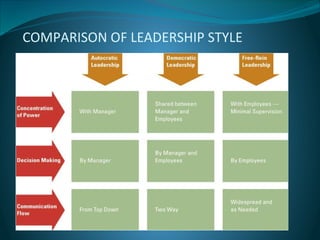
This document discusses leadership styles and their definitions. It defines leadership as influencing others towards goals and outlines three main styles: autocratic, where the leader makes all decisions; democratic, where the leader involves others in decision making; and laissez-faire, where the leader gives employees freedom to make decisions. It also discusses factors that influence leadership style choice like the task, organization traditions, and personality. Overall it provides an overview of leadership styles and considerations for managers.