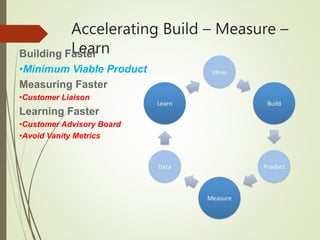
The document discusses the Lean Startup methodology, which aims to shorten product development cycles through validated learning and iterative releases. It describes the methodology, debunks common myths, and outlines its five principles: entrepreneurs are everywhere, entrepreneurship is management, validated learning, build-measure-learn feedback loops, and innovation accounting using metrics. The principles advocate for developing minimum viable products and pivoting based on customer feedback to accelerate learning.