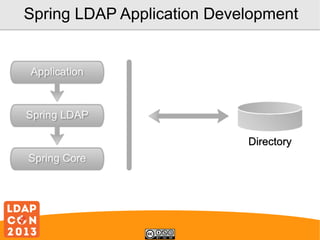
This document provides an overview of application development using Spring LDAP. It begins with introducing the presenter and agenda. It then covers JNDI and its drawbacks for LDAP operations. The bulk of the document discusses Spring LDAP, including its features, core concepts like context source and LdapTemplate, and examples of template usage, ODM, and integration testing with LdapUnit. It also shows how Spring LDAP can simplify authentication compared to standard JNDI. The presentation concludes by asking for any other ways Spring LDAP could be improved.






![JNDI – Performing LDAP Operation
SearchControls searchControls = new SearchControls();
searchControls.setSearchScope(SearchControls.SUBTREE_SCOPE);
searchControls.setReturningAttributes(new String[]{"givenName", "sn",
"telephoneNumber"});
searchResults = context.search(BASE_PATH, "(objectClass=inetOrgPerson)",
searchControls);
while (searchResults.hasMore()) {
SearchResult result = searchResults.next();
Attributes attributes = result.getAttributes();
// Read single valued attributes
String firstName = (String)attributes.get("givenName").get();
String lastName = (String)attributes.get("sn").get();
// Read the multi-valued attribute
Attribute phoneAttribute = attributes.get("telephoneNumber");
String[] phone = new String[phoneAttribute.size()];
NamingEnumeration phoneValues = phoneAttribute.getAll();
for(int i = 0; phoneValues.hasMore(); i++) {
phone[i] = (String)phoneValues.next();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/springldap-131120045203-phpapp02/85/LDAP-Development-Using-Spring-LDAP-8-320.jpg)