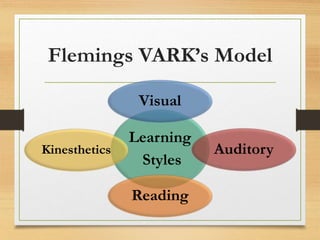
The document discusses various learning styles, highlighting that individuals absorb, comprehend, and retain information differently. It outlines four primary types of learners: visual, auditory, reading/writing, and kinesthetic, each with unique preferences and methods of learning. The content emphasizes how understanding these styles can enhance educational approaches and learning effectiveness.