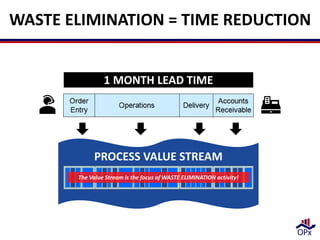
Lean aims to improve efficiency by identifying and eliminating waste, or non-value added activities. It focuses on delivering what customers want, when they want it, in the desired quantity, while minimizing the use of resources. There are seven types of manufacturing waste - transportation, inventory, motion, waiting, overprocessing, overproduction, and defects. Eliminating these wastes reduces lead times and improves process flow. Lean analysis identifies value-added versus non-value added steps to remove unnecessary activities from the process.