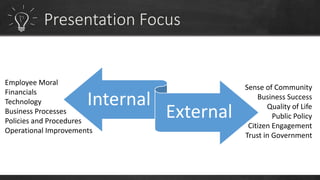
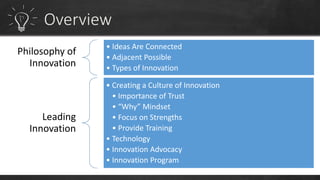
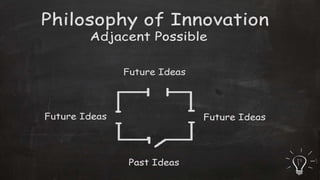
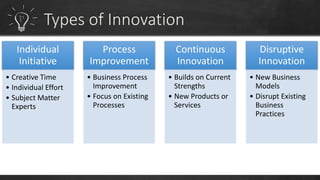
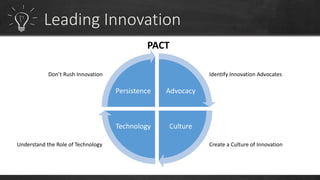
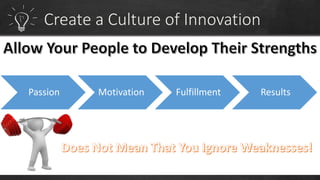
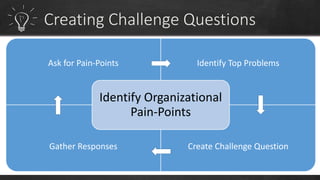
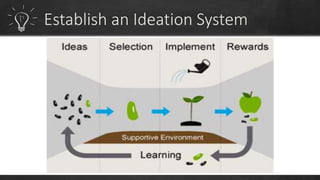
To have a sustainable innovation strategy, organizations should focus on process improvement and continuous innovation by building on their current strengths to develop new products and services, as well as focusing on improving existing business processes. They should also advocate for a culture of innovation, understand the role of technology, and create an innovation program to identify pain points and challenges to drive the development of innovative solutions.