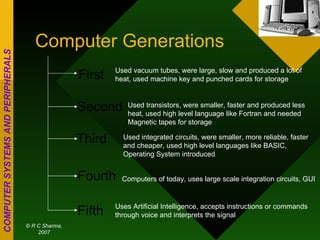
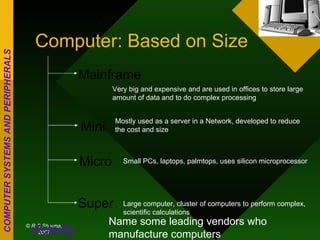
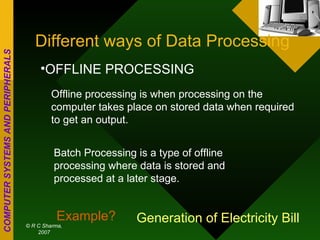
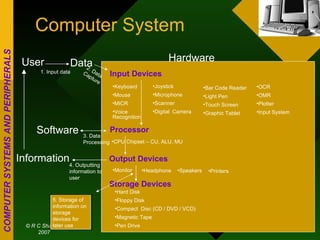
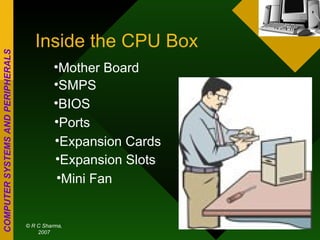
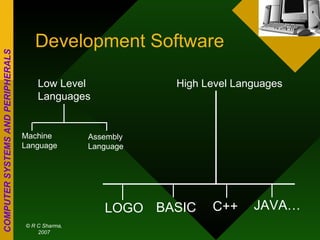
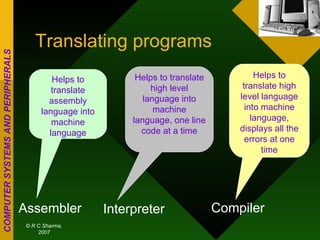
The document discusses different types of computers based on generation, size, and purpose. It also discusses uninterruptible power supply (UPS) technologies including offline, online, and line-interactive UPS systems. Offline UPS systems provide minimal power protection and output voltage regulation, while line-interactive UPS systems provide better filtering and voltage regulation compared to offline systems. Antivirus software consists of computer programs that attempt to identify, prevent, and remove computer viruses and other malware by scanning files against known virus definitions and identifying suspicious program behavior.