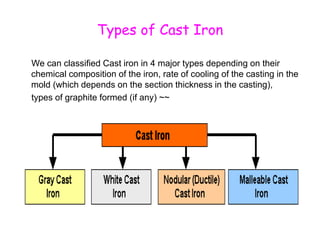
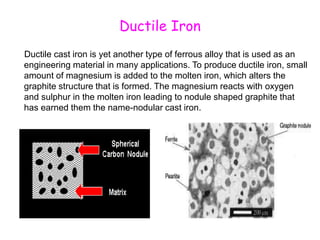
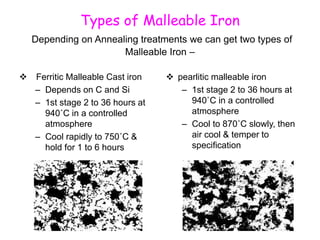
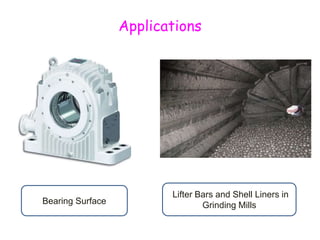
The document provides an overview of engineering cast iron, detailing its definition, types, and properties. It explains the different classifications of cast iron, including gray, ductile, malleable, and white cast iron, along with their applications and advantages. Additionally, it discusses the effects of various alloying elements on the properties of cast iron.