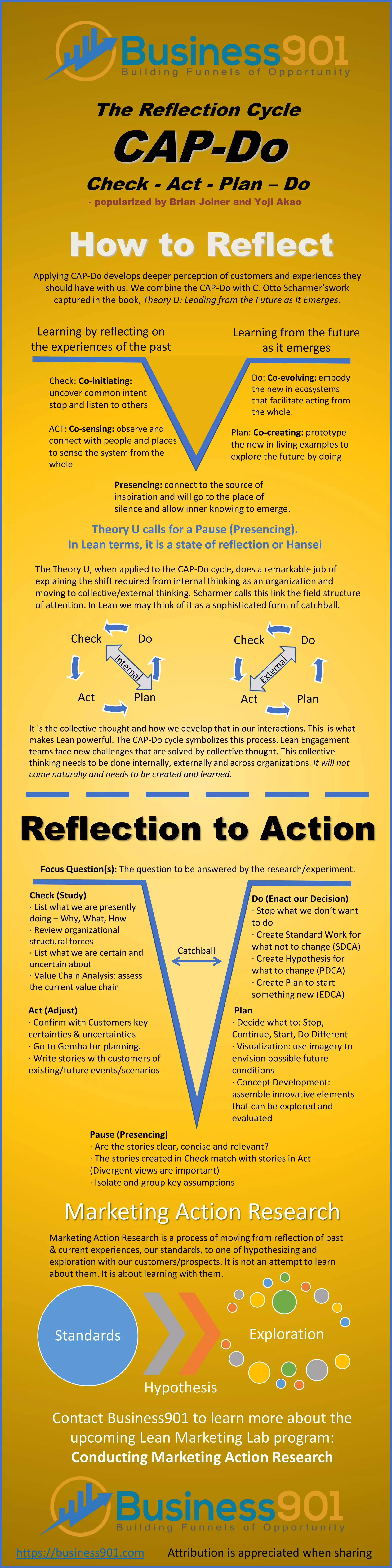
The document discusses the CAP-DO reflection cycle, emphasizing the integration of Brian Joiner and Yoji Akao's model with Otto Scharmer's Theory U to enhance collective thinking in organizations. It outlines the stages of the cycle: co-evolving, co-initiating, co-sensing, co-creating, and presencing, which facilitate deeper customer engagement and organizational learning. Additionally, it highlights the importance of collective thought and learning from experiences as essential components of effective lean engagement and marketing action research.