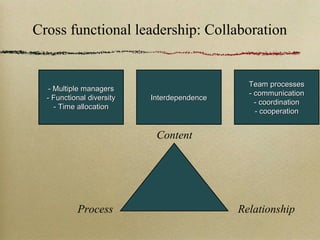
The document explores the concept of leadership without authority, emphasizing the importance of motivating individuals through both extrinsic and intrinsic factors. It highlights different sources of power leaders can wield, the significance of networking, and the complexities of leading in a culturally diverse environment. Additionally, it outlines a model for effective change management and underscores the necessity of understanding these dynamics to foster collaboration and achieve common goals.