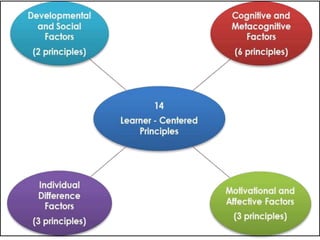
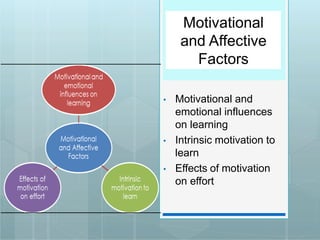
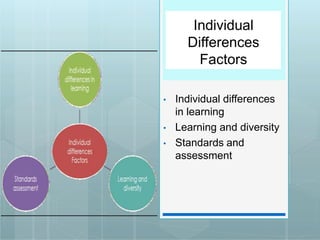
The document outlines 14 principles for learner-centered teaching established by the American Psychological Association. The principles are divided into cognitive/metacognitive factors, motivational/affective factors, developmental/social factors, and individual difference factors. They state that learning is most effective when it is an intentional process, learners pursue personally meaningful goals, new information can be linked to existing knowledge, learners have various thinking strategies, motivation and environment influence learning, development and individual differences are accounted for, and standards and assessment support the learning process.