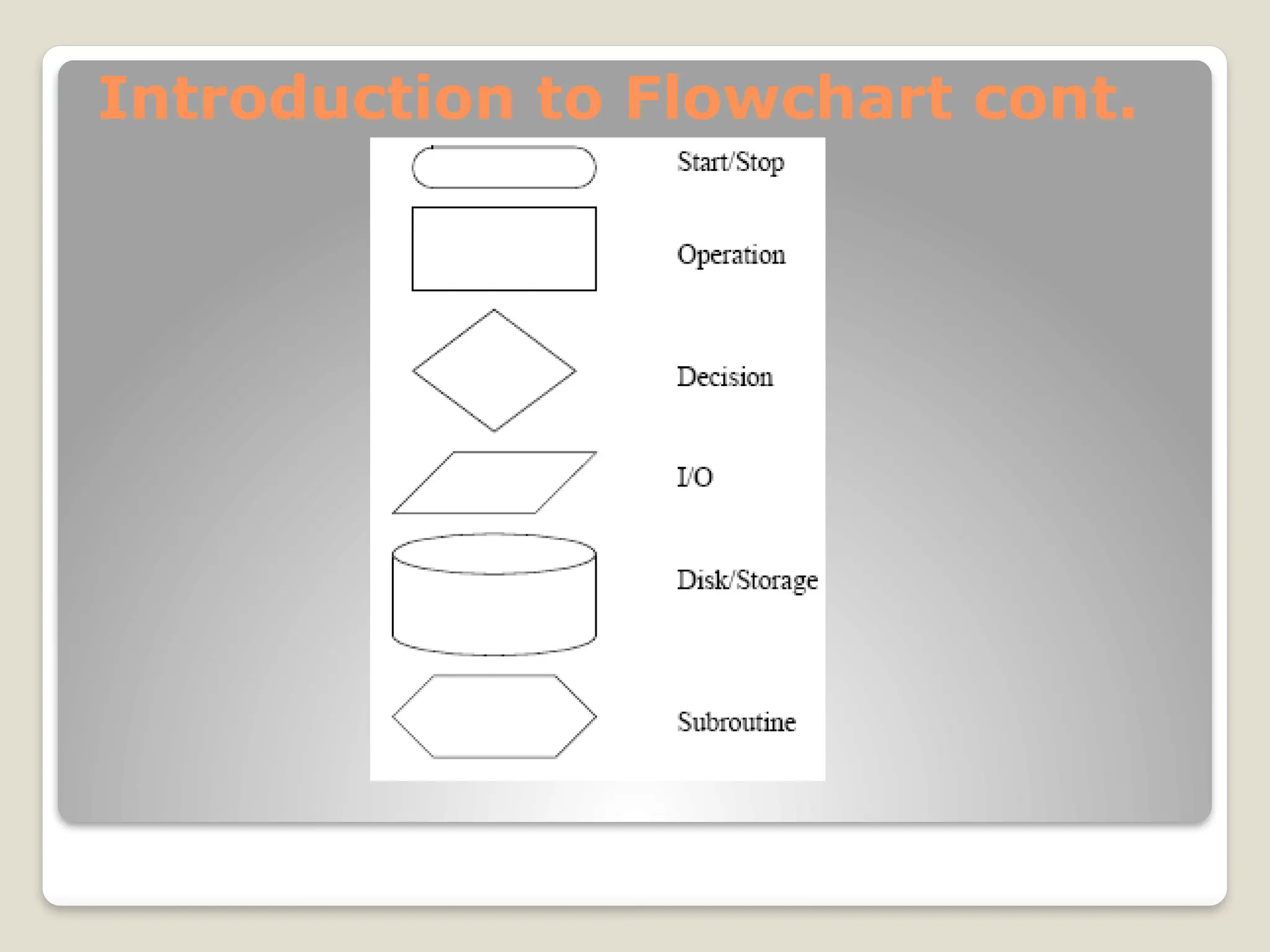
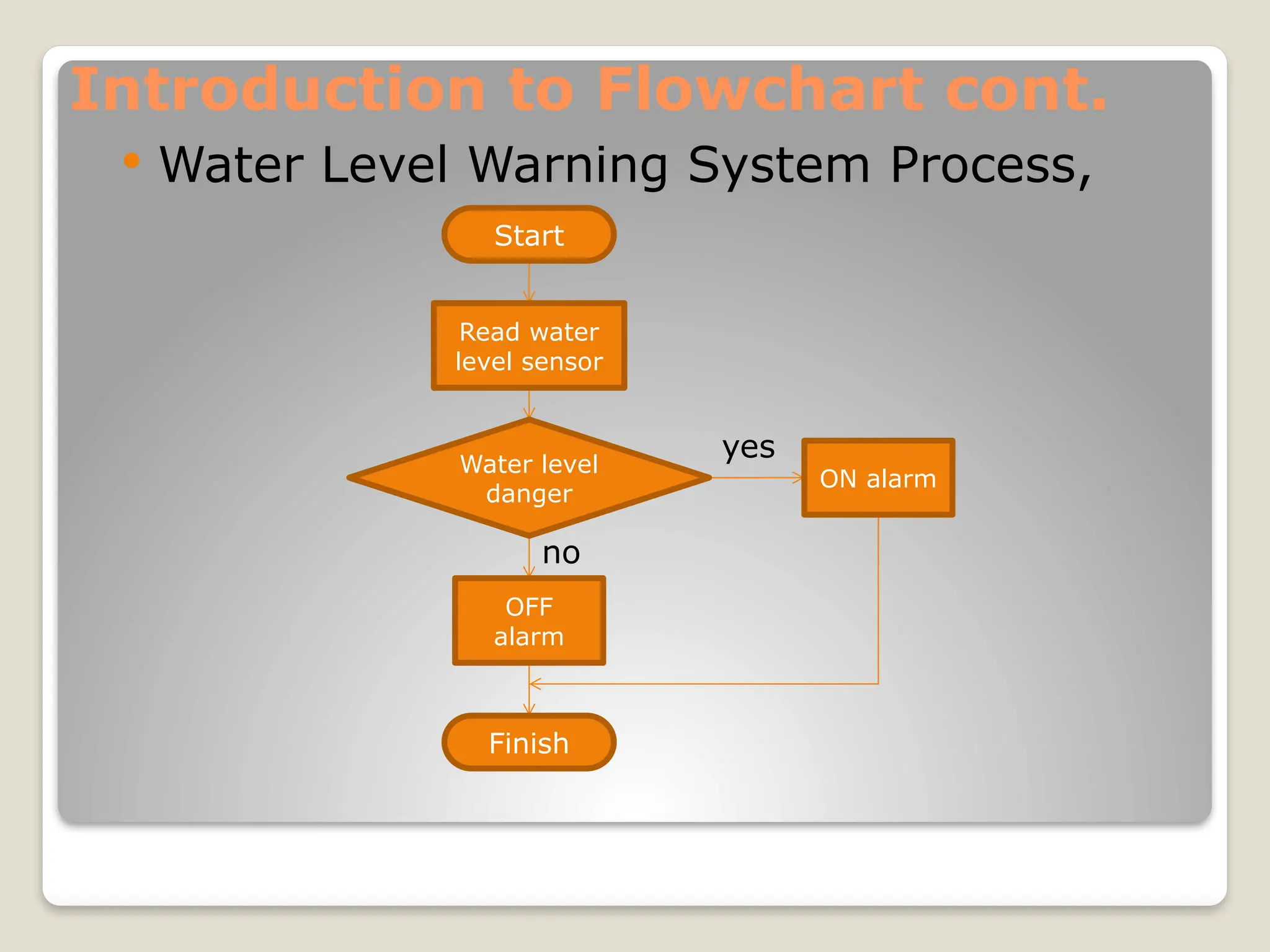
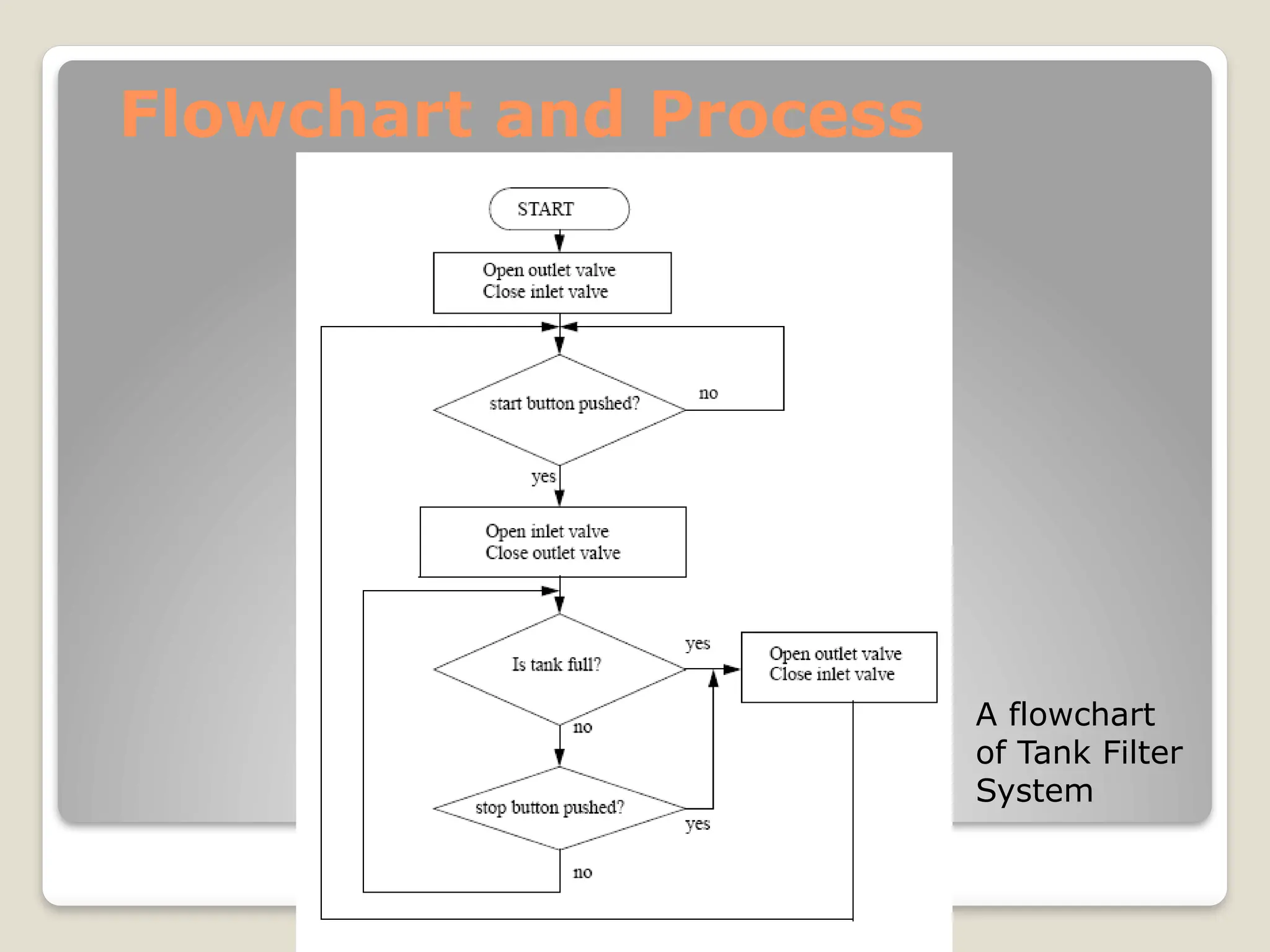
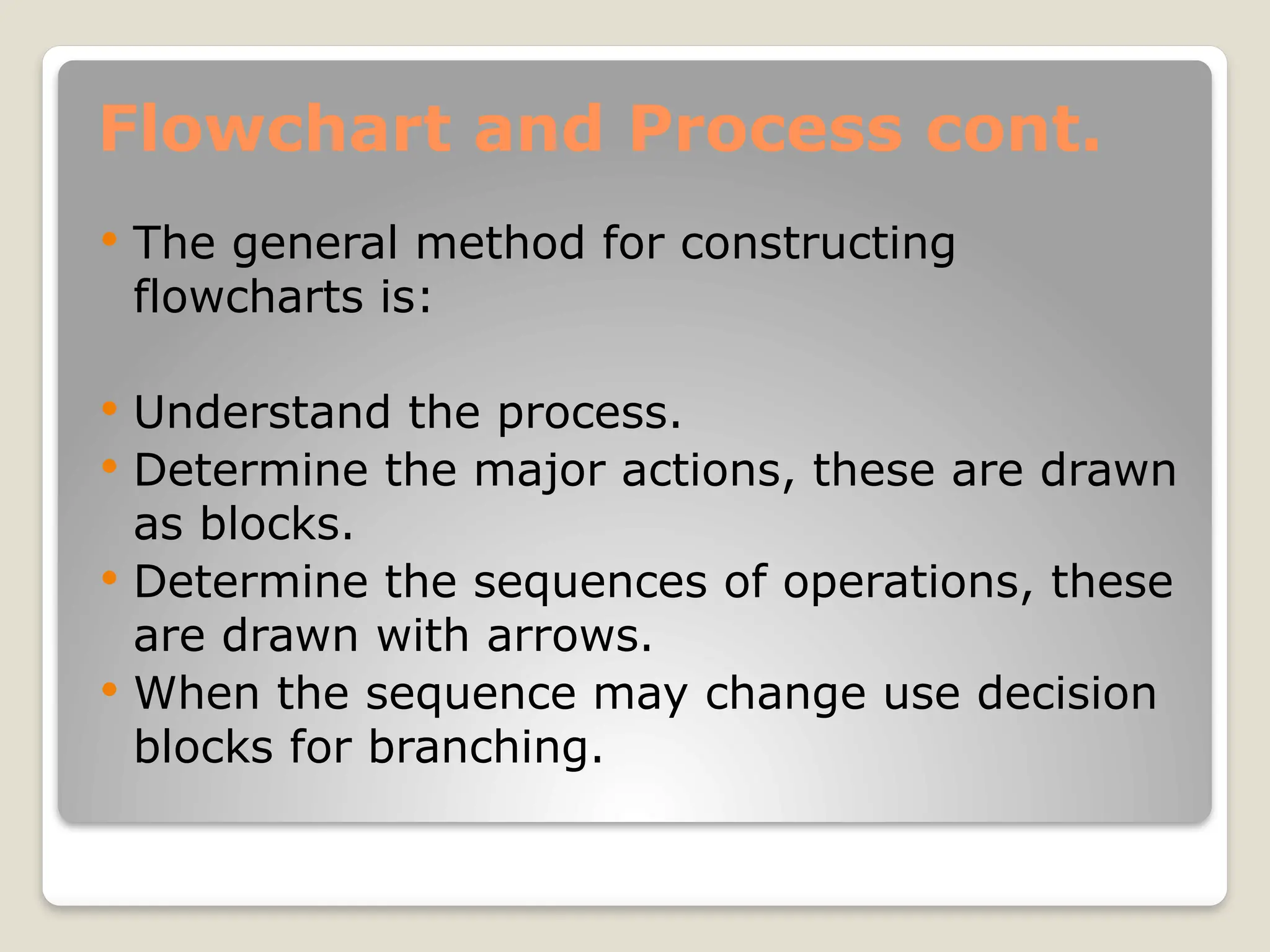
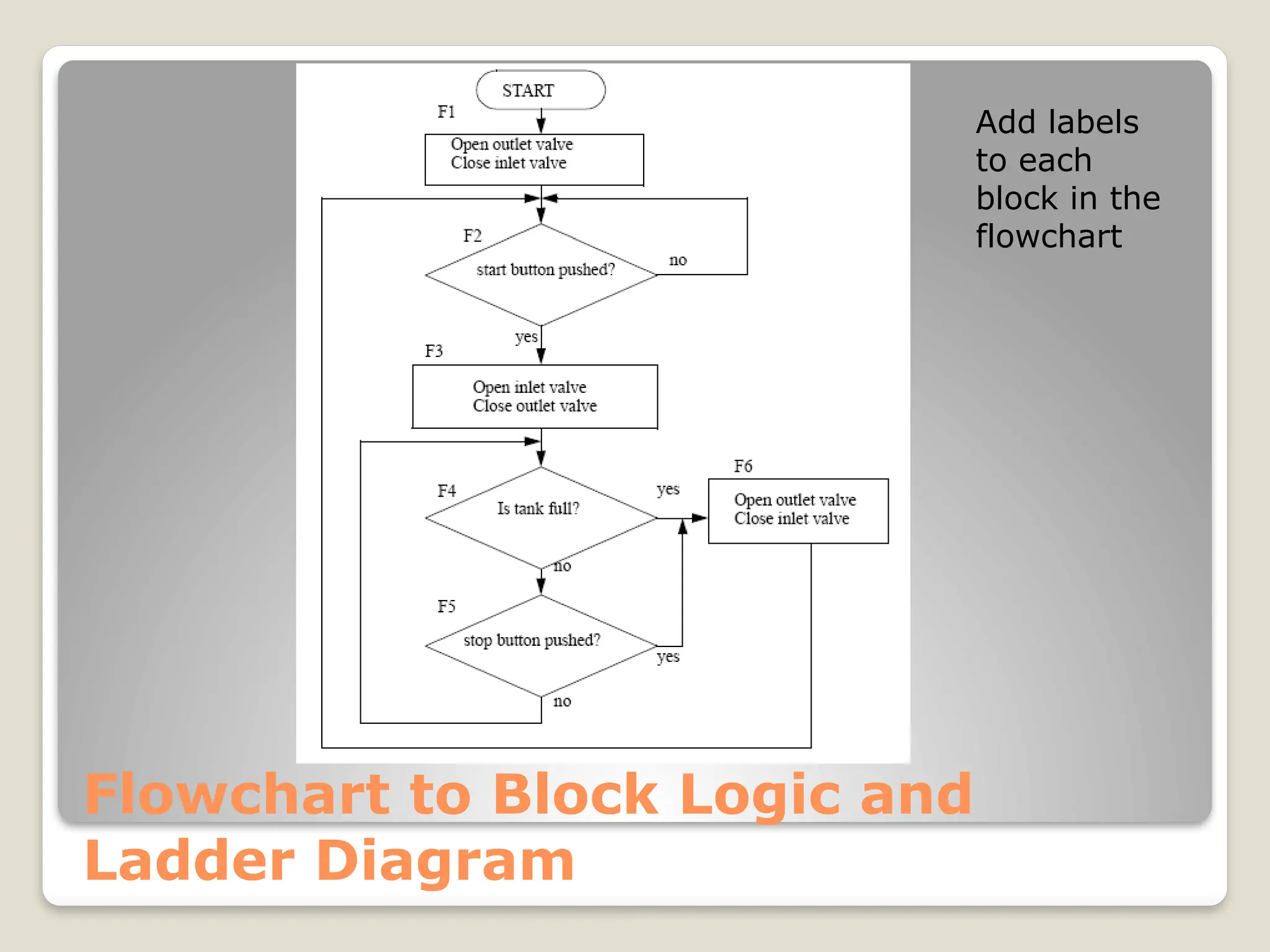
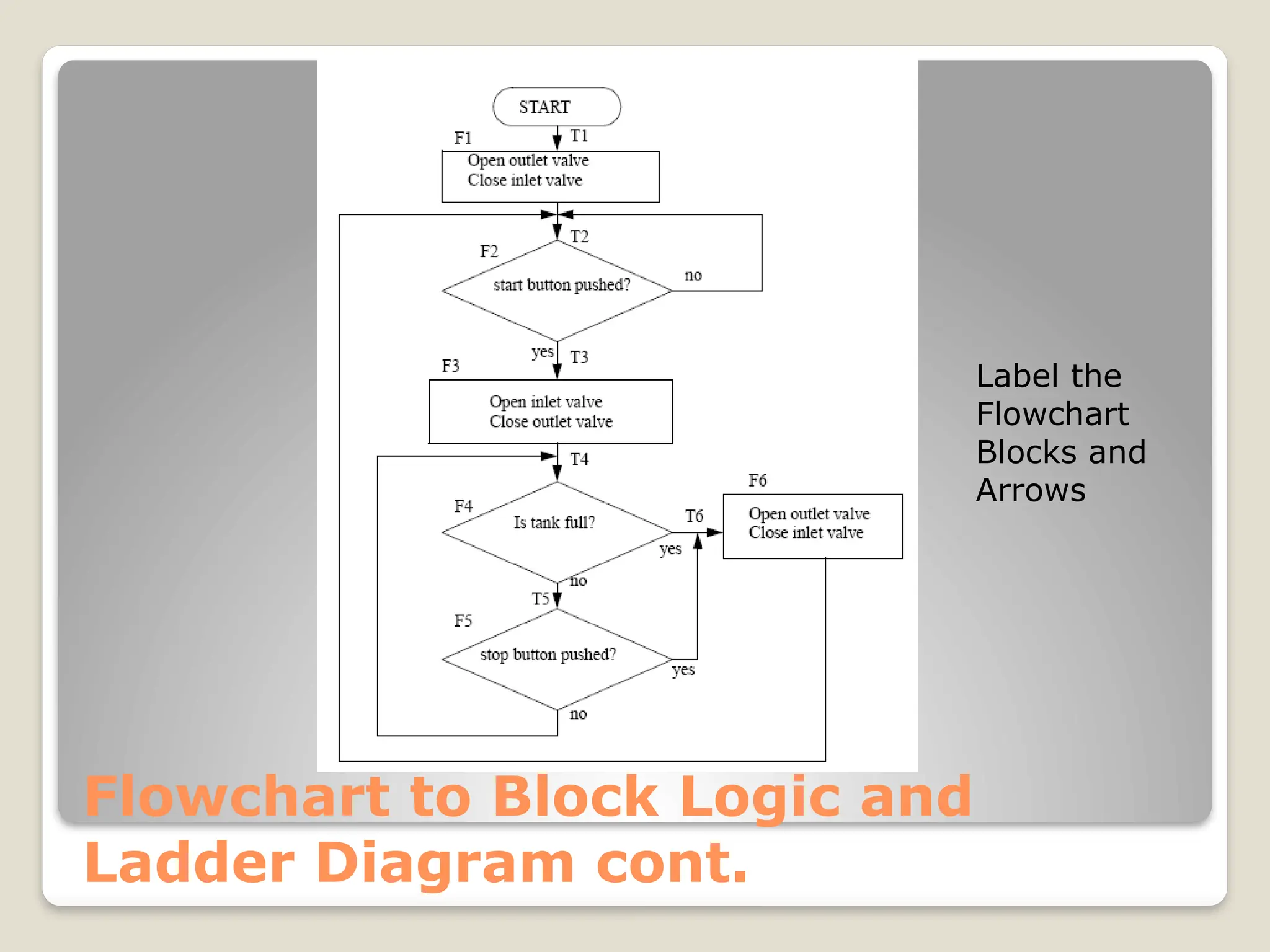
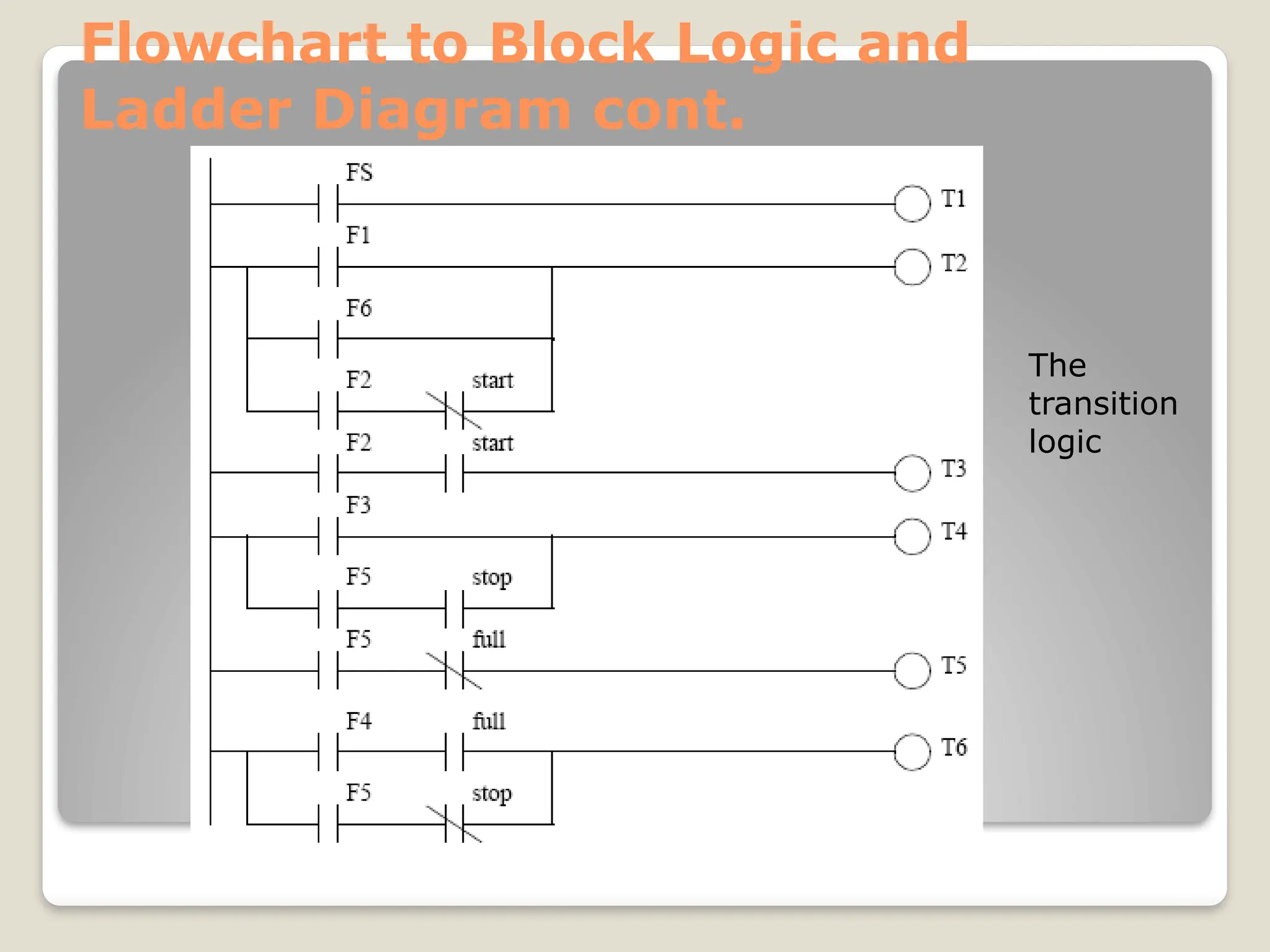
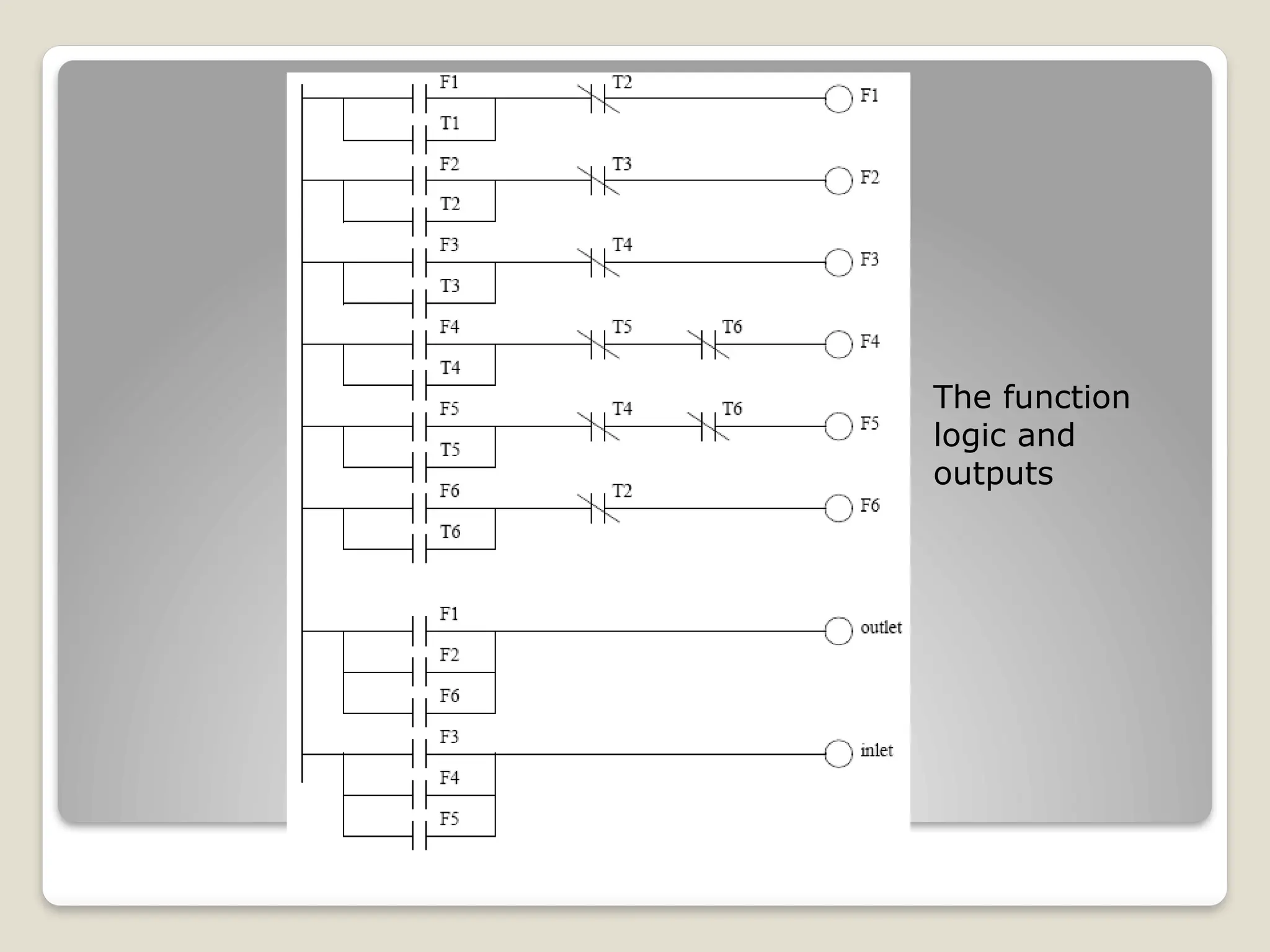
This document introduces flow charts and timing diagrams as essential tools for programming PLC applications. It outlines the process of problem-solving, emphasizing the creation and conversion of flowcharts to ladder diagrams, as well as methodical approaches to defining and analyzing control problems. The document also details the construction of flowcharts through understanding processes, sequencing operations, and utilizing decision blocks for branching.