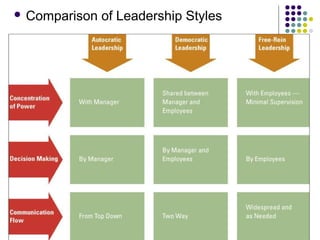
The document discusses various leadership styles including autocratic, bureaucratic, democratic, laissez-faire, team leader, coaching, task-oriented, people-oriented, transactional, and transformational. It notes that leadership involves influencing a group to achieve goals and can lift performance above normal limitations. Effective leadership realizes an additional 40% potential in people. While some are born with leadership traits, leadership can also be developed. The best leaders adapt their style to fit the task, organization, people, and time.