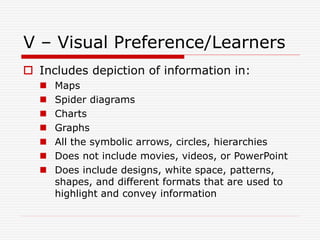
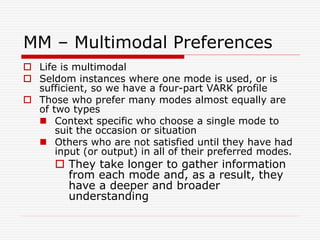
The VARK model outlines four learning styles: visual, aural, read/write, and kinesthetic, to help individuals identify their learning preferences and improve their study strategies. Visual learners benefit from diagrams and charts, auditory learners excel with spoken information, read/write learners prefer text-based inputs, and kinesthetic learners engage best through hands-on activities. The model also acknowledges multimodal learners who utilize multiple styles depending on the context.