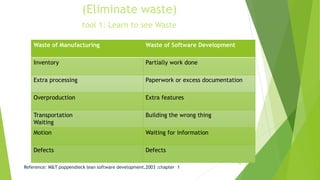
Toyota revolutionized manufacturing starting in the 1980s with their lean manufacturing approach, which aimed to eliminate waste and streamline value chains. Mary and Tom Poppendieck later transferred these lean principles to software development. The document outlines the seven principles of lean - eliminate waste, amplify learning, decide late, deliver fast, empower teams, build integrity, see the whole. It also details 22 lean tools for software development and compares lean to agile methods.