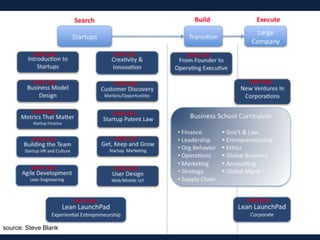
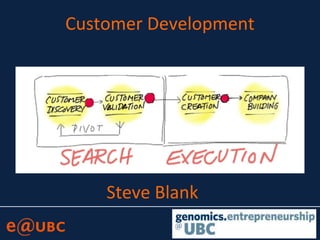
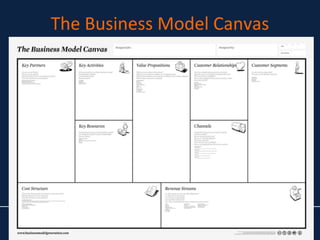
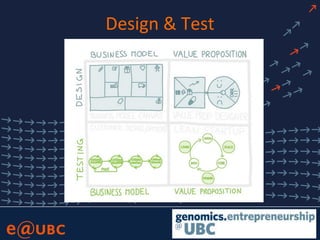
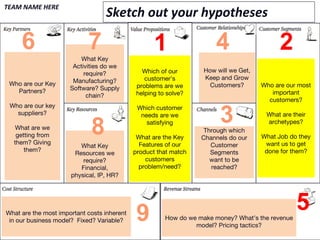
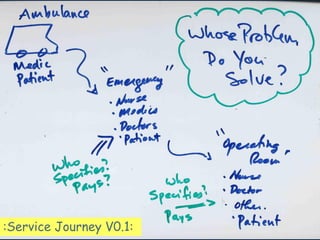
The document discusses lessons learned from the Lean Launchpad (LLP) accelerator program, detailing its structure, objectives, and the importance of customer development in startups. It emphasizes that startups often fail due to a lack of understanding customer needs rather than product issues, and outlines the rigorous processes involved in the LLP curriculum. Additionally, it reflects on the challenges faced by teams during the program and suggests solutions for better preparation and ongoing support for participants.