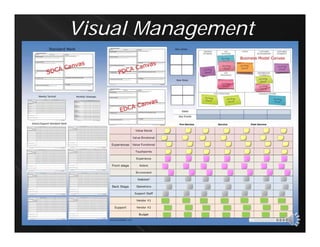
The document discusses the importance of standard work in lean design and project management, emphasizing the need for clarity, accountability, and consistent execution through methods like SDCA (standard, do, check, act). It outlines a structured approach to establishing team goals, empowering team members, and utilizing visual management tools for effective communication and workflow monitoring. Additionally, it introduces various quality tools to analyze and improve processes, aiming for continuous improvement in sales and marketing.