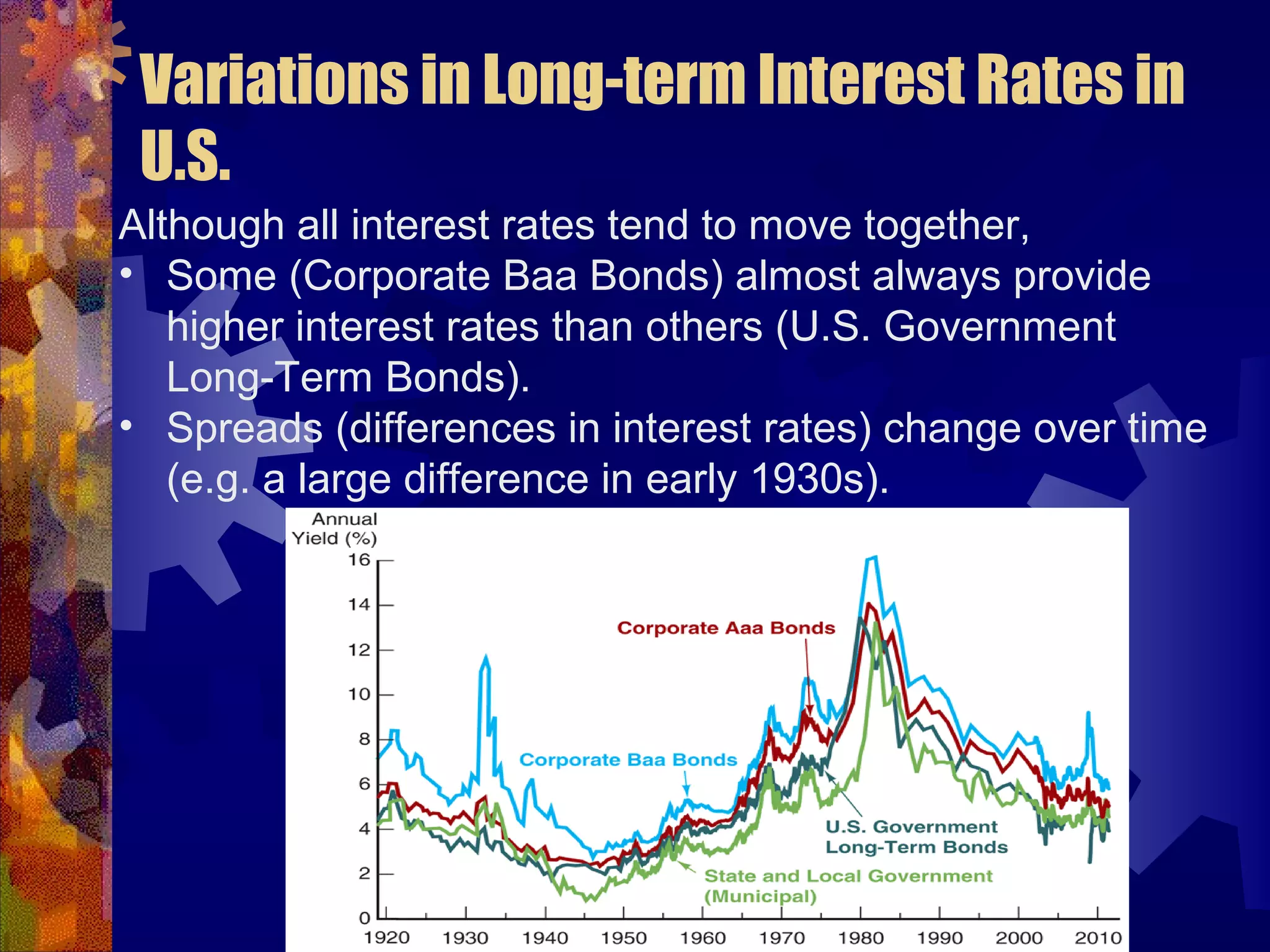
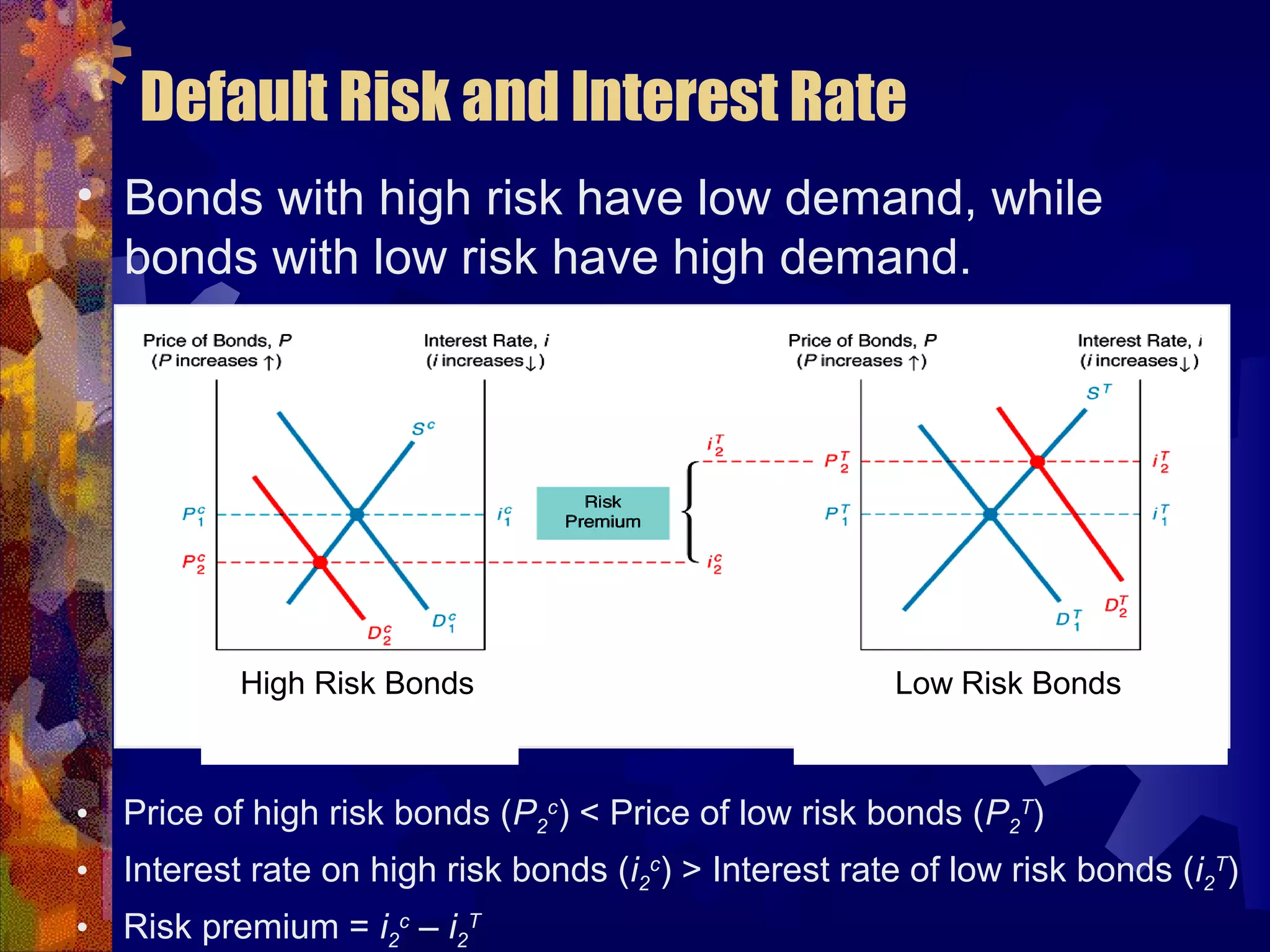
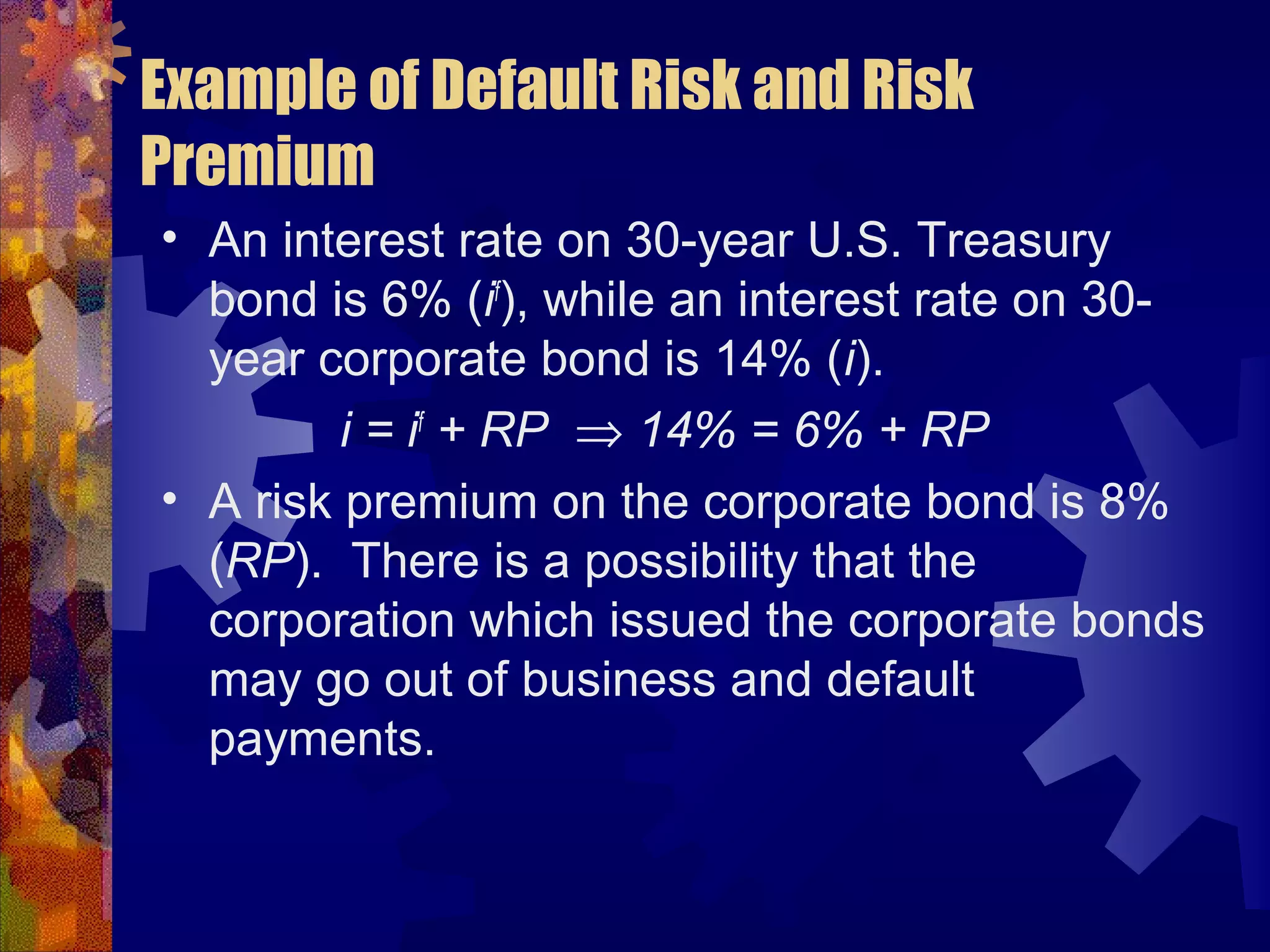
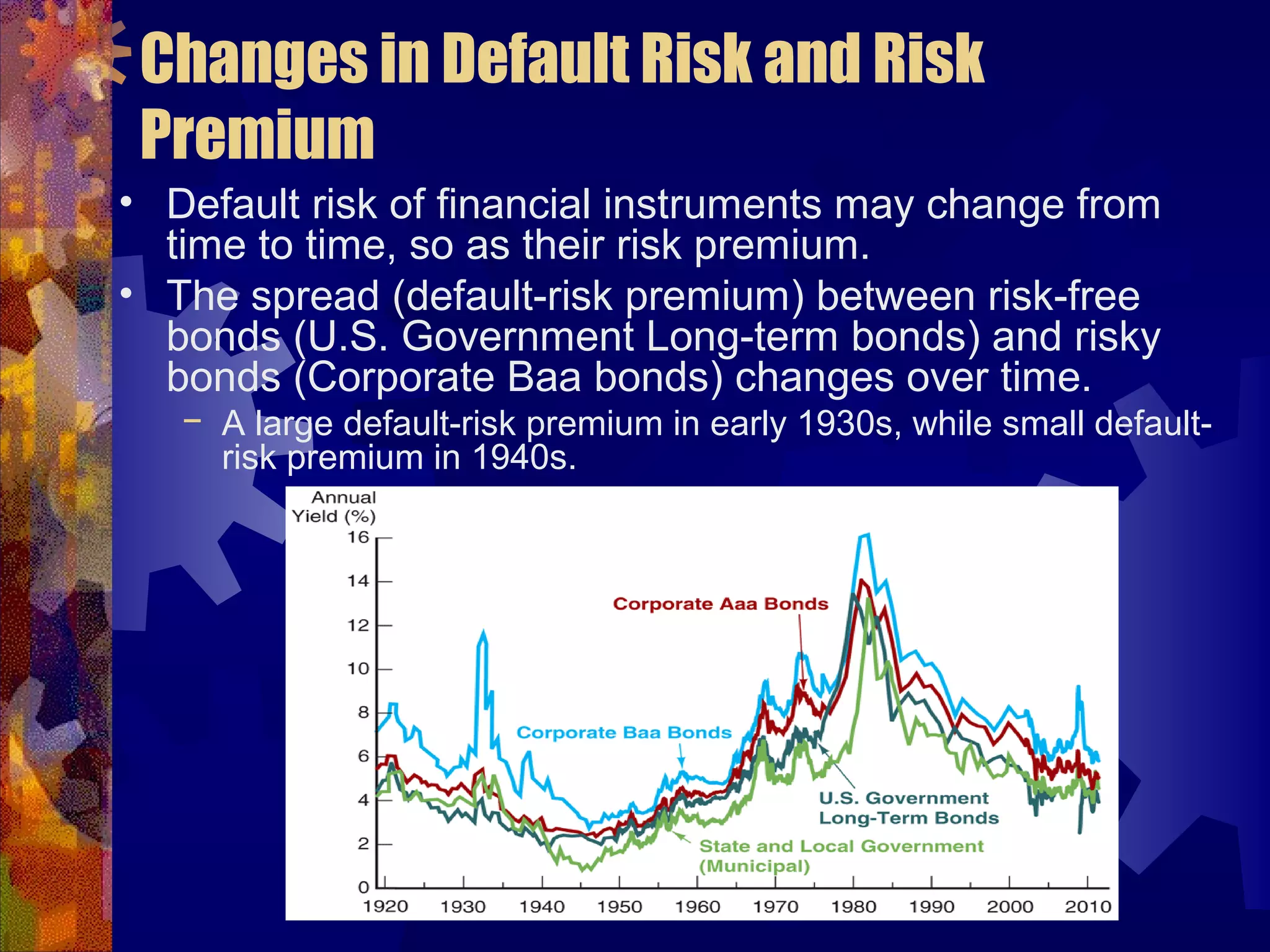
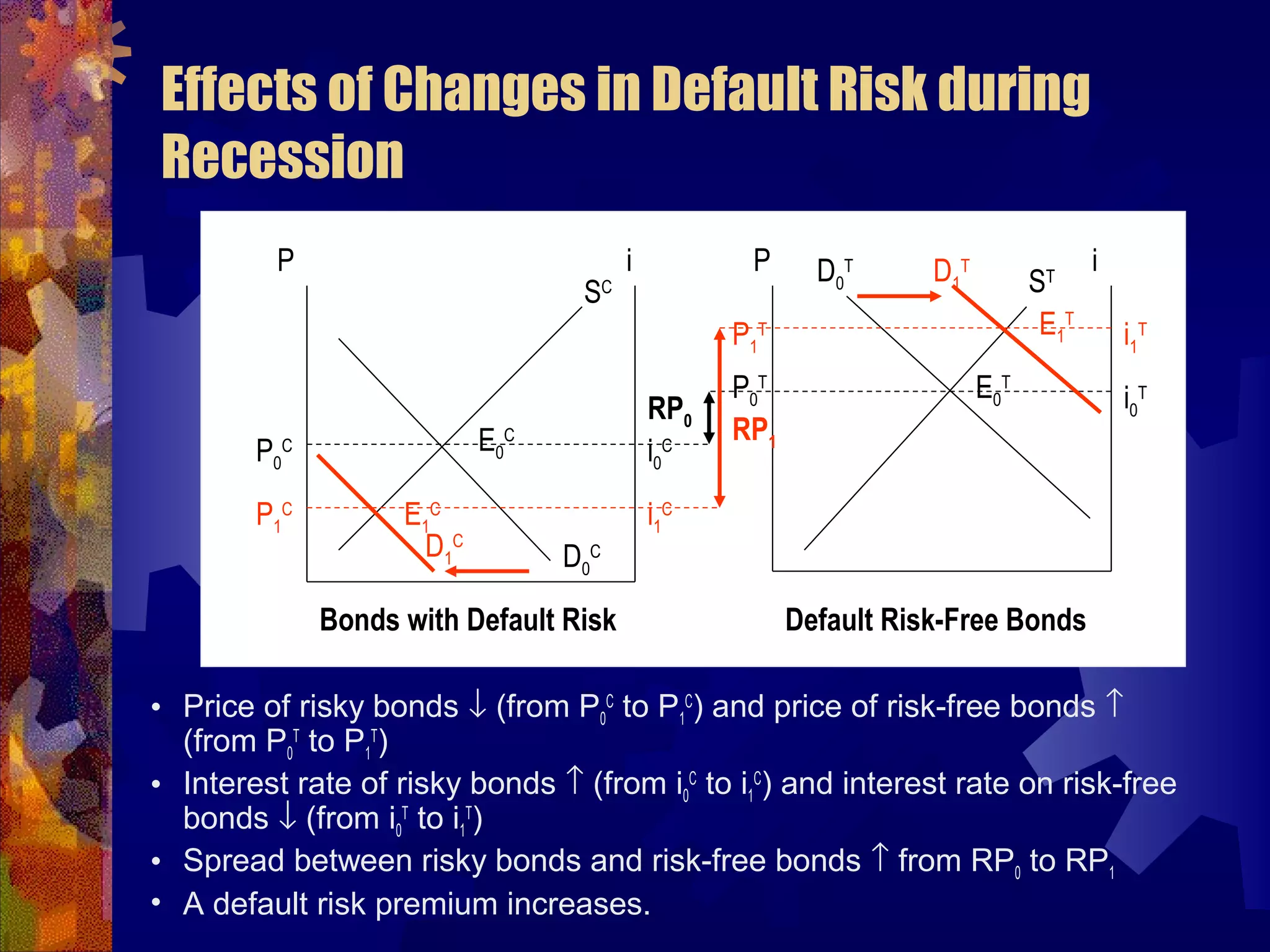
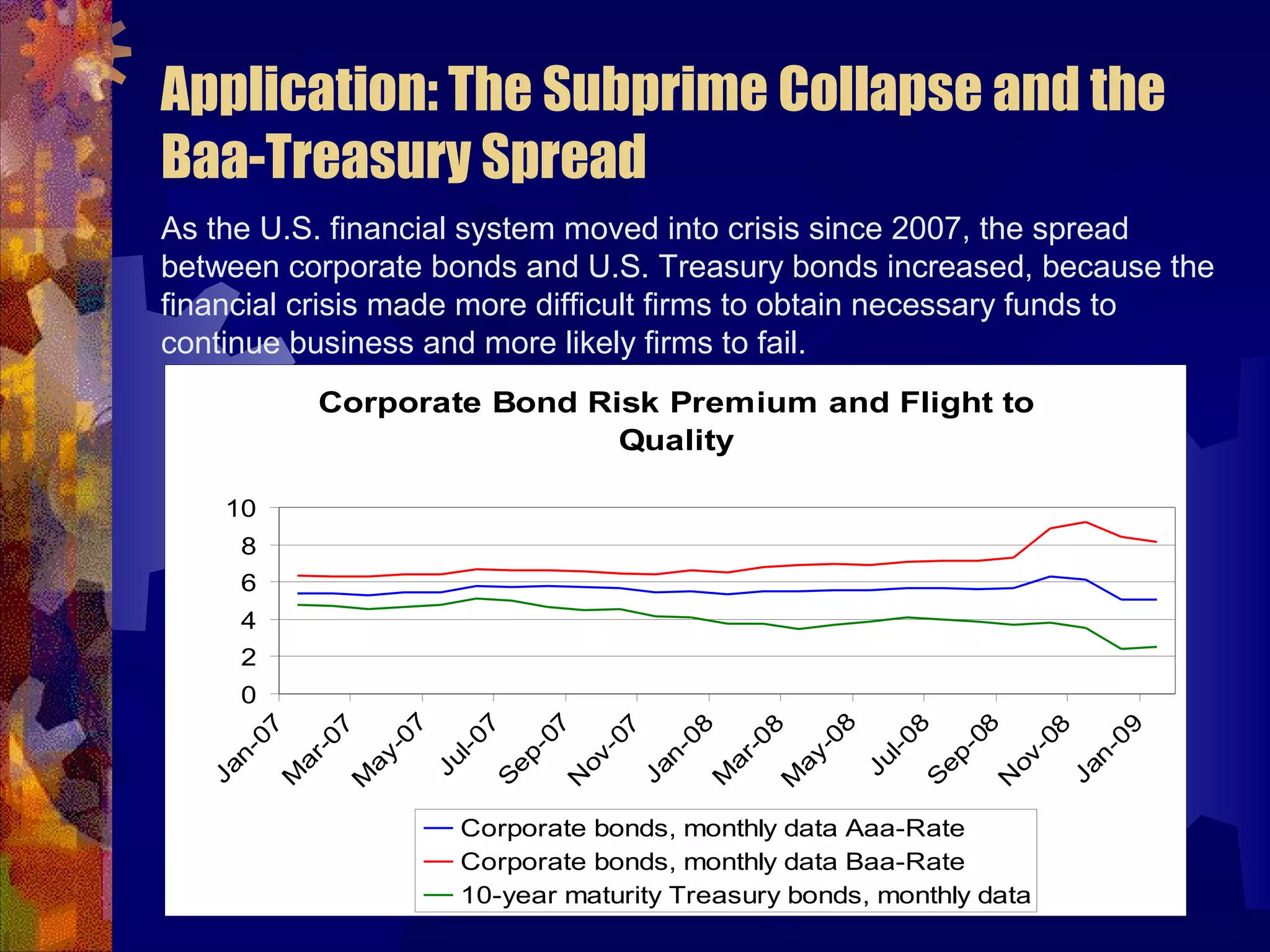
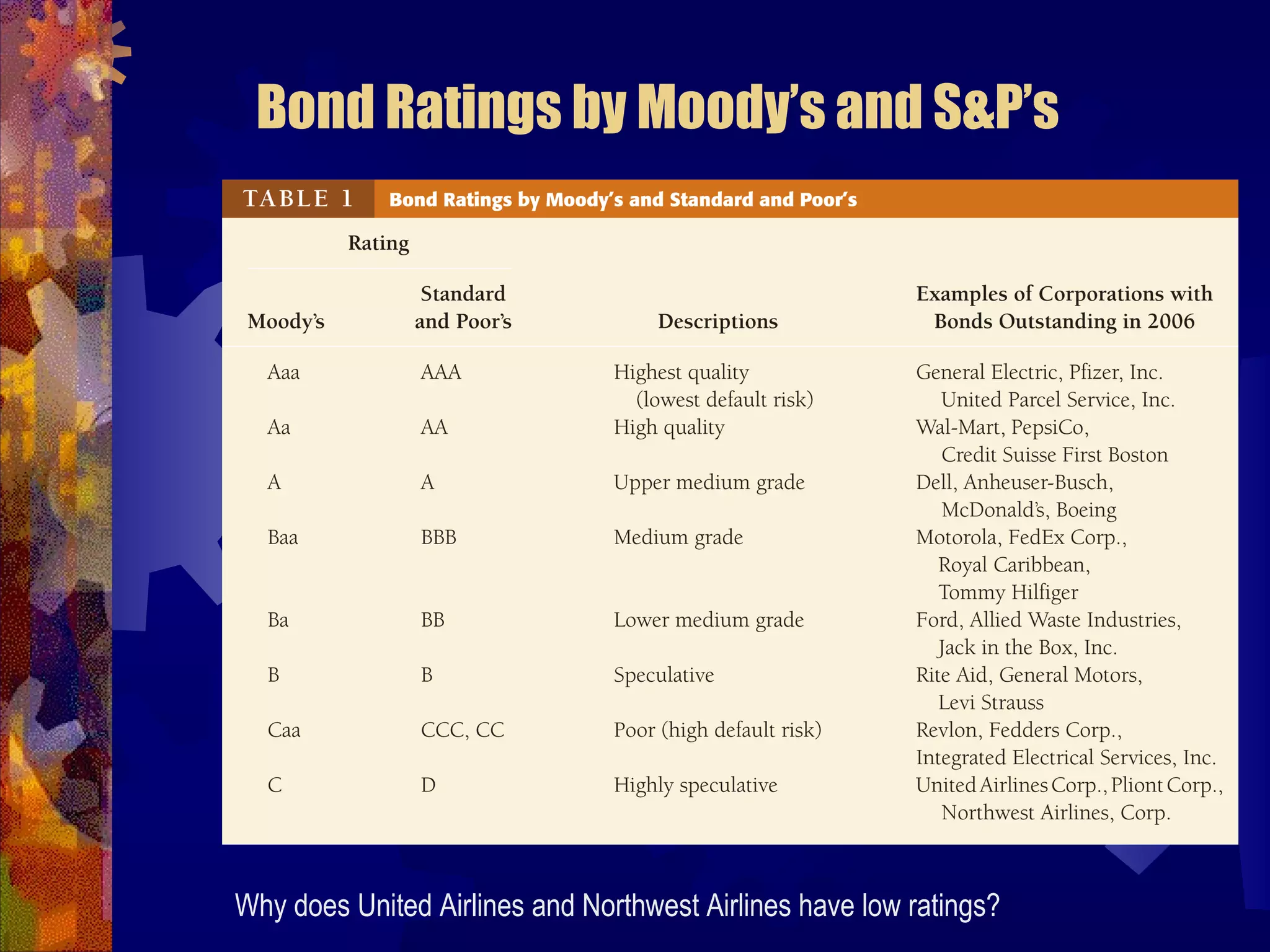
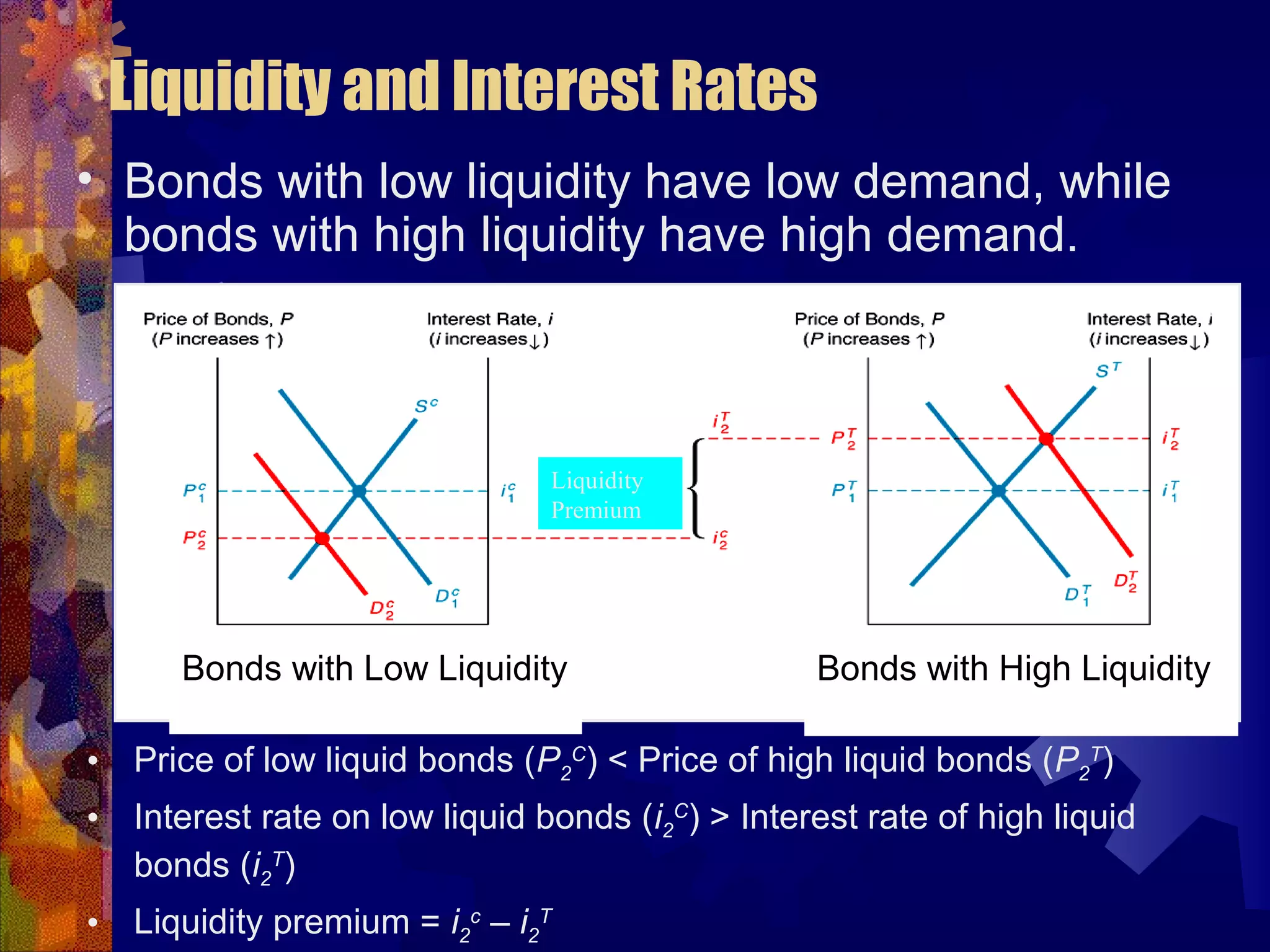
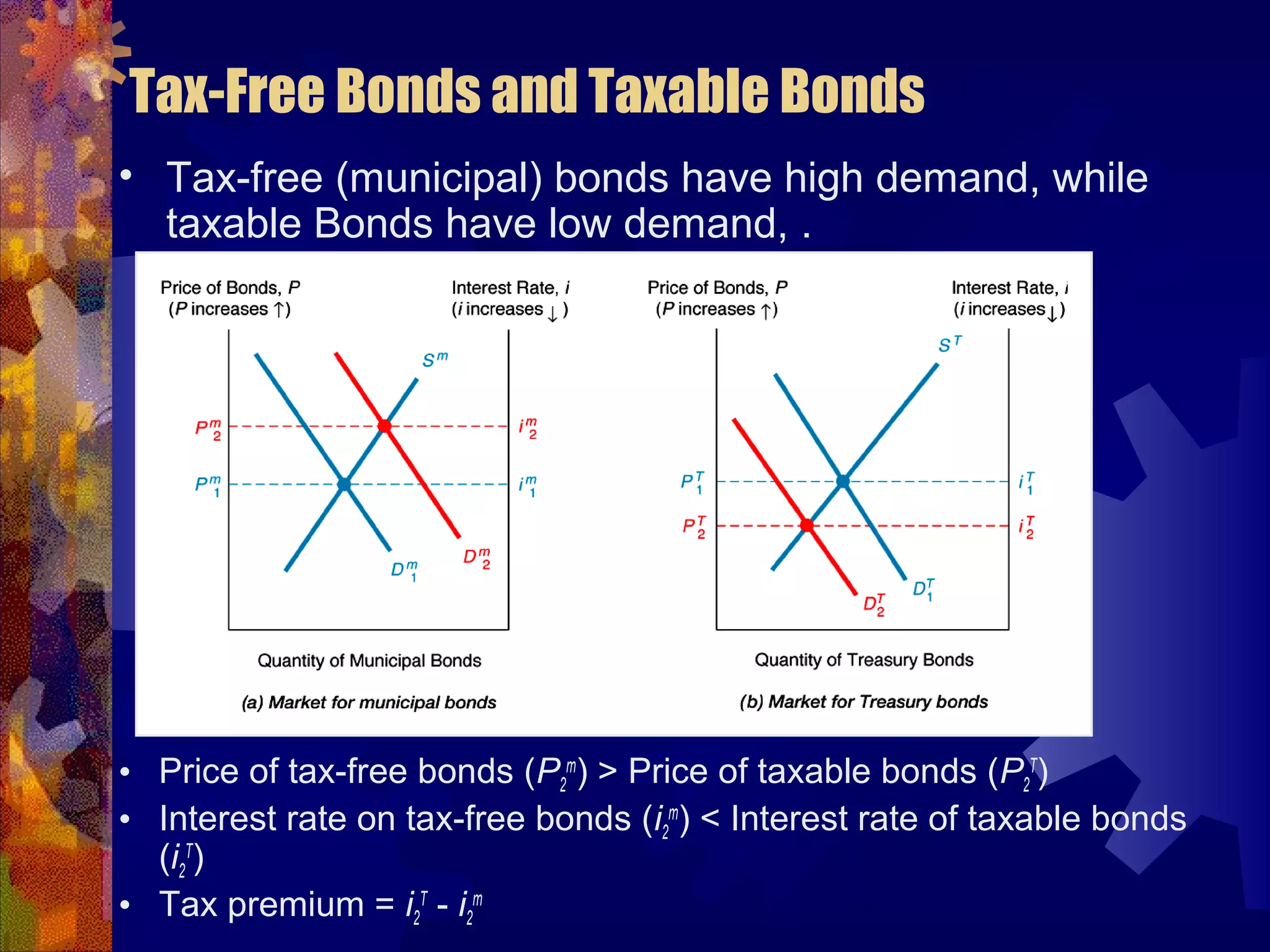
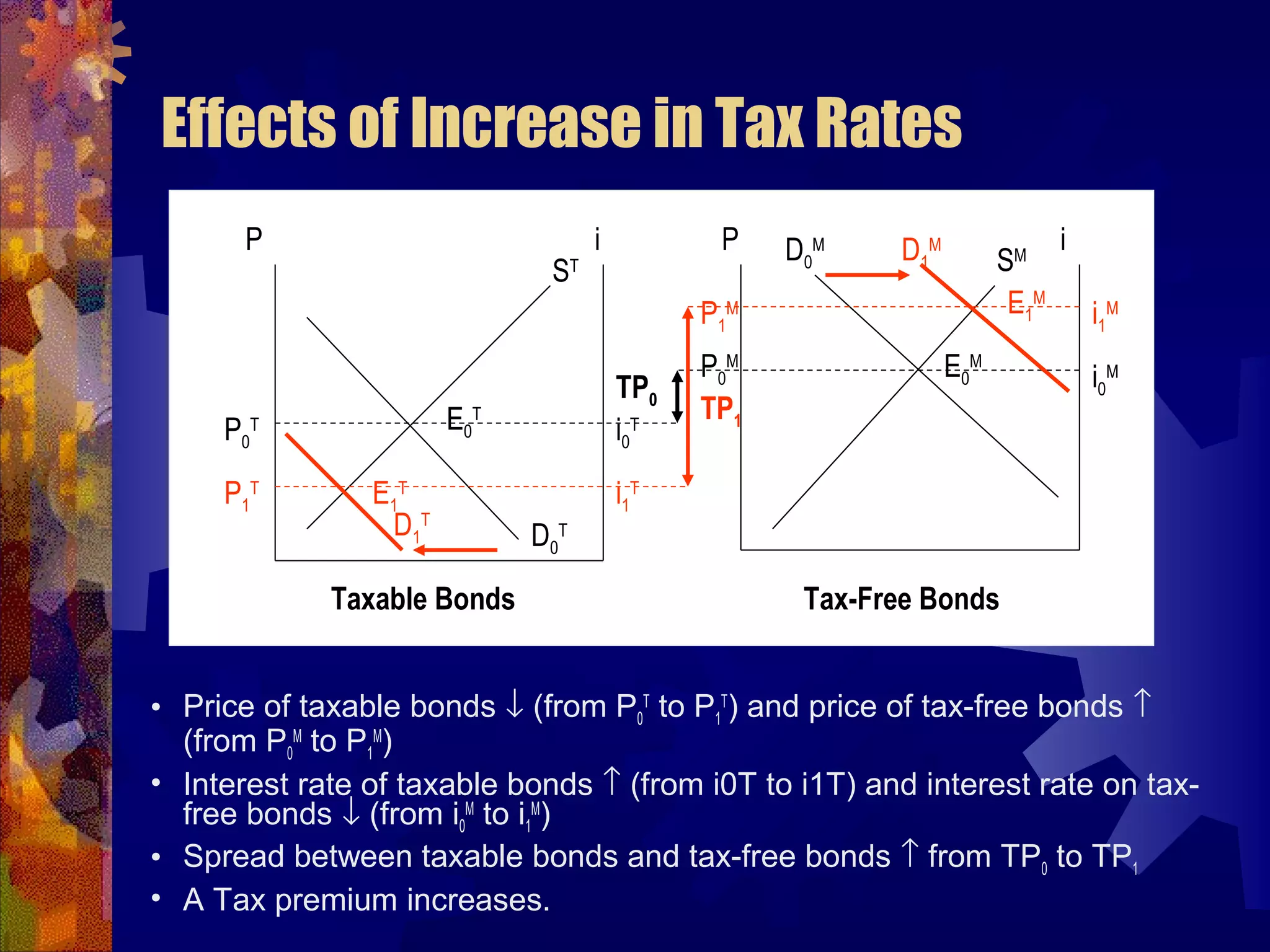
This document discusses why there are different interest rates in the economy. It explains that interest rates vary based on the risk, liquidity, and tax attributes of different financial instruments. Bonds have different interest rates depending on their default risk, with riskier corporate bonds paying higher rates than safer Treasury bonds. Liquidity also impacts rates, with less liquid bonds paying more than more liquid ones. Tax attributes matter as well, as tax-exempt municipal bonds pay lower rates than taxable bonds. The document provides examples of how risk premiums, liquidity premiums, and tax premiums contribute to the different interest rates observed in the market.