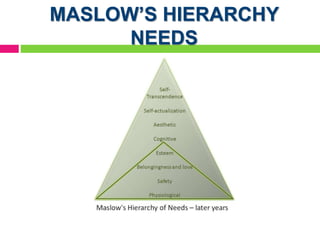
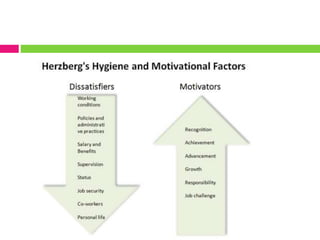
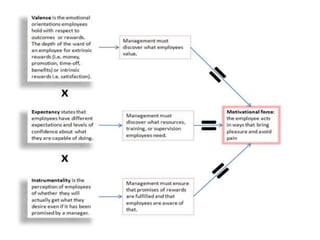
The document provides insights into leadership and human behavior, emphasizing the importance of understanding human needs as outlined by Maslow's hierarchy. It discusses various motivational theories, including Herzberg's hygiene and motivator factors, and McGregor's Theory X and Y, highlighting the impact of these theories on workplace dynamics. Finally, it introduces Vroom's expectancy theory of motivation and its components, focusing on the connection between effort, performance, and reward.