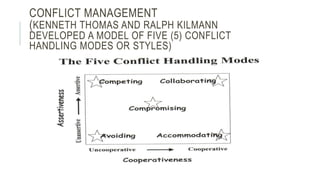
This document discusses leadership coaching and provides content on leadership, interpersonal communication, conflict management, and problem solving. It defines leadership as the ability to influence others with or without authority. It also describes five conflict handling modes: avoiding, accommodating, competing, collaborating, and compromising. Additionally, it discusses brainstorming as a problem solving technique and defines leadership coaching as a collaborative relationship between a leader and coach.